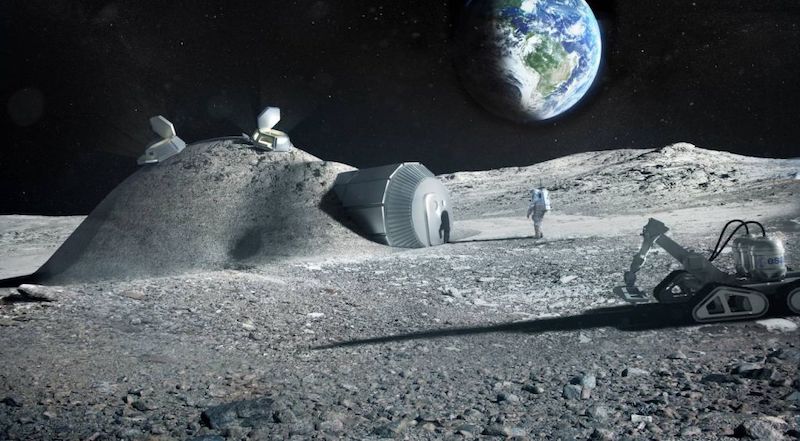
When it comes to building architecture in space, researchers, scientists, and architects have been offering up possible solutions for years. Concrete made from soil, ice shelters, and those grown from fungus have all been offered up as possible building materials. But a new possible building method may just use the most unique component of them all: urine.
Norwegian, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch scientists, together with the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA), have conducted experiments using urea from urine as a superplasticizer for lunar geopolymer mixtures that can then be used to 3D print structures. The scientists presented their findings in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
In their paper titled "Utilization of urea as an accessible superplasticizer on the moon for lunar geopolymer mixters," the scientists say urea can break hydrogen bonds and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. And since urea is the second most abundant component of urine (water being the first), it would be readily available, even in a location as barren and distant as the moon.
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
"Addition of urea has been compared with polycarboxylate and naphthalene based superplasticizers, and with a control mixture without superplasticizer. When curing the sample containing urea at 80 °C, the initial setting time became longer. The samples containing urea or naphthalene-based superplasticizers could bear heavy weights shortly after mixing, while keeping an almost stable shape. Samples without superplasticizer or containing the polycarboxylate-based admixture were too stiff for mold-shaped formation after casting. Samples containing urea and naphthalene-based admixtures could be used to build up a structure without any noticeable deformation," according to the paper.
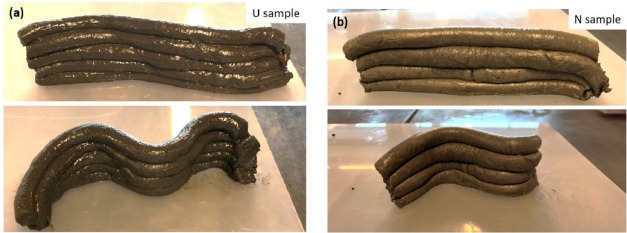
Additionally, the samples with urea also had higher compressive strength than the other two specimens containing superplasticizers, "and it continued to rise even after 8 freeze-thaw cycles."
The scientists conclude the paper by explaining further studies are needed to assess how the lunar regolith geopolymers will behave under the severe lunar conditions, which include a vacuum that can cause the volatile components to evaporate and large temperature fluctuations that can cause the structure to crack.
But if all goes according to plan, Moon Base Number 1 may have a more literal meaning than anyone ever anticipated.
Related Stories
75 Top Building Products | Dec 12, 2019
Top Building Envelope Products for 2019
Sto's beetle-inspired exterior coating and Dörken Systems' UV-resistant vapor-permeable barrier are among the 28 new building envelope products to make Building Design+Construction's 2019 101 Top Products report.
| Sep 13, 2019
ABC Supply Co. opens a branch in Sharonville, Ohio
ABC Supply Co. opens a branch in Sharonville, Ohio
Building Materials | Nov 9, 2018
As trade war heats up, long-term impact is anyone’s guess
Seven months into Trump’s trade war, the jury is still out.
Sponsored | Building Materials | Aug 17, 2018
Creating an identity for the New England Conservatory Student Life and Performance Center
The first New England Conservatory building to be added in 60 years presents a singular vision.
Sponsored | Building Materials | Aug 1, 2018
Building for now... and the future
Metal building systems are often selected for large-sized structures, and with good reason.
Office Buildings | Jul 25, 2018
New study on occupant comfort advances Saint Gobain’s design approach for renovation and new construction
The building products giant gauges its employees’ perceptions of old and new headquarters environments.
Great Solutions | Jul 13, 2018
Fungus may be the key to colonizing mars
A Cleveland-based architect and a NASA Ames researcher have a novel idea for building on Mars.
| May 30, 2018
Accelerate Live! talk: T3 mass timber office buildings
In this 15-minute talk at BD+C’s Accelerate Live! conference (May 10, 2018, Chicago), architect and mass timber design expert Steve Cavanaugh tells the story behind the nation’s newest—and largest—mass timber building: T3 in Minneapolis.
BD+C University Course | May 24, 2018
Accommodating movement in building envelope materials [AIA course]
We may think of the building envelope as an inanimate object, but in reality its components can be quite mobile. This AIA CES course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.














