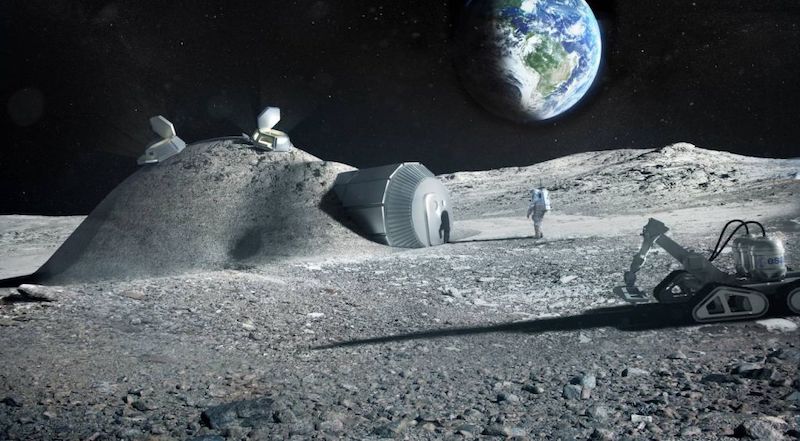
When it comes to building architecture in space, researchers, scientists, and architects have been offering up possible solutions for years. Concrete made from soil, ice shelters, and those grown from fungus have all been offered up as possible building materials. But a new possible building method may just use the most unique component of them all: urine.
Norwegian, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch scientists, together with the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA), have conducted experiments using urea from urine as a superplasticizer for lunar geopolymer mixtures that can then be used to 3D print structures. The scientists presented their findings in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
In their paper titled "Utilization of urea as an accessible superplasticizer on the moon for lunar geopolymer mixters," the scientists say urea can break hydrogen bonds and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. And since urea is the second most abundant component of urine (water being the first), it would be readily available, even in a location as barren and distant as the moon.
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
"Addition of urea has been compared with polycarboxylate and naphthalene based superplasticizers, and with a control mixture without superplasticizer. When curing the sample containing urea at 80 °C, the initial setting time became longer. The samples containing urea or naphthalene-based superplasticizers could bear heavy weights shortly after mixing, while keeping an almost stable shape. Samples without superplasticizer or containing the polycarboxylate-based admixture were too stiff for mold-shaped formation after casting. Samples containing urea and naphthalene-based admixtures could be used to build up a structure without any noticeable deformation," according to the paper.
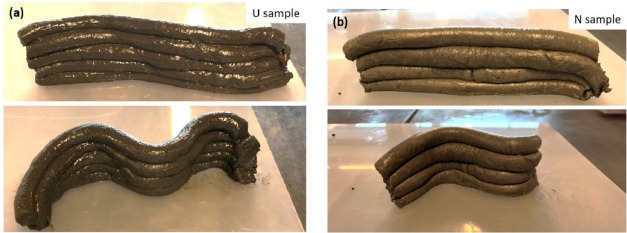
Additionally, the samples with urea also had higher compressive strength than the other two specimens containing superplasticizers, "and it continued to rise even after 8 freeze-thaw cycles."
The scientists conclude the paper by explaining further studies are needed to assess how the lunar regolith geopolymers will behave under the severe lunar conditions, which include a vacuum that can cause the volatile components to evaporate and large temperature fluctuations that can cause the structure to crack.
But if all goes according to plan, Moon Base Number 1 may have a more literal meaning than anyone ever anticipated.
Related Stories
Sponsored | Glass and Glazing | Oct 1, 2021
Specifying Responsibly to Save Birds’ Lives
Realizing sustainable, bird-friendly glass design
Sponsored | Glass and Glazing | Oct 1, 2021
Seizing the Daylight with BIPV Glass
Glass has always been an idea generator. Now, it’s also a clean energy generator.
Wood | May 14, 2021
What's next for mass timber design?
An architect who has worked on some of the nation's largest and most significant mass timber construction projects shares his thoughts on the latest design trends and innovations in mass timber.
3D Printing | Nov 27, 2020
The Fibonacci House: A test case of 3D construction printing
The Fibonacci House, which we have named after Leonardo Fibonacci, the medieval Italian mathematician, illustrates the potential of 3DCP and demonstrates how a complex design and challenging logistics can be solved through pragmatic planning and 3DCP technology.
Building Materials | Jul 5, 2020
A new report predicts significant demand growth for mass timber components
There should be plenty of wood, but production capacity needs to catch up.
Sponsored | Voice of the Brand | Jun 5, 2020
Practice Style Transcendence with Brick
Get inspired! Brick’s adaptability has made it the premier building material for centuries even as styles come and go. Nothing says “classic” like brick, but nothing says “innovative” like brick either. Check out some examples of how fired clay brick remains a major presence in the 21st Century designer’s palette.
Building Materials | Jun 4, 2020
The world’s first building made from carbon-fiber reinforced concrete starts construction in Germany
But greater use of these materials still faces obstacles.