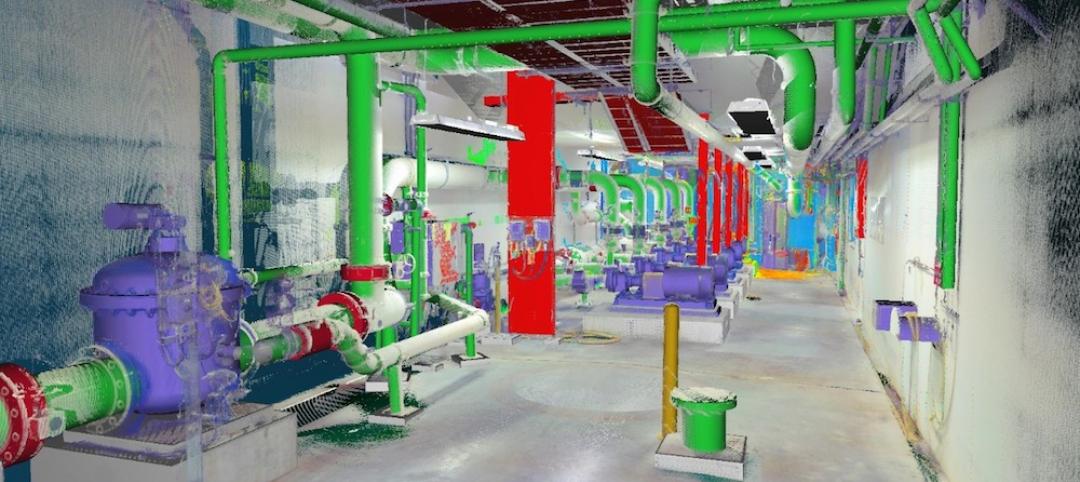
In the world of architecture and engineering, laboratory buildings are among the most complex buildings to design, plan, and document. Traditional methods rely on the use of photographs, hand drawings, or notes to document not only the building but also the equipment that makes up a laboratory. This makes the process difficult, tedious, time consuming, and even allows for documentation errors.
Currently, the most advanced state-of-the-art technology is combining Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) technology with Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology. LIDAR is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges to Earth. BIM is workflow process software used to model and optimize projects.
The latest LIDAR technology is available in the current version of hand-held devices that are used for field documentation. These devices come equipped with a very reliable LIDAR scanner, which allows one to easily document and scan in a point cloud all the existing conditions of the building like its space, function, and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) needs.
Following the LIDAR scan, advanced software is deployed to transfer the data into a point cloud. This serves as a reliable reference to take measurements, to know where equipment is, and what its MEP needs are. Once in the point cloud, it is then exported into Autodesk ReCap Pro, and later to Autodesk Revit, which are BIM solutions.
Here it is not only inserted into the point cloud to corroborate measurements, locations and needs. It is also with the use of BIM technology and the use of special equipment families, that the foundations for the use of 7D Management of the laboratory equipment and MEP items can be developed into a 7D BIM Model.
A digital twin, which is a digital representation of a physical object or process in a digital version of its environment, can also be developed from this point. Digital twins can help an organization simulate real situations and their outcomes, ultimately allowing it to make better decisions.
LIDAR and BIM technology for building data collection
LIDAR and BIM technology such as Revit allows the existing conditions captured on site to be preserved in the digital model, allowing for measurements, orientation to aspects of the model, etc. without having to be physically on site, and more importantly, to have an orientation as to where each piece of equipment is and what the MEP needs are.
Even for any highly experienced architect or BIM modeler, just using photographs or hand drawings can be overwhelming and very complicated. Using this process, the Revit model serves as a replica of the existing conditions of each space and equipment. During a building expansion, being able to compare existing equipment in the new space is more accurate and easier to understand.
For example, Hampton Roads Sanitation District (HRSD) in Virginia Beach, Va., used LIDAR and BIM technology to develop precise building and equipment data for a planned expansion of its Central Environmental Laboratory.
The process involved meticulously scanning each space relevant to the project. This comprehensive scan aimed to capture every corner accurately. Following the scanning phase, the data was processed, generating a point cloud in ReCap Pro format. With the point cloud, we harnessed the advantages of LIDAR technology such as digitally acquiring existing conditions of the building and equipment, essentially providing a virtual on-site experience with just a click, eliminating the need for physical site visits.
This technology has enabled us to create detailed digital 3D families for every existing piece of equipment and its needs, as well as to capture more accurate existing conditions for the building. In the past, our approach relied solely on on-site measurements and photographs, leading to continuous errors and laborious, time-consuming tasks.
The previous method also necessitated numerous site visits for data verification. The implementation of this advanced technology and streamlined process has not only saved time and money but has also significantly enhanced our efficiency. For instance, all of that work required in the past to digitally model from notes, photographs, existing building plans, etc. has been condensed to the import and refinement of the point cloud data into the modeling environment.
Related Stories
Big Data | May 5, 2016
Demand for data integration technologies for buildings is expected to soar over the next decade
A Navigant Research report takes a deeper dive to examine where demand will be strongest by region and building type.
BIM and Information Technology | May 2, 2016
How HDR used computational design tools to create Omaha's UNO Baxter Arena
Three years after writing a white paper about designing an arena for the University of Nebraska Omaha, HDR's Matt Goldsberry says it's time to cherry-pick the best problem-solving workflows.
Virtual Reality | Apr 29, 2016
NBBJ to develop virtual reality productivity platform
The Seattle design firm has partnered with Visual Vocal, a startup VR company.
Drones | Apr 25, 2016
The Tremco SkyBEAM UAV is the first to be approved by the FAA for nighttime commercial operation
The SkyBEAM UAV is used for identifying energy leaks, rooftop damage, deteriorating façades, and safety issues without requiring scaffolding or cranes.
AEC Tech | Apr 15, 2016
Should architects learn to code?
Even if learning to code does not personally interest you, the growing demand for having these capabilities in an architectural business cannot be overlooked, writes computational design expert Nathan Miller.
Building Tech | Apr 12, 2016
Should we be worried about a tech slowdown?
Is the U.S. in an innovative funk, or is this just the calm before the storm?
AEC Tech | Apr 12, 2016
Startup introduces PaperLight, an interactive projection screen for AEC pros
The device lets users edit sketches, plans, and images with a stylus or their fingers.
AEC Tech | Mar 31, 2016
Deep Learning + AI: How machines are becoming master problem solvers
Besides revolutionary changes to the world’s workforce, artificial intelligence could have a profound impact on the built environment and the AEC industry.
AEC Tech | Mar 17, 2016
Managing risks with laser scanning gives AEC firms an edge
The more that clients demand the service, the easier it is to justify the cost of laser scanning equipment and software.
AEC Tech | Mar 15, 2016
Two to tango: Project Tango isn’t just for entertainment, it also has a wide range of possibilities relating to the professional world
Making things like augmented reality, precise measurements of indoor spaces, and indoor wayfinding possible, Google’s Project Tango has all the makings to become a useful and ubiquitous tool in the AEC market.