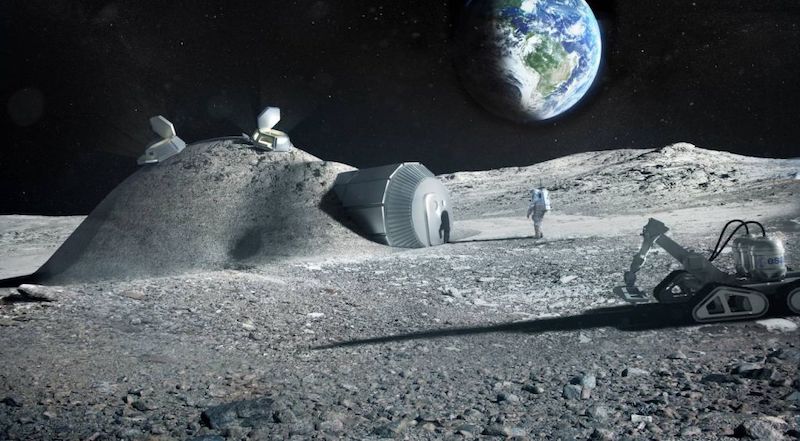
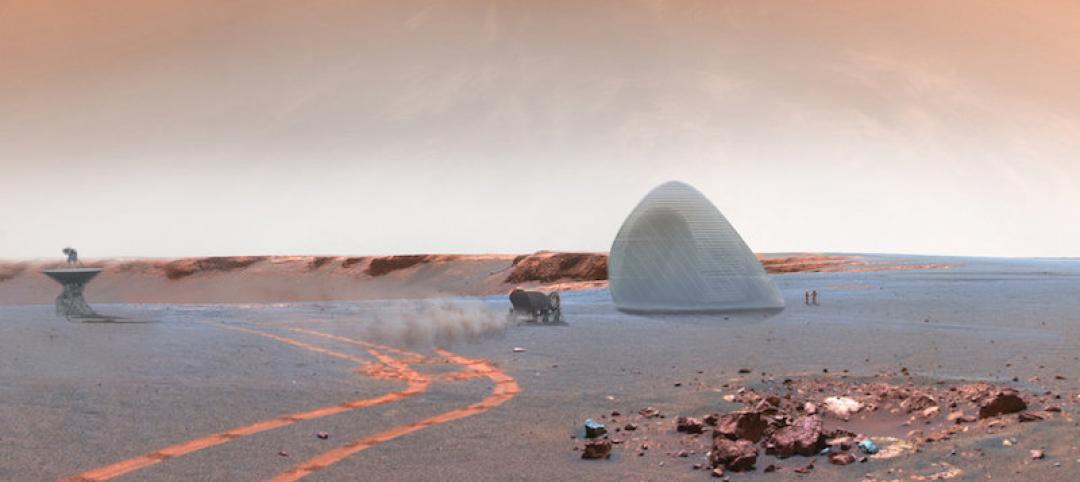
When it comes to building architecture in space, researchers, scientists, and architects have been offering up possible solutions for years. Concrete made from soil, ice shelters, and those grown from fungus have all been offered up as possible building materials. But a new possible building method may just use the most unique component of them all: urine.
Norwegian, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch scientists, together with the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA), have conducted experiments using urea from urine as a superplasticizer for lunar geopolymer mixtures that can then be used to 3D print structures. The scientists presented their findings in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
In their paper titled "Utilization of urea as an accessible superplasticizer on the moon for lunar geopolymer mixters," the scientists say urea can break hydrogen bonds and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. And since urea is the second most abundant component of urine (water being the first), it would be readily available, even in a location as barren and distant as the moon.
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
"Addition of urea has been compared with polycarboxylate and naphthalene based superplasticizers, and with a control mixture without superplasticizer. When curing the sample containing urea at 80 °C, the initial setting time became longer. The samples containing urea or naphthalene-based superplasticizers could bear heavy weights shortly after mixing, while keeping an almost stable shape. Samples without superplasticizer or containing the polycarboxylate-based admixture were too stiff for mold-shaped formation after casting. Samples containing urea and naphthalene-based admixtures could be used to build up a structure without any noticeable deformation," according to the paper.
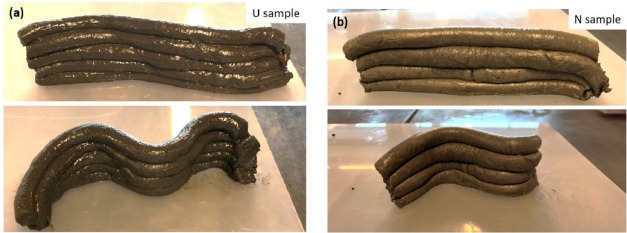
Additionally, the samples with urea also had higher compressive strength than the other two specimens containing superplasticizers, "and it continued to rise even after 8 freeze-thaw cycles."
The scientists conclude the paper by explaining further studies are needed to assess how the lunar regolith geopolymers will behave under the severe lunar conditions, which include a vacuum that can cause the volatile components to evaporate and large temperature fluctuations that can cause the structure to crack.
But if all goes according to plan, Moon Base Number 1 may have a more literal meaning than anyone ever anticipated.
Related Stories
Building Materials | Mar 3, 2017
Perkins+Will white paper: Antimicrobial building products should be avoided whenever possible
Antimicrobial products contain ingredients that may have adverse environmental or human health impacts.
Building Materials | Feb 15, 2017
New metamaterial cools roofs without any energy consumption
The material is barely thicker than aluminum foil and can be economically manufactured for large-scale residential and commercial applications.
Sponsored | Building Materials | Jan 17, 2017
Handbook of Architectural Expansion Joints & Fire Barriers
Building Materials | Jan 9, 2017
Architects and researchers are developing new techniques for building in space
As setting foot on Mars becomes a more realistic goal, the search for how to best develop Architecture for the Red Planet is heating up.
Walls and Partitions | Dec 14, 2016
New wall system eliminates the need for most studs
The company, BamCore, says its new product can save money and quicken the framing process.
75 Top Building Products | Dec 7, 2016
101 Top Products: Building Envelope
Among the best building envelope products included in BD+C's inaugural Top 101 Products report are BASF's Neopor Plus Insulation, Dri-Design's Shadow Series Aluminum Panels, and Garland's Optimax Roof Membrane.
Building Materials | Dec 2, 2016
These are the top 10 tile trends to keep an eye on in 2017
Design styles such as bits & pieces, gritty chic, and metallics are among the ten tile trends to watch as we enter 2017.
Sponsored | Building Materials | Sep 7, 2016
Peeling Back the Layers: The Case for Monolithic Foam Seals in Expansion Joint Systems.
Sponsored | Building Materials | Aug 22, 2016
Mind the Gap
Temporary Expansion Joints in Large Structures