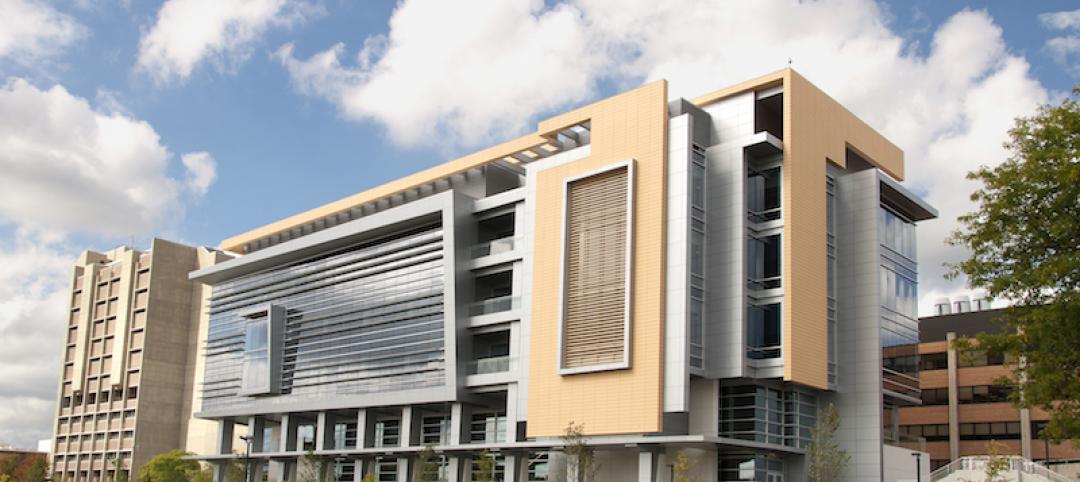
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) at Kansas City University was designed to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy. The project program supported the mission of training leaders in osteopathic medicine with a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training.
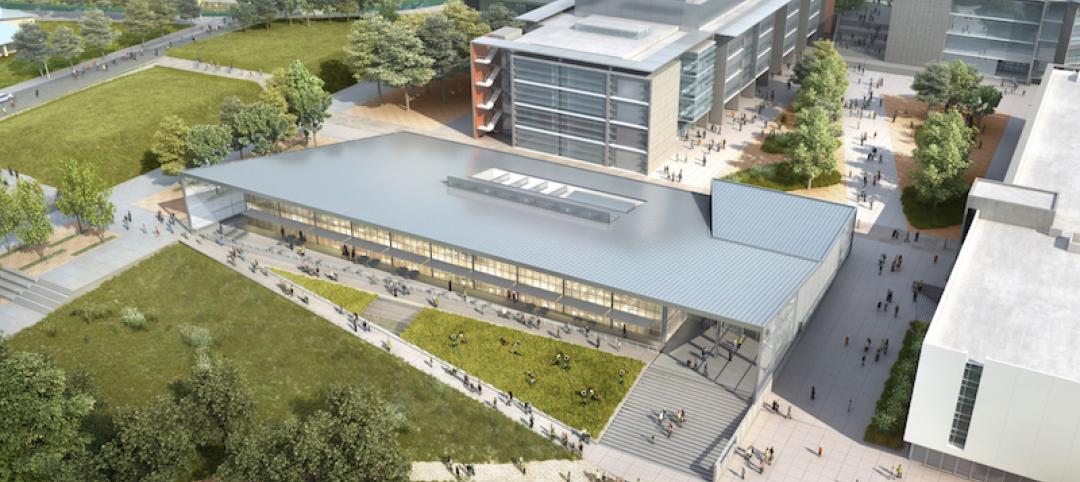
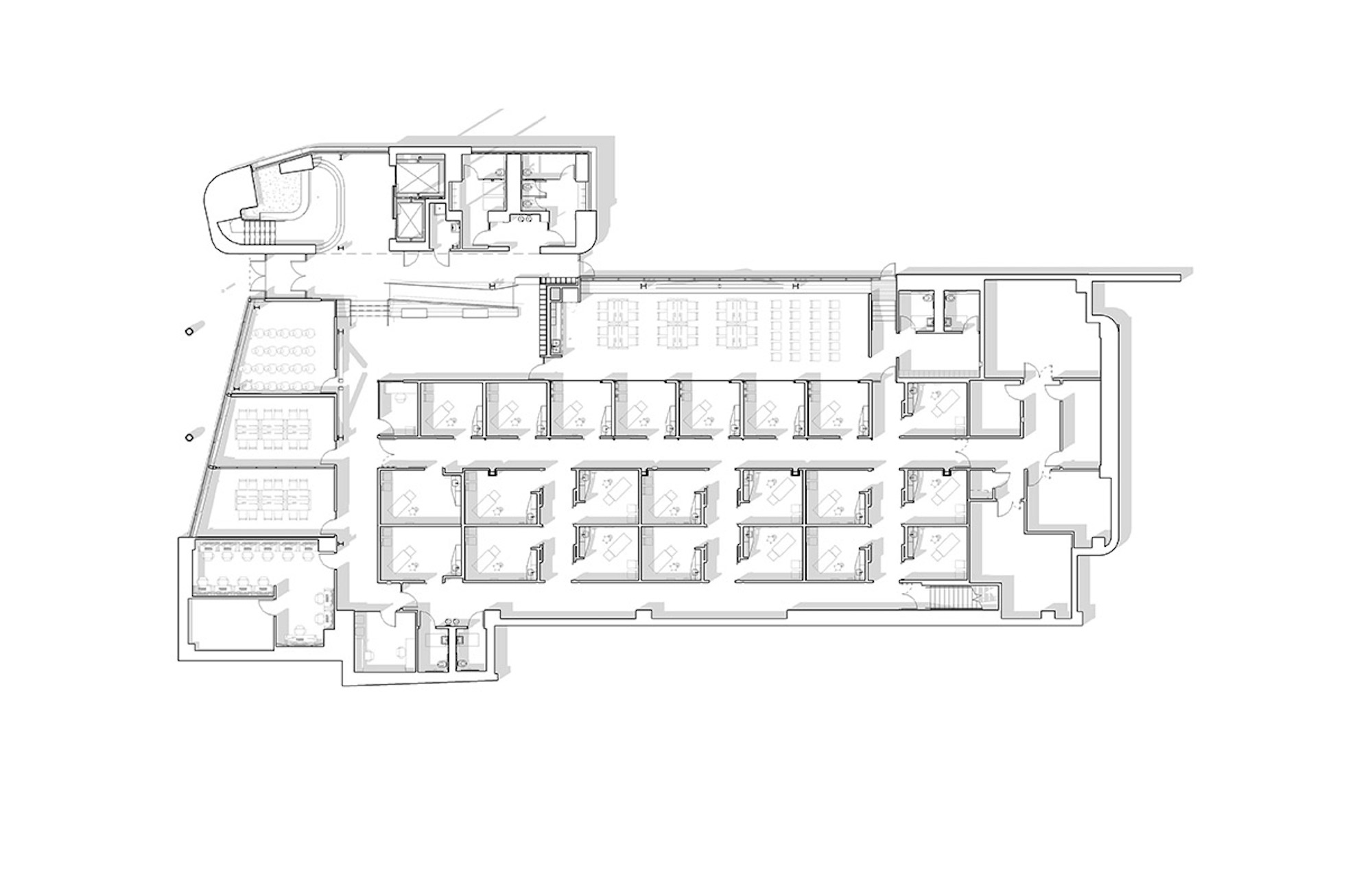
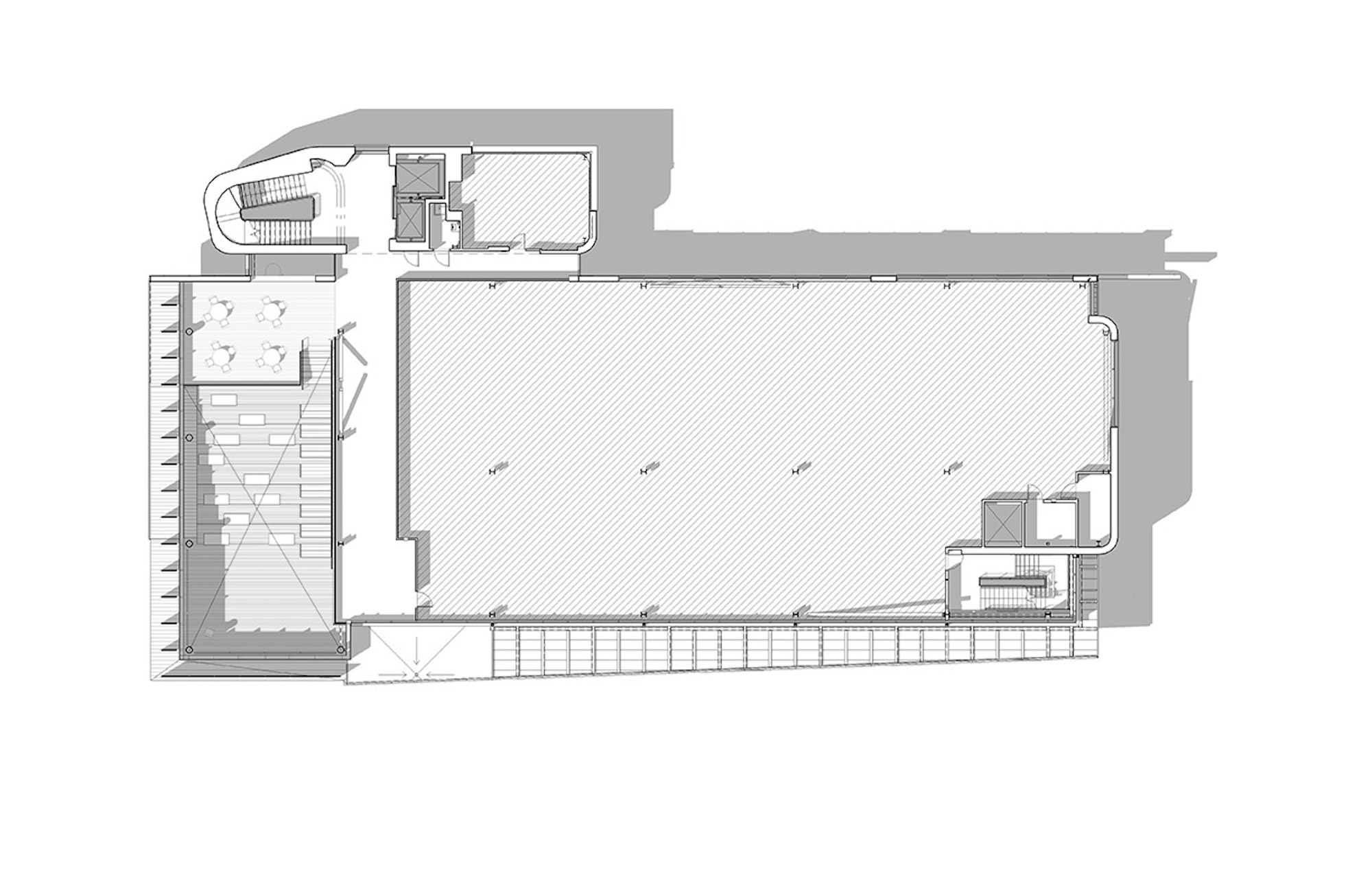
The four-story, 56,000-sf medical education facility and an adjacent two-level free-standing parking structure were designed with key themes of transparency and multi functionality. The building consists of about 26,000 sf of assignable medical education space and an additional 9,500 sf of shelled classroom space.
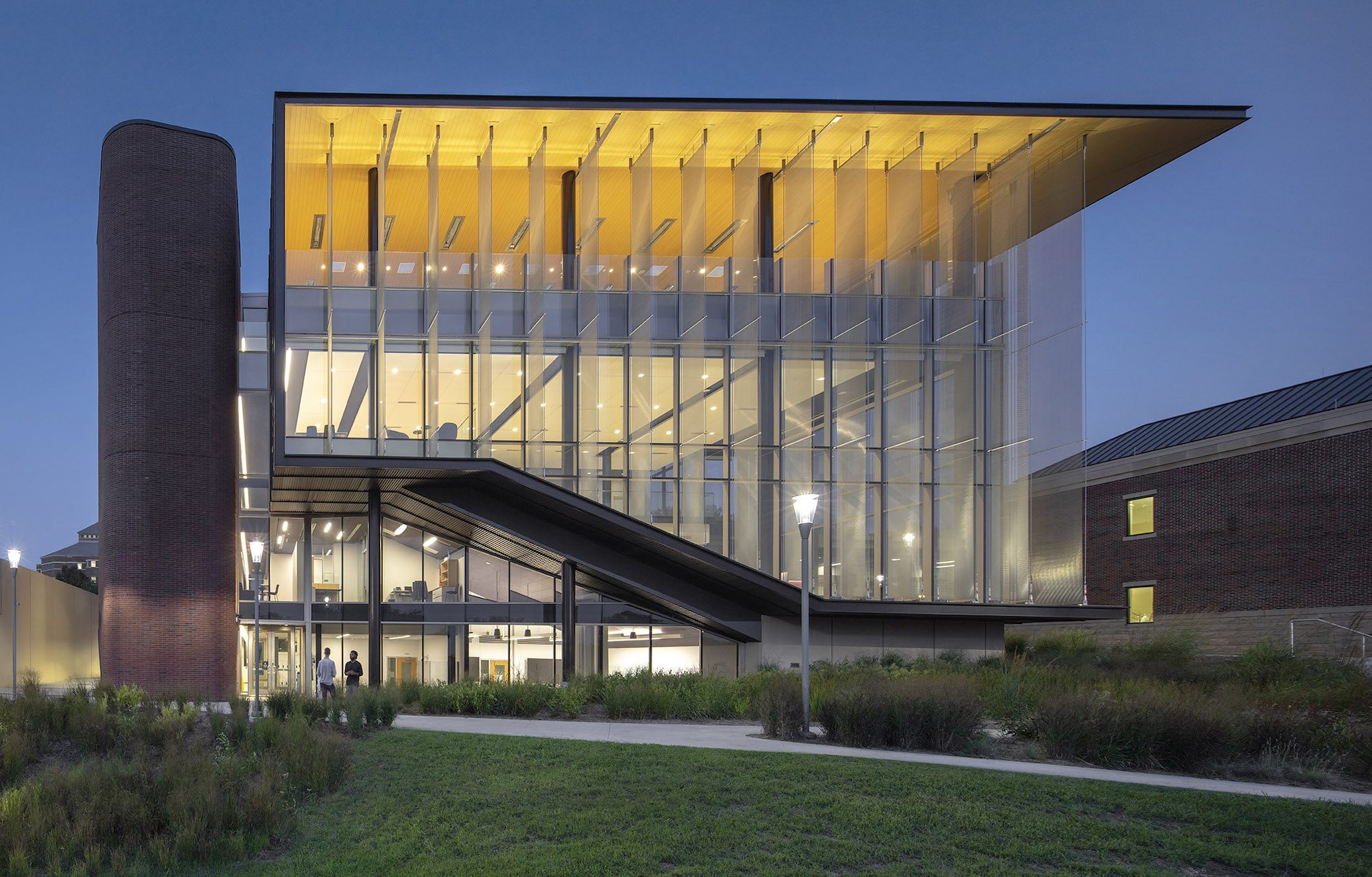
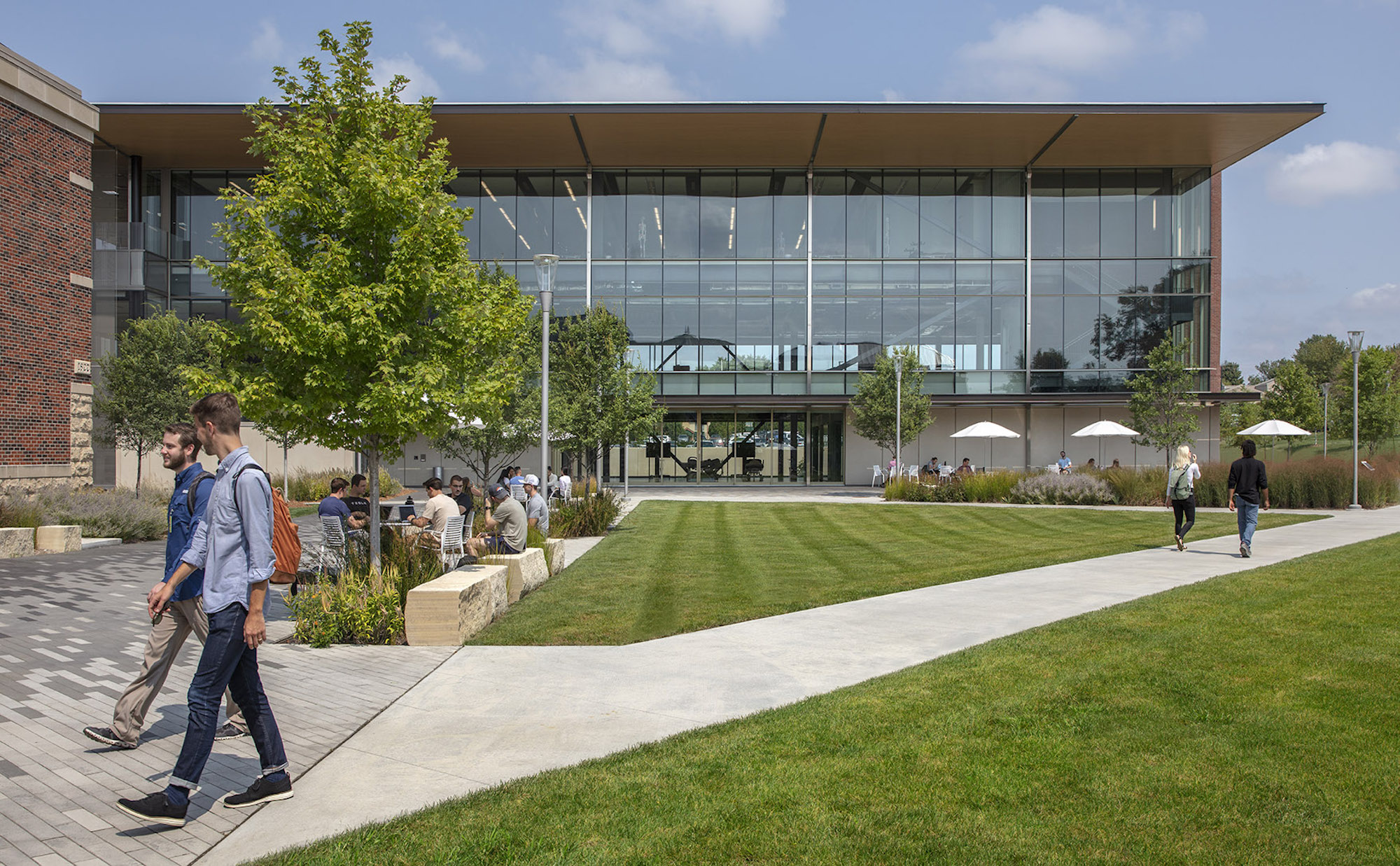
The CMEI helps define a new campus entry and lower quad. The pavilion-like four-story building takes advantage of the site’s sloping topography while maintaining the scale of the existing campus by lowering one floor into the sloping site. This approach creates the illusion of a three-story structure on the campus quad.
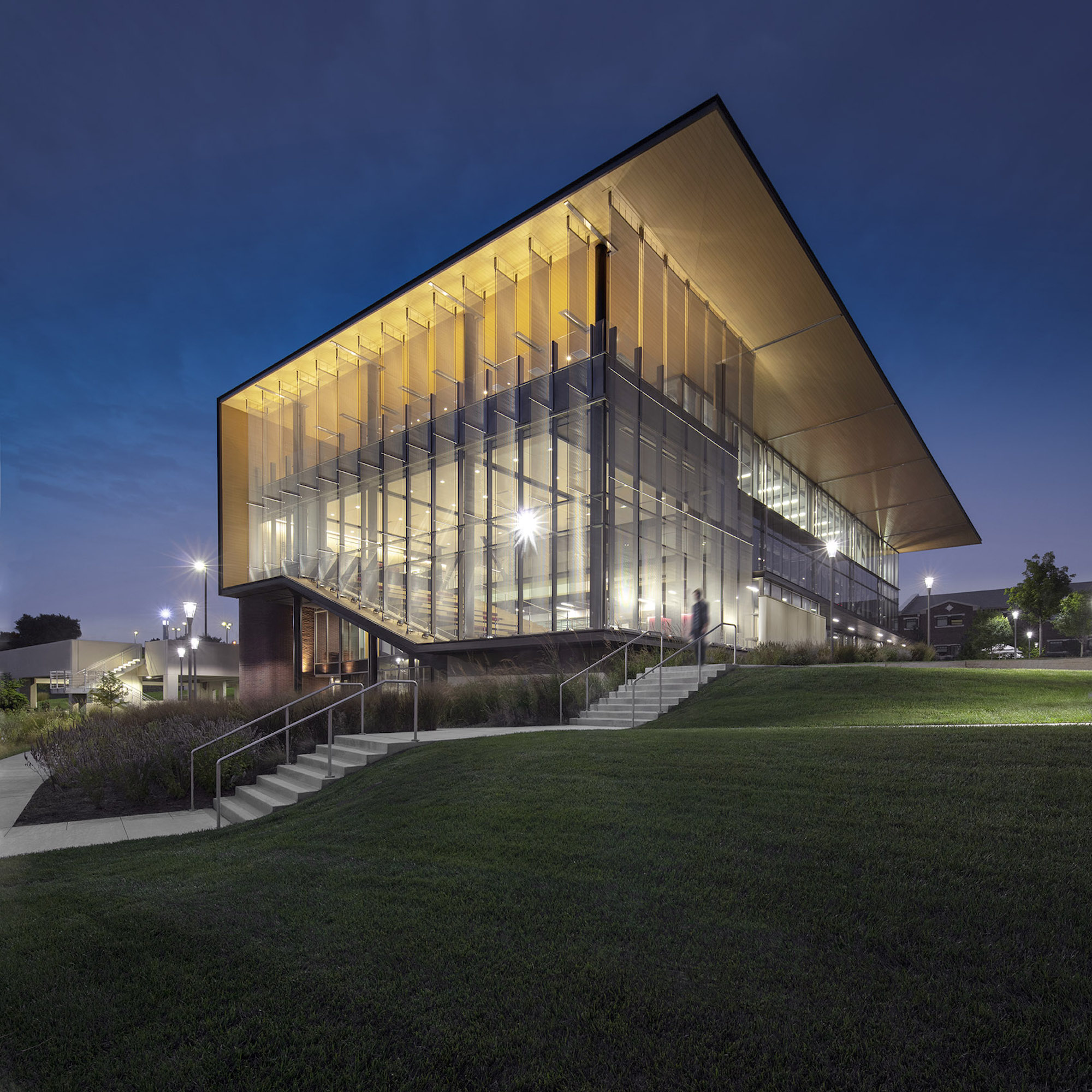
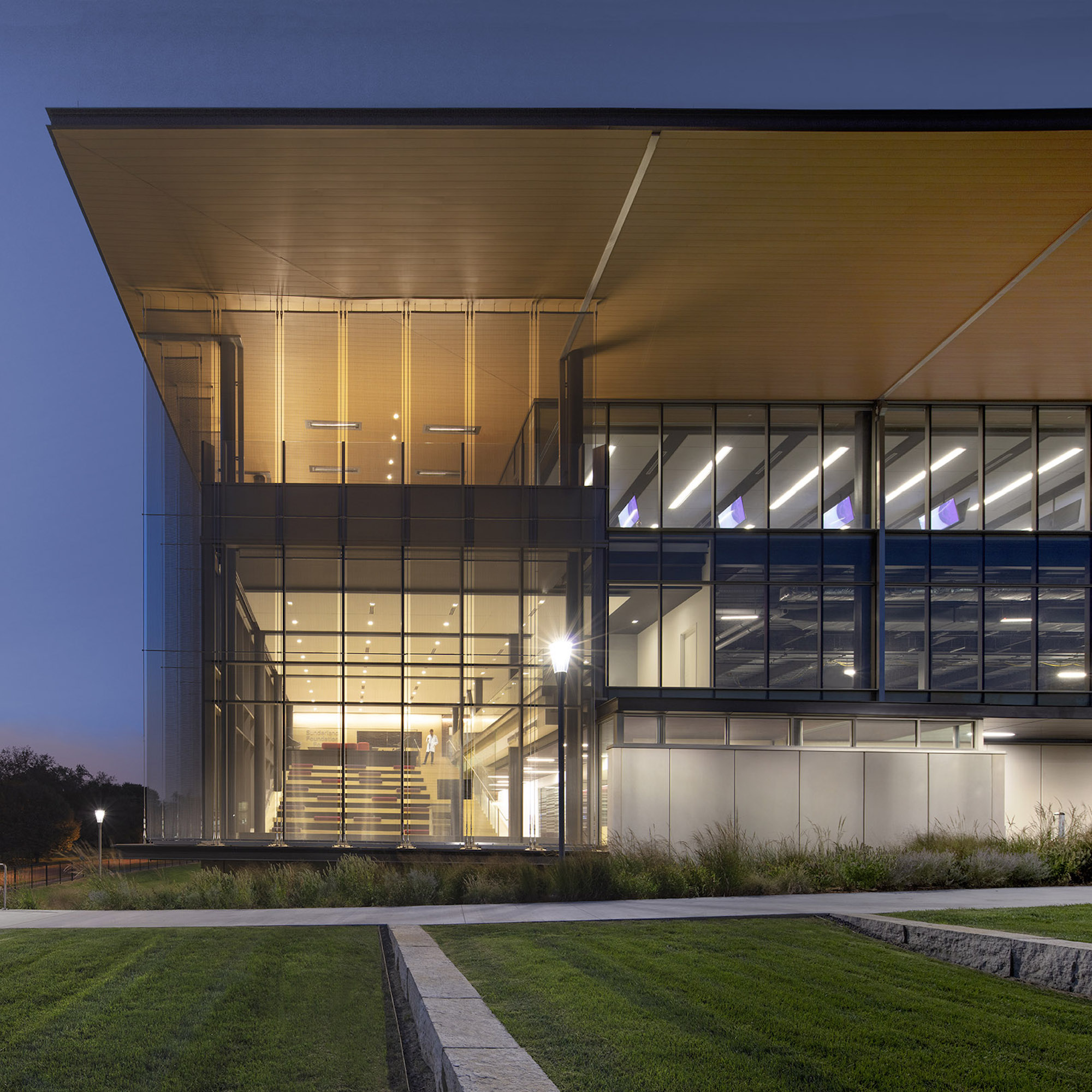
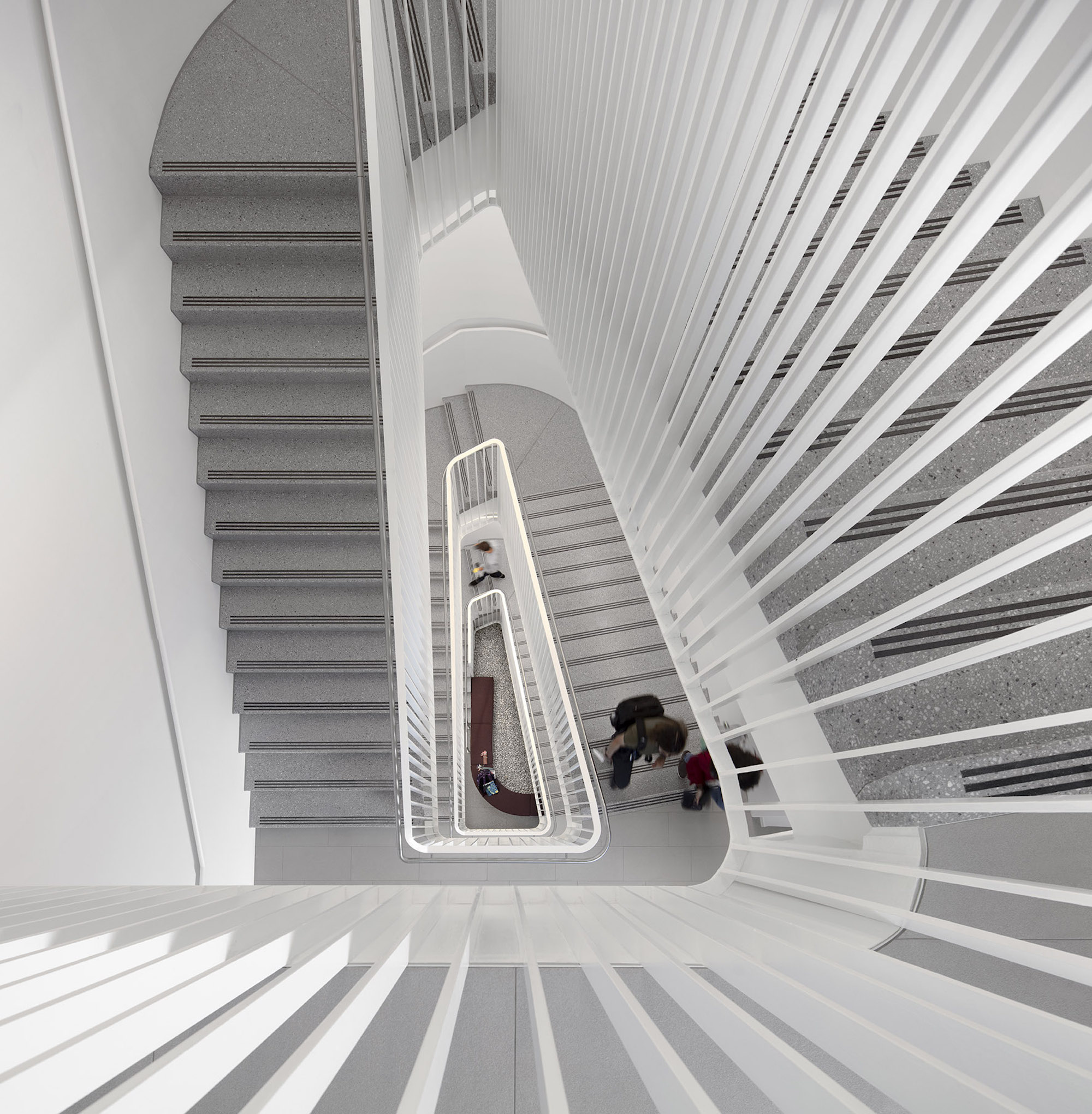
Users are introduced to the building through the connective, multi-level, 3,000 sf lobby that doubles as a public forum to provide waiting, colloquia, study, and briefing functions. The raked, glazed two-story lobby and third-floor terrace appear to hover over the ground plane to offer a panoramic view of downtown Kansas City. The pavilion is wrapped with a single folding-plane gesture, which begins at the articulated lobby floor, bends upward to form the north wall, and crests to create a dramatically extended roof to help shade the south-facing glass elevation.
Transparency guided the articulation of the glass curtain wall to showcase the next-generation medical education environments within. The glazing defines the visually open facility, highlighting its learning activities during the day, and transforming into a subtle, illuminated beacon on campus at night. Evoking the heritage of the campus’ brick-clad buildings, the materials palette is rounded out with low-maintenance brick, metal panel, and precast concrete.
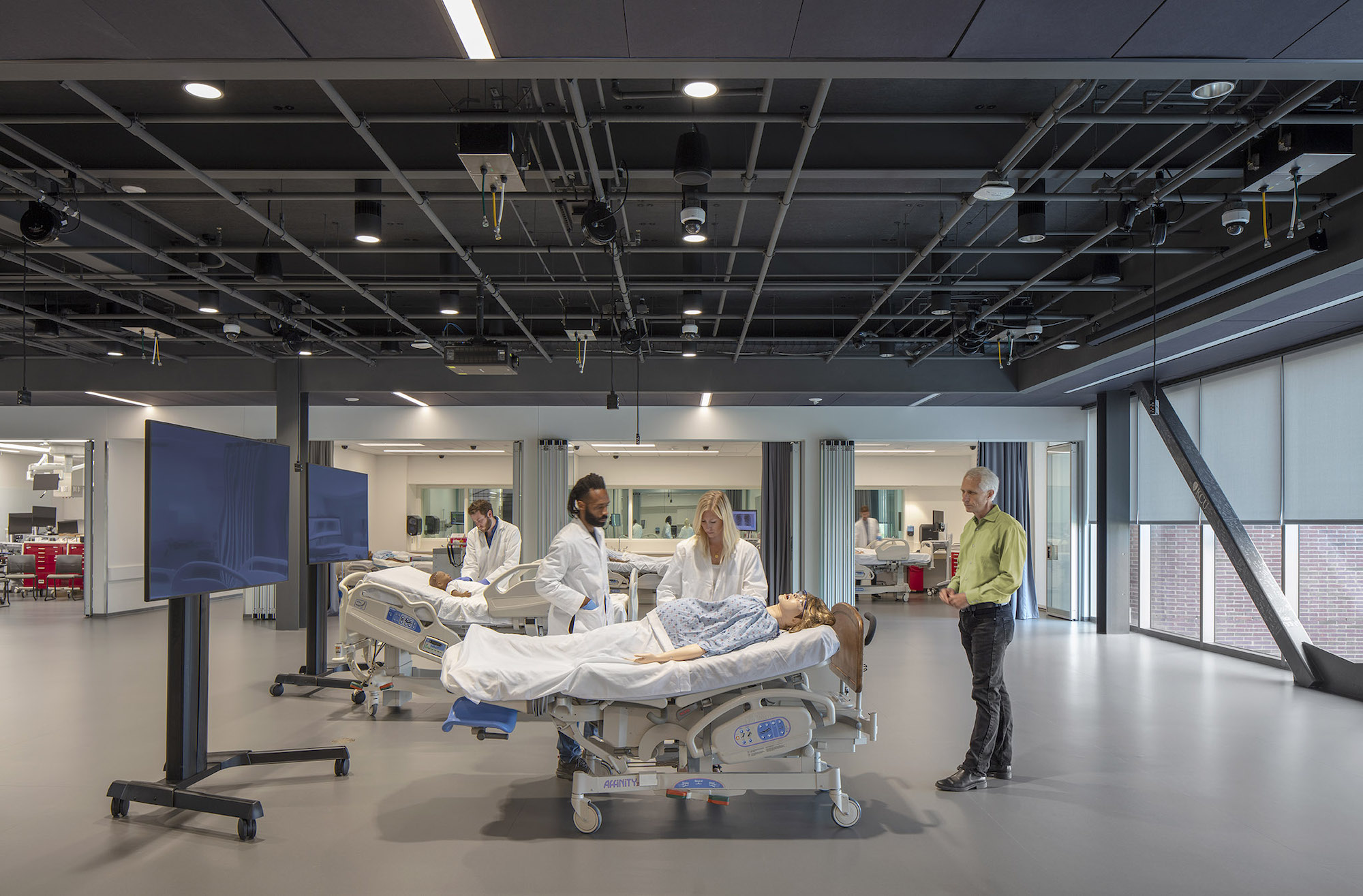
The building can adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy with a 2,800 sf simulation deck, clinical skills suite with 22 mock exam rooms, a 6,500 sf osteopathic manipulative medicine lab, and multi‐use forum that support multiple functions. The simulation suite houses an innovative and adaptable “black box” stage that can accommodate small-scale scenarios as well as large trauma events. The open ceiling utilizes a theater grid of steel tubes to supply air, vacuum, electricity, and data for simulation use, as well as hanging lights and simulation equipment that can be freely arranged throughout the space.
Situating the simulation suite at grade with its 40-foot opening to the exterior enables the space to expand onto the adjacent campus quad. Operable walls along exam rooms allow the standardized patient lounge to flex as a health assessment lab or serve as an after-hours student study space.
On the project team:
Owner and/or developer: Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences
Design architect: CO Architects
Architect of record: Helix Architecture + Design
MEP engineer (and lighting): Henderson Engineers
Structural (and civil) engineer: Walter P Moore
Acoustical, AV/IT Design: The Sextant Group (now NV5)
Landscape: Confluence
General contractor/construction manager: JE Dunn Construction
KCUMB Video from CO Architects on Vimeo.
A vision of the future of medical education buildings
Here is the design statement from architect CO Architects:
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) project for Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences (KCU) in Kansas City, MO, is the first of a new generation of buildings at KCU aimed at fostering growth within the ever-evolving field of osteopathic medical education. Designed by CO Architects in collaboration with Helix Architecture + Design, the $33-million CMEI has an iconic design that bridges KCU’s history and traditions with its forward-looking role as a leader in osteopathic medicine.
Sited on approximately 4.5 acres of previously undeveloped green space on the west edge of campus, the CMEI helps define a new campus entry and Lower Quad. The pavilion-like four-story building takes advantage of the site’s sloping topography while maintaining the scale of the existing campus by lowering one floor into the sloping site, creating the illusion of a three-story structure on the campus quad.
Users are introduced to the building through the connective, multi-level, multi-functional, 3,000-square-foot lobby that doubles as a public forum to provide waiting, colloquia, study, and briefing functions. The raked, glazed two-story lobby and third-floor terrace appear to hover over the ground plane to offer a panoramic view of downtown Kansas City, thereby visually connecting the university with the city to emphasize KCU’s mission of improving the well-being of the larger community. The pavilion is wrapped with a single folding-plane gesture, which begins at the articulated lobby floor, bends upward to form the north wall, and then crests to create a dramatically extended roof to help shade the south-facing glass elevation.
Transparency is a key element of the design of the CMEI, guiding the articulation of the glass curtain wall to showcase the next-generation medical education environments within. The glazing defines the visually open facility, highlighting its learning activities during the day, and transforming into a subtle, illuminated beacon on campus at night. The building is a dramatic anchor to a future new campus entry. Evoking the heritage of the campus’ brick-clad buildings, the materials palette is rounded out with low-maintenance brick, metal panel, and precast concrete.
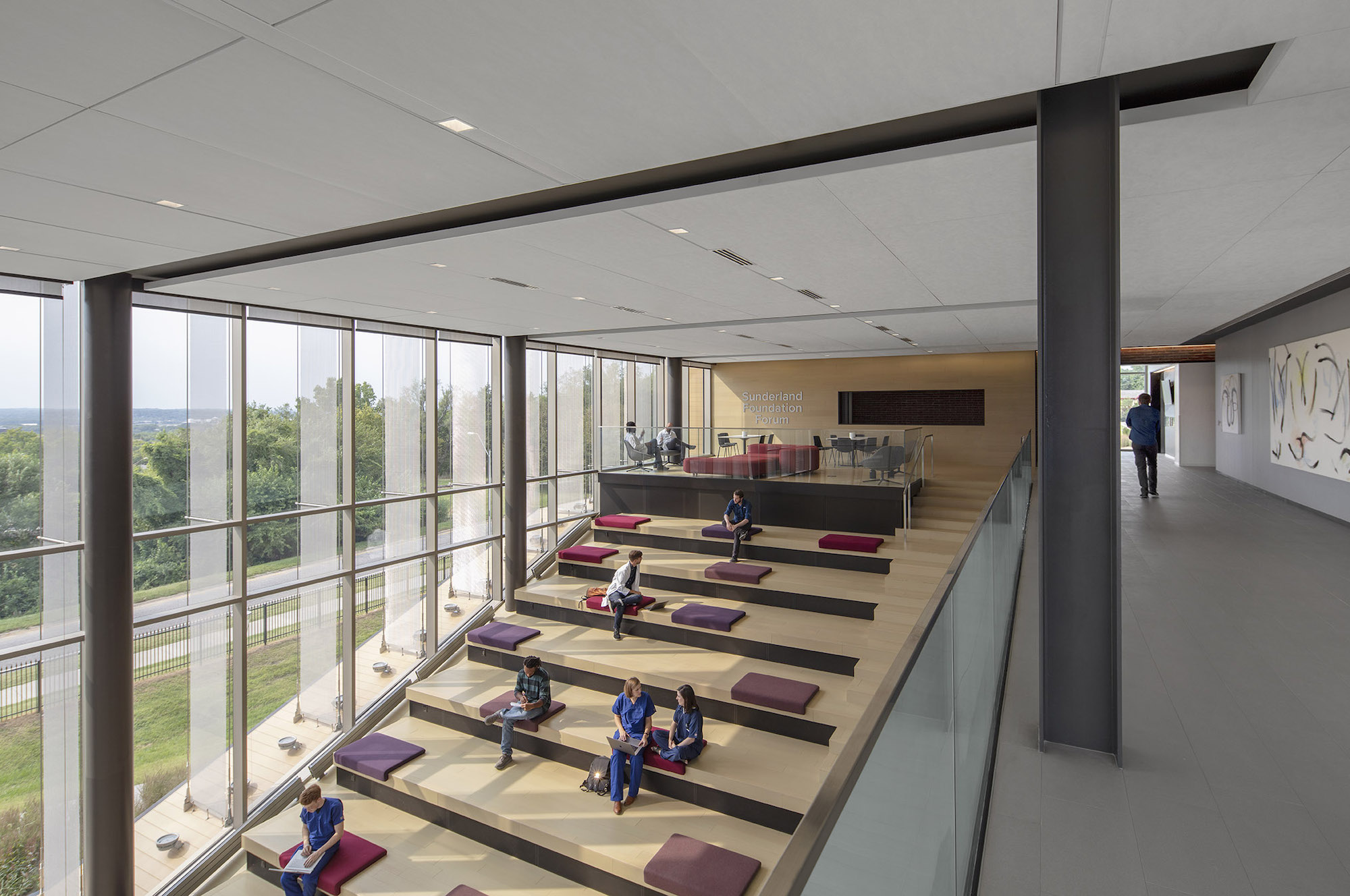

Paramount to the success of the project is the building’s ability to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy, and for the programed spaces—a 2,800-square-foot simulation deck, clinical skills suite with 22 mock exam rooms, 6,500-square-foot osteopathic manipulative medicine lab, and multi‐use forum—to support multiple functions. The simulation suite houses an innovative and adaptable “black box” stage that can accommodate small-scale scenarios as well as large trauma events.
The open ceiling above utilizes a theater grid of steel tubes to supply air, vacuum, electricity, and data for simulation use, as well as hanging lights and simulation equipment that can be freely arranged throughout the space. Situating the simulation suite at grade with its 40-foot opening to the exterior enables the space to expand onto the adjacent campus quad. Operable walls along exam rooms allow the standardized patient lounge to flex as a health assessment lab, or serve as an after-hours student study space.
The design of the CMEI, which is LEED certified, addresses sustainability from multiple fronts. The building form was conceived to strengthen performance: It is oriented lengthwise in the east/west direction, so solar heat gain is easier to control on the longer north and south façades. The broad, 24-foot-deep cantilevered roof fully shades the south façade during the summer. Brick construction on the east façade blocks harsh early morning sunlight, and semi-transparent metal-mesh fins on the west side shade the glazing while maintaining the impressive views of the Kansas City skyline. The metal-mesh system, which features a horizontal pattern at 50% opacity, attaches to the building via ultra-thin cable rail, which allowed the design team to meet challenging wind-load requirements.
CMEI supports the University’s educational mission to train compassionate and competent leaders in osteopathic medicine by creating a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training. Through its sensitive yet bold architectural design—with the key themes of transparency and multi functionality—the building reflects both the University’s heritage and tradition as well as its vision for the future of medical education and community engagement.




Related Stories
University Buildings | Nov 18, 2016
Stephen F. Austin State University’s new STEM building breaks ground
Kirksey Architecture designed the building that ‘will serve as a landmark for SFA.’
University Buildings | Oct 25, 2016
Columbia University dedicates its new campus with great fanfare
Transparency to the surrounding community played a big role in the campus’s design.
School Construction | Oct 23, 2016
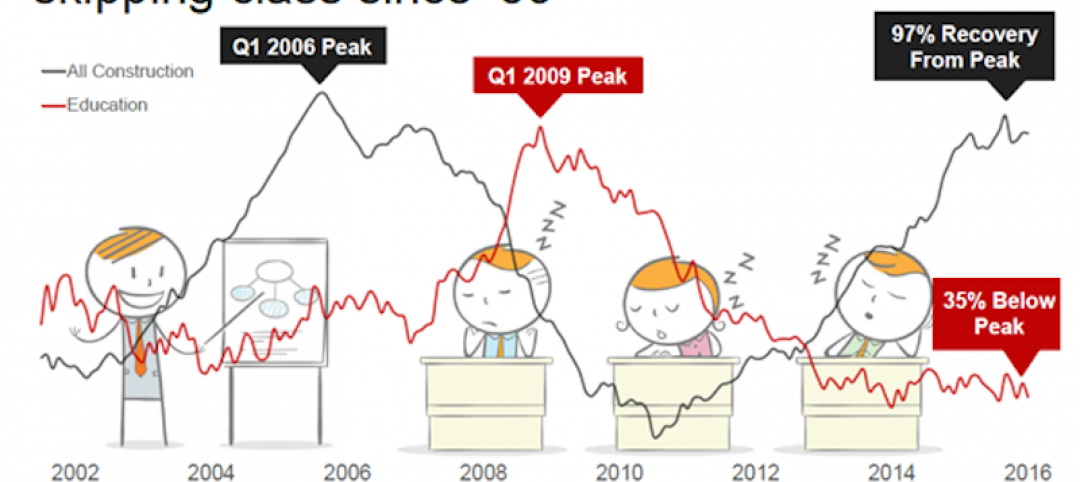
As construction rebounds, education sector spending flattens
Post-recession slump suggests a settling in at a “normal” level similar to the mid aughts.
University Buildings | Oct 19, 2016
UC Merced to nearly double its size by 2020
Its growth strategy includes adding 1.2 million sf of space for teaching, housing, and research.
University Buildings | Oct 12, 2016
The new Hancher Auditorium opens on University of Iowa campus
The building replaces the previous Hancher, which was irreparably damaged in the 2008 flood.
University Buildings | Oct 11, 2016
The University of Iowa gets a new Visual Arts Building
The building was a collaborative effort between BNIM and Steven Holl Architects and marks the sixth facility the two firms have worked together on
Sponsored | University Buildings | Oct 3, 2016
Enhancing university life: The smart shower bead
Residential spaces that need to meet high traffic demands while accommodating an ever-changing populace creates a unique set of obstacles for any educational institution’s housing.
Sponsored | University Buildings | Sep 29, 2016
UWM’s Kenwood Interdisciplinary Research Complex: The most distinctive building on campus
The largest building on campus, it was designed by Flad Architects to comply with LEED Gold Certification standards and to meet a wide range of current and future academic needs.
University Buildings | Sep 12, 2016
The University of Chicago’s newest residence halls are designed to be more like home
Abundant common spaces give students more chances to interact.
University Buildings | Aug 17, 2016
Supporting communities of motivated learners: reflections on SCUP-51
The two themes that were consistently woven into different topics were institutional transformation and connection with students.