On February 8, 2024, Mayor Muriel Bowser presented the Zero Waste DC Plan to the Council, outlining policies, programs, and initiatives to meet the District’s aim of reducing per capita waste generation by 15% and transitioning from a disposable culture to a circular economy. Of the 43 actions in the plan, a handful are essential for building owners and design professionals to know about now.
Overview of the Zero Waste DC Plan
In 2013, the District enacted the Sustainable DC Plan and established the ambitious goal of diverting 80% of the citywide waste stream away from landfills and incineration. For 2018, that citywide waste stream was estimated at over 1.1 million tons. Previously established guidelines from the 2019 Sustainable DC 2.0 Plan and the Zero Waste Omnibus Amendment Act of 2020 guided development of the Zero Waste DC Plan, finalized in early 2024 after years of research and public engagement. Originally, the target year to achieve 80% diversion of solid waste was 2032, but technical analysis that modeled rates of adoption, participation, and materials capture guided extension of the zero-waste target year to 2040.
What most DC residents and business owners will be talking about in the months ahead are the plan provisions for phasing out single-use plastics and other disposable items beginning next year, with a ban on throwaway plastics by 2030. Other noteworthy action items include mandatory recycling and composting, policies to increase reusable and refillable packaging, and requirements for donation of surplus food and materials.
What might not be the talk of the town – at least not right away – are some of the demands on building owners and design professionals that will impact construction projects.
Construction and Demolition
The primary objective of the Zero Waste DC Plan is articulated in “Goal 1: Reduce Per Capita Waste Generation.” Without a significant drop in waste, the plan will fail to achieve the 80% cut in the volume of material that winds up in landfills and incinerators. Of critical importance to building owners, property managers, and design professionals is Action 5 under this Goal, which calls for updating the DC Green Construction Code to require all new construction, demolition, and building retrofit projects to submit a Deconstruction Plan. Eighty percent of recoverable materials, including lumber, metal, stone, brick, and electrical and plumbing fixtures, will need to be salvaged and contributed toward the development of affordable housing. How this will be achieved is yet to be determined, but the timeframe for implementation is listed as “Medium Term,” which could be as soon as five years from now.
In the short term, Action 25 seeks to expand Extended Producer Responsibility requirements for hard-to-recycle materials, including some construction waste, such as paint, carpet, textiles, and solar panels. Upon implementation, anticipated within the next few years, disposal of covered materials in landfills or incinerators will be banned.

Recycling and Composting
Under “Goal 3: Increase Recycling and Composting Participation and Accessibility,” Action 14 calls for adoption of a universal recycling and composting ordinance that will require owners and facility managers of all commercial, institutional, governmental, and multi-family residential buildings to provide for the separation and collection of recyclable materials (e.g. plastics, glass, paper, aluminum, and cardboard), as well as compost (including food scraps and compostable containers). The plan looks to adopt this ordinance by 2025, which means facility managers should plan as soon as possible for this change in operations. Design professionals and property owners alike should consider the space requirements for sorting and collection.
To this end, Action 24 calls for revision of the DC Green Construction Code to require all new multi-family residential construction to include dedicated space for recycling and composting. By 2032, existing multi-family residential properties must be retrofitted to meet this requirement, as well.
Enforcement
Community education is a key part of the plan, from training programs for property managers on preventing food waste to hands-on learning about composting in school cafeterias. Robust enforcement, though, is also a critical component. Action 38 aims to increase the number of inspectors – and impose fines – for building owners and businesses that fail to comply. To place oversight directly into the hands of the community, Action 39 establishes a new Zero Waste Tip-Line for residents to report non-compliant commercial buildings and businesses.
Zero Waste Financial Assistance
Implementing recycling and composting collection, providing for recoverable construction waste diversion, and arranging producer recovery of hard-to-recycle materials, along with navigating operational changes to eliminate food waste and disposable products, won’t be cheap. Under “Goal 5: Build an Inclusive and Local Circular Economy,” Action 32 calls for expanding financial assistance programs – and creating new ones – particularly for small businesses, nonprofits, and institutions. Zero Waste tax credits and other incentives are also on the agenda to help owners manage these costs, with planned implementation by 2028.
Ahead of the Curve
To prepare for these changes, building owners, property managers, and design professionals should begin coordinating with suppliers and contractors to discuss implications for any upcoming construction projects. Reusing existing materials, particularly for historic buildings, may already be part of the plan for rehabilitation or restoration efforts, but newer buildings, too, should look at ways to salvage and reuse. As for composting and recycling, with demand surging over the coming months in response to the new plan, it’s a good idea to start preparing early, especially if retrofitting designated sorting and collection spaces will require building modifications.
Even if the initiatives under the Zero Waste DC Plan aren’t fully in force right away, it’s good practice to start implementing the policies now, where feasible. Early adoption will not only lead the pack on cutting down waste, but also allows time to practice new procedures at an unhurried pace before mandates force a hasty effort to comply.
This material is for informational purposes. Before taking action, consult a design professional.
Hoffmann Architects + Engineers (www.hoffarch.com) is a design professional firm specializing in the rehabilitation of building exteriors, with offices in Alexandria Va., New York, and New Haven Conn.
Related Stories
| Dec 24, 2013
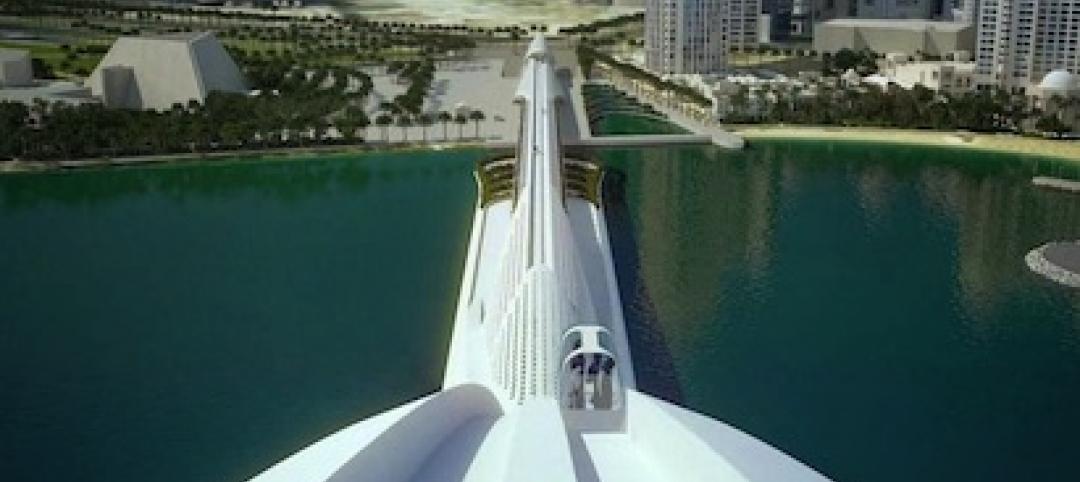
First Look: Calatrava's Sharq Crossing in Doha, Qatar [video]
The government of Qatar has released details of Sharq Crossing, a massive infrastructure project designed by Spanish architect Santiago Calatrava.
| Dec 23, 2013
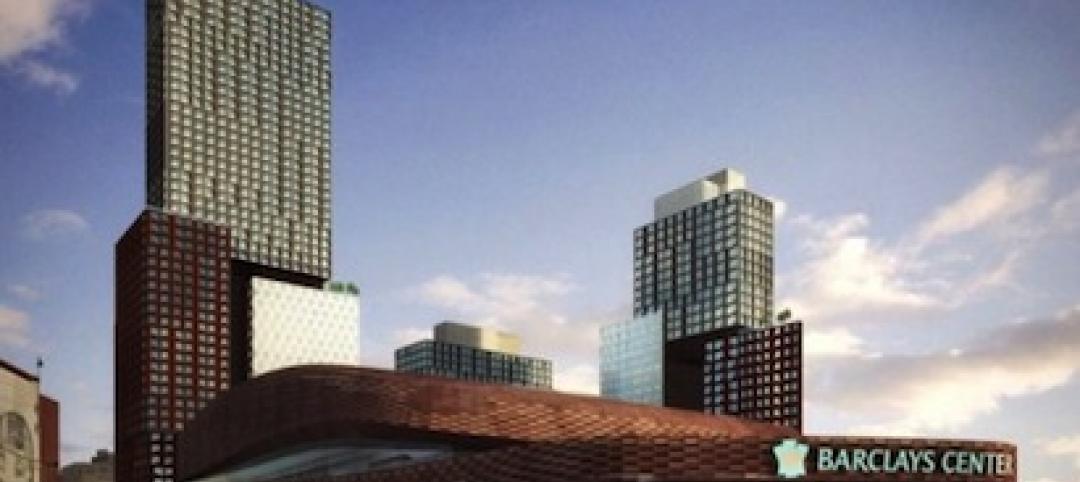
MBI commends start of module setting at B2, world's tallest modular building
The first modules have been set at B2 residential tower at Atlantic Yards in New York, set to become the tallest modular building in the world.
| Dec 23, 2013
First Look: KPF's dual-tower design for Ziraat Bank in Istanbul
Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates (KPF) is designing a new headquarters for Turkey’s largest and oldest financial institution, Ziraat Bank, in a modern, suburban district of Istanbul.
| Dec 20, 2013
Top healthcare sector trends for 2014 (and beyond)
Despite the lack of clarity regarding many elements of healthcare reform, there are several core tenets that will likely continue to drive transition within the healthcare industry.
| Dec 20, 2013
Must see for the holidays: Architects re-create iconic structures using gingerbread
Gensler, PBK, Page Sutherland Page, and Kirksey were among the firms to compete in the 5th Annual Gingerbread Build-Off.
| Dec 20, 2013
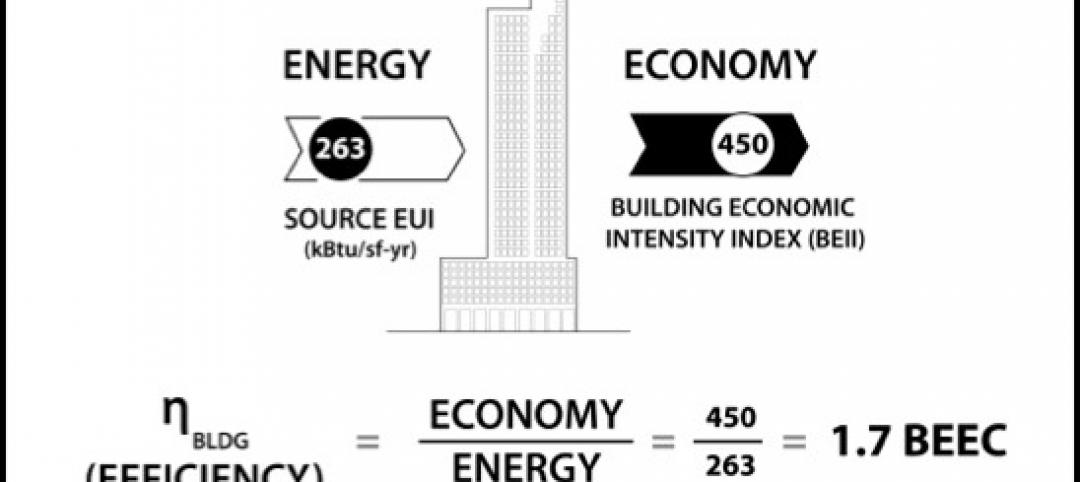
Can energy hogs still be considered efficient buildings? Yes, say engineers at Buro Happold
A new tool from the engineering firm Buro Happold takes into account both energy and economic performance of buildings for a true measure of efficiency.
| Dec 20, 2013
Ten spectacular contemporary churches [slideshow]
German building-information provider Emporis compiles a photographic tour of inspirational spaces.
| Dec 19, 2013
NRDC report relates green infrastructure investments to commercial property value [Infographic]
The Natural Resources Defense Council has released The Green Edge: How Commercial Property Investment in Green Infrastructure Creates Value -- a first-ever illustrative and well-documented report that helps demonstrate the value of green infrastructure. It draws from available published material to capture the multitude of tangible, monetizable non-water quality and water quality benefits that green infrastructure investments (trees, rain gardens, and porous pavement, rainwater harvesting cisterns, bioswales, etc.) can unlock for the commercial real estate sector, including commercial property owners and their tenants.
| Dec 19, 2013
Mastering the art of crowd control and visitor flow in interpretive facilities
To say that visitor facility planning and design is challenging is an understatement. There are many factors that determine the success of a facility. Unfortunately, visitor flow, the way people move and how the facility accommodates those movements, isn’t always specifically considered.
| Dec 19, 2013
Urban populations, climate change demand resilient design: Report
With over fifty percent of the population already living in urban areas, cities must grapple with the potentially catastrophic effects of climate change (think: Superstorm Sandy in New York). In a new report, Jones Lang LaSalle has identified steps cities can take to make their infrastructure more resilient to changing climate conditions.