Grumman|Butkus Associates, a firm of energy efficiency consultants and sustainable design engineers, recently released the results of its 2023 Hospital Energy and Water Benchmarking Survey, focusing on healthcare facilities’ resource usage trends and costs for calendar years 2021 and 2022.
For the first time, the report charts and historical data are available at a dedicated website, including pull-down menus for sorting data by facility characteristics (for instance, hospitals with purchased steam or in-house laundry). These tools will make it easier for users to make comparisons between the survey data and patterns in their own facilities.
Users can also choose some aspects of data presentation (for instance, $/therm vs. $/MMBtu in the fossil fuel energy chart).
Hospital Energy and Water Use Trends
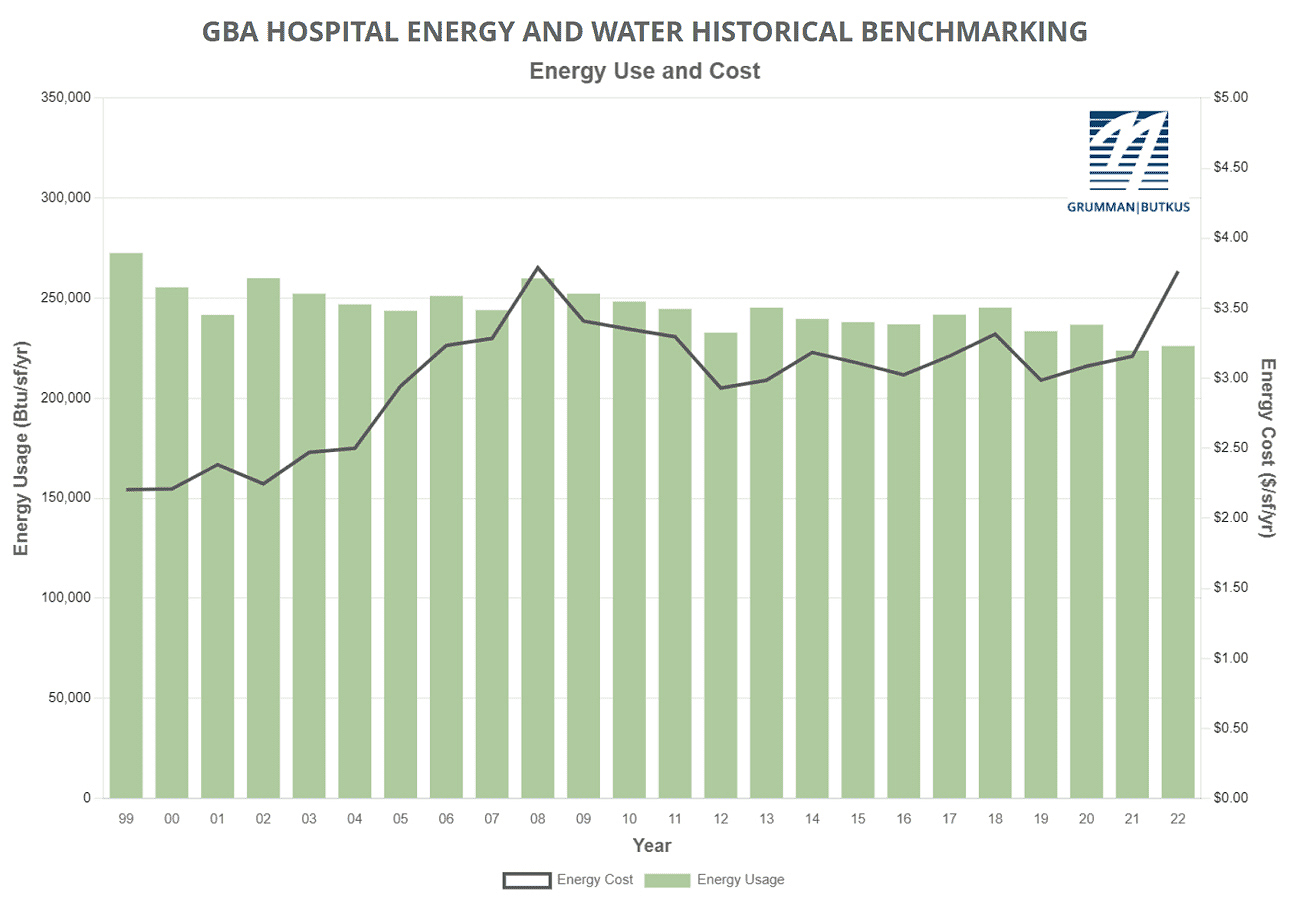
Since GBA initiated the survey nearly 30 years ago, hospitals’ overall fossil fuel use has trended downward, but electricity use isn’t declining as much. The average combined Btu/ft2 (electricity plus gas/steam) for participating facilities was 223,778 in 2021 and 226,081 in 2022, both down from the 236,743 Btu/ft2 reported in CY2020. However, interpretation of year-to-year trends should be tempered by the realization that the respondent pool for 2020-22 would have usage patterns influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Square-foot prices for gas/steam rose ($0.75 in 2021 and $0.98 in 2022, compared with $0.65 in 2020). Square-foot prices for electricity fluctuated ($2.40 in 2021 and $2.78 in 2022, compared with $2.44 in 2020). The overall result is that total reported ft2 costs for energy (gas/steam plus electric) have increased: $3.16 in 2021 and $3.76 in 2022, compared with $3.09 for 2020.
Hospitals’ average carbon footprint has remained fairly steady at 50 to 60 pounds of CO2 equivalent per ft2 per year since GBA began calculating carbon data in 1999. However, Scope 1 and Scope 2 CO2 footprint in 2022 was the lowest it has been since GBA started reporting on carbon emissions (36.96 average CO2 equivalent per ft2 per year). This pattern is likely related to changes in the electric grid, as utilities themselves strive to decarbonize.
Participating facilities displayed a broad range of energy usage patterns. For instance, a few of this year’s survey participants reported fossil fuel consumption of more than 200,000 Btu/sf/year, compared with the general mid-range of facilities (about 130,000 Btu/sf/year) and those that used the least (75,000 Btu/sf/year or less). These variations mean that hospital fossil fuel energy costs may exceed $2.00/sf/year or come in at less than $0.50/sf/year.
Similarly, several hospitals reported consuming more than 40 kWh/sf/year in electrical energy, compared with a mid-range of about 27 kWh/sf/year. A few survey participants squeaked in at less than 20 kWh/sf/year. The wide differences in usage mean that some participants are paying well over $4.00/sf/year for electrical energy, while many are getting by with less than $2.50 and a few with less than $1.75.
“Facilities that have high unit costs for energy should view this as an opportunity,” says GBA-Illinois Chairman Dan Doyle. “For example, a project that would have a five-year payback at an ‘average’ facility may have a payback of just 2.5 or three years at a facility with higher unit costs for energy.”
Hospital water/sewer use has been gradually declining, but was up in both 2021 and 2022, at 42 and 51 gallons per square foot per year, respectively, compared with about 36 gallons per square foot per year in CY2020. The leap between 2021 and 2022 was likely a statistical anomaly caused by different respondent mix between those two years. Costs for water/sewer are undoubtedly rising, however. Respondents reported costs of $0.46/square foot in 2021 and $0.43/square foot in 2022, compared with the $0.27/ft2 that hospitals were spending in 2006, the year GBA began tracking water/sewer use.
“GBA expects the general trend of rising water and sewer costs to continue,” says Doyle. “Price hikes not only reflect increasing costs to extract and treat the water, but also the expense of upgrading or replacing aging infrastructure. In addition, some cash-strapped governmental entities may view water as a revenue sources.”
Since 1995, the GBA survey has provided a free annual benchmarking resource. Hospitals are invited to participate by submitting responses to a short list of questions. Information for this edition was provided by a combined total of 181 hospitals located in Illinois, Wisconsin, New Jersey, Indiana, Michigan, Nevada, and numerous other states coast-to-coast.
Full results and analysis, as well as information about participating in the 2024 survey (2023 data), are available at the firm’s website: grummanbutkus.com/HES.
For additional information, contact Dan Doyle (ddoyle@grummanbutkus.com) or Julie Higginbotham (jhigginbotham@grummanbutkus.com).
Related Stories
| Aug 16, 2022
Cedars-Sinai Urgent Care Clinic’s high design for urgent care
The new Cedars-Sinai Los Feliz Urgent Care Clinic in Los Angeles plays against type, offering a stylized design to what are typically mundane, utilitarian buildings.
| Aug 15, 2022
IF you build it, will they come? The problem of staff respite in healthcare facilities
Architects and designers have long argued for the value of respite spaces in healthcare facilities.
AEC Tech | Aug 8, 2022
The technology balancing act
As our world reopens from COVID isolation, we are entering back into undefined territory – a form of hybrid existence.
| Aug 3, 2022
Designing learning environments to support the future of equitable health care
While the shortage of rural health care practitioners was a concern before the COVID-19 pandemic, the public health crisis has highlighted the importance of health equity in the United States and the desperate need for practitioners help meet the needs of patients in vulnerable rural communities.
Healthcare Facilities | Aug 1, 2022
New Phoenix VA outpatient clinic is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
The new Phoenix 32nd Street VA Clinic, spanning roughly 275,000 sf over 15 acres, is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
Building Team | Jul 12, 2022
10 resource reduction measures for more efficient and sustainable biopharma facilities
Resource reduction measures are solutions that can lead to lifecycle energy and cost savings for a favorable return on investment while simultaneously improving resiliency and promoting health and wellness in your facility.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 22, 2022
Arizona State University’s Health Futures Center: A new home for medical tech innovation
In Phoenix, the Arizona State University (ASU) has constructed its Health Futures Center—expanding the school’s impact as a research institution emphasizing medical technology acceleration and innovation, entrepreneurship, and healthcare education.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 20, 2022
Is telehealth finally mainstream?
After more than a century of development, telehealth has become a standard alternative for many types of care.
Codes and Standards | Jun 14, 2022
Hospitals’ fossil fuel use trending downward, but electricity use isn’t declining as much
The 2021 Hospital Energy and Water Benchmarking Survey by Grumman|Butkus Associates found that U.S. hospitals’ use of fossil fuels is declining since the inception of the annual survey 25 years ago, but electricity use is dipping more slowly.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 13, 2022
University of Kansas Health System cancer care floors foster community and empathy
On three floors of Cambridge Tower A at The University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, patients being treated for blood cancers have a dedicated space that not only keeps them safe during immune system comprising treatments, but also provide feelings of comfort and compassion.

















