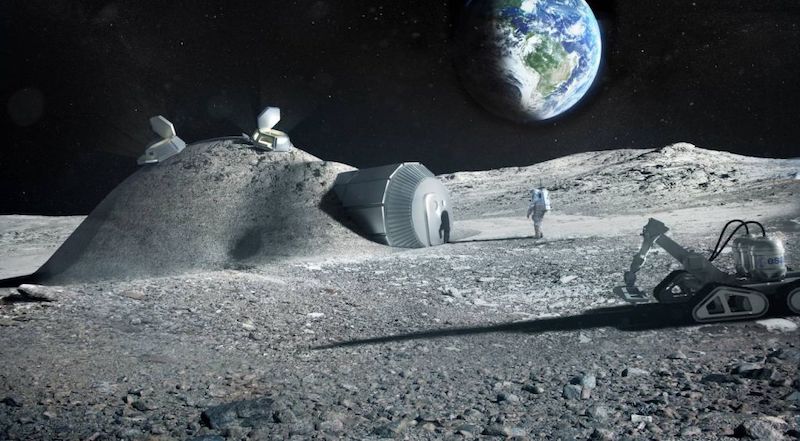
When it comes to building architecture in space, researchers, scientists, and architects have been offering up possible solutions for years. Concrete made from soil, ice shelters, and those grown from fungus have all been offered up as possible building materials. But a new possible building method may just use the most unique component of them all: urine.
Norwegian, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch scientists, together with the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA), have conducted experiments using urea from urine as a superplasticizer for lunar geopolymer mixtures that can then be used to 3D print structures. The scientists presented their findings in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
In their paper titled "Utilization of urea as an accessible superplasticizer on the moon for lunar geopolymer mixters," the scientists say urea can break hydrogen bonds and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. And since urea is the second most abundant component of urine (water being the first), it would be readily available, even in a location as barren and distant as the moon.
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
"Addition of urea has been compared with polycarboxylate and naphthalene based superplasticizers, and with a control mixture without superplasticizer. When curing the sample containing urea at 80 °C, the initial setting time became longer. The samples containing urea or naphthalene-based superplasticizers could bear heavy weights shortly after mixing, while keeping an almost stable shape. Samples without superplasticizer or containing the polycarboxylate-based admixture were too stiff for mold-shaped formation after casting. Samples containing urea and naphthalene-based admixtures could be used to build up a structure without any noticeable deformation," according to the paper.
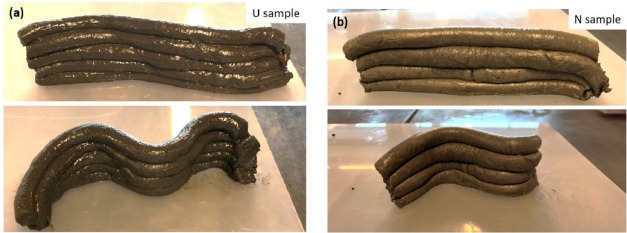
Additionally, the samples with urea also had higher compressive strength than the other two specimens containing superplasticizers, "and it continued to rise even after 8 freeze-thaw cycles."
The scientists conclude the paper by explaining further studies are needed to assess how the lunar regolith geopolymers will behave under the severe lunar conditions, which include a vacuum that can cause the volatile components to evaporate and large temperature fluctuations that can cause the structure to crack.
But if all goes according to plan, Moon Base Number 1 may have a more literal meaning than anyone ever anticipated.
Related Stories
Concrete | Jan 15, 2016
Fallingwater to Sydney Opera House: Ranking the world’s best concrete buildings
Large and small, some of the most iconic structures of all time were made of the composite building material.
| Jan 14, 2016
How to succeed with EIFS: exterior insulation and finish systems
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
Building Materials | Nov 16, 2015
A new database sheds more light on building products’ content
The Quartz Project’s collaborators, which include Google, hope these data will better inform design decisions.
Building Materials | Nov 5, 2015
U.S. Naval Research Lab develops transparent aluminum
The material is made out of highly compressed aluminum powder.
Architects | Oct 20, 2015
Four building material innovations from the Chicago Architecture Biennial
From lightweight wooden pallets to the largest lengths of CLT-slabs that can be shipped across North America
Building Materials | Oct 16, 2015
Challenges in arctic, subarctic regions subject of new ASHRAE guide
Cold, remoteness, limited utilities, and permafrost addressed.
Building Materials | Sep 25, 2015
Dept. of Agriculture encouraging tall wood structure construction
Prize awarded for 10-story or higher wooden buildings
Building Materials | Aug 28, 2015
Structural steel buildings specification available for second public review
Next year's specification open for comments until Sept. 21
Sponsored | Building Materials | Jul 29, 2015
Glulam provides aesthetic, structural, and safety solution for Appleton Mills project
The Appleton Mills complex includes 5 million square feet of space, with an original structure built in the 1870s and another building added in 1906
Sponsored | | Jul 24, 2015
Nature in Design: The Biophilia Effect
The preference for nature has a name: biophilia, which literally means “love of life.”

















