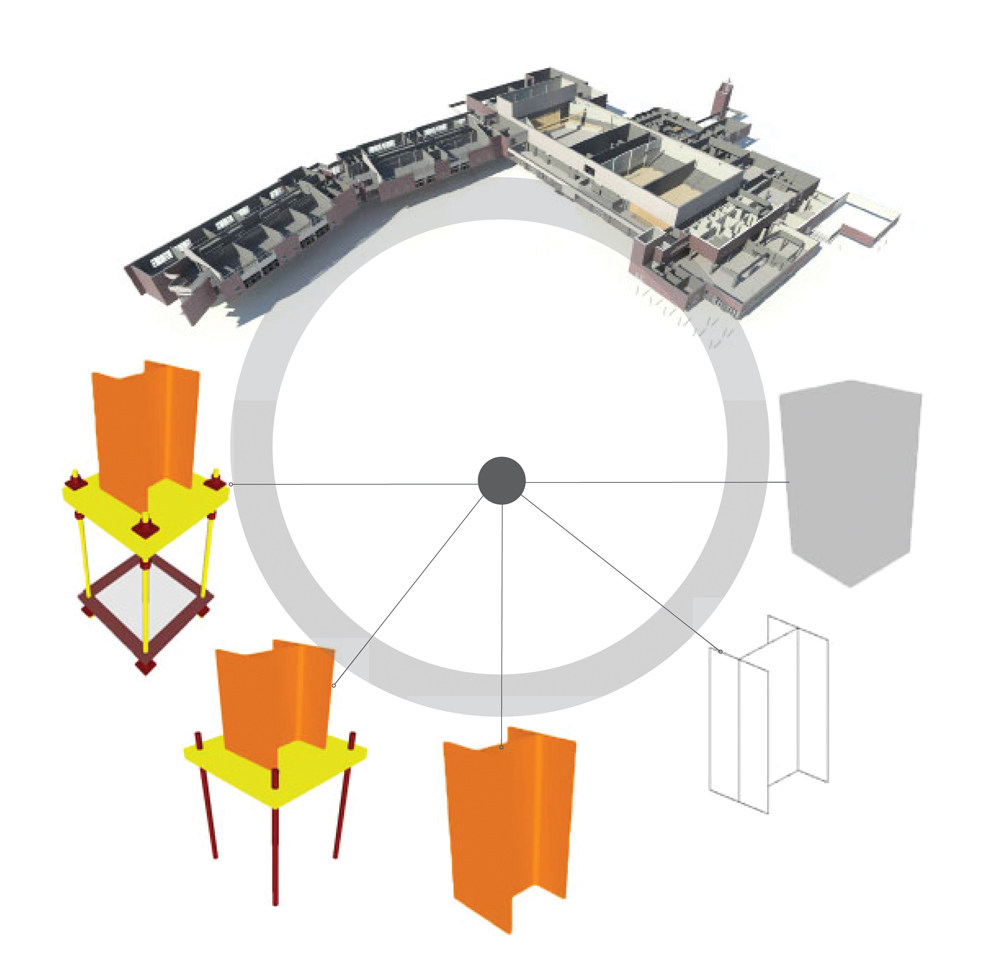
In 2008, the American Institute of Architects released its first BIM contract document—AIA E202 Building Information Modeling Protocol Exhibit—which outlined five “levels of development” (LOD 100-500) for defining the amount of detail in a particular BIM model. E202 provided basic definitions of each LOD but left a lot open to interpretation.
“The E202 was a huge first step in that it provided the first viable vehicle for defining a BIM model at the element level and enabling downstream users to rely on it,” says James Bedrick, FAIA, LEED AP, Founder and Principal of AEC Process Engineering (www.aecpe.com). “Practitioners found, though, that the LOD definitions were being interpreted differently, and that there was a need for more clarity. What does LOD 200 specifically mean, for example, for a door?”
None of the LODs offered a graphical representation of what a model at that level would look like or detailed instructions for how to use models in each LOD for a variety of disciplines. The document, which the AIA has since updated and published as the AIA G202-2013 Project Building Information Modeling Protocol Form (June 2013), had no specific rules or requirements for exactly what’s in a model at each level. As a result, design firms, general contractors, and subcontractors have no idea exactly what they would be handing off or receiving by way of the BIM model.
Level of Development Specification Definitions
• LOD 100 — The model element may be graphically represented in the model with a symbol or other generic representation, but does not satisfy the requirements for LOD 200. Information related to the model element (i.e., cost/sf, tonnage of HVAC, etc.) can be derived from other model elements.• LOD 200 — The model element is graphically represented within the model as a generic system, object, or assembly with approximate quantities, size, shape, location, and orientation. Nongraphic information may also be attached to the model element.
• LOD 300 — The model element is graphically represented within the model as a specific system, object, or assembly in terms of quantity, size, shape, location, and orientation. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the model element.
• LOD 350 — The model element is graphically represented within the model as a specific system, object, or assembly in terms of quantity, size, shape, orientation, and interfaces with other building systems. Nongraphic information may also be attached to the model element.
• LOD 400 — The model element is graphically represented within the model as a specific system, object, or assembly in terms of size, shape, location, quantity, and orientation with detailing, fabrication, assembly, and installation information. Nongraphic information may also be attached to the model element.
• LOD 500 — The model element is a field-verified representation in terms of size, shape, location, quantity, and orientation. Nongraphic information may also be attached to the model element.
Source: BIMForum and American Institute of Architects
A new standard promises to lend much-needed clarity to the BIM model detail issue. BIMForum, a multidisciplinary group of BIM users, has released its first BIM deliverable document, the Level of Development Specification. Working under an agreement with the AIA, the BIMForum LOD committee added context and meaning to the AIA G202-2013 definitions for levels 100, 200, 300, and 400, and added a new level (350) for trade coordination. It enables Building Teams to specify and articulate with a high level of clarity the content and reliability of BIM models at various stages, allowing downstream users to clearly understand the usability and limitations of models they are receiving. It’s organized by CSI Uniformat 2010, but expands the subclasses to Level 4 to provide a detailed breakdown and more clarity to the element definitions.
“The key to being able to break out of this quasi-definition cycle is collaboration,” says James Vandezande, AIA, Principal at HOK (www.hok.com), who served on BIMForum’s LOD committee. “It’s a stepping stone to get from document deliverables to model deliverables. This particular stepping stone is the tool that levels expectations between different stakeholders and provides an apples-to-apples comparison.”
“The LOD Specification is not prescribing a particular progression or approach for creating models,” says Jan Reinhardt, Principal at Adept Project Delivery (www.adeptprojectdelivery.com) and Co-chair of the LOD committee. “It only provides clear language for communicating, describing, and agreeing on a progression and quality of a model that is specific for a particular project.”
Built by a Building Team
The LOD committee was set up on a multidisciplinary basis, with Reinhardt (a GC) and Bedrick (an architect) overseeing committee members organized in several domain-specific groups (e.g., structural, interior construction, exterior skin). Each group had one construction professional and one designer to represent their respective points of view during the development process.
LOD 500: The coming O+M BIM model
Early on in the process of deciding what to include in the first Level of Development Specification, the BIMForum LOD committee concluded that level 500 would have to be put on hold. AIA E202 defines LOD 500 this way: “Model elements are modeled as constructed assemblies, actual and accurate in terms of size, shape, location, quantity, and orientation. Non-geometric information may also be attached to modeled elements.”As the industry struggles with the concept of using BIM models for facilities management (FM) tasks, this definition could be construed to be an operations and maintenance level, or as a model for as-built conditions.
“For the first phase of the rollout, we decided to concentrate on levels 100-400 as a starting point,” says Jan Reinhardt, Principal at Adept Project Delivery and Co-chair of the LOD committee. Reinhardt says the committee felt that many common FM-related tasks could be accomplished by using lower-level BIM models, especially when it comes to document management.
A growing number of building owners are demanding BIM models that can be used for FM purposes, but there is little consensus on how to achieve this goal. At a BIMForum meeting last winter in Tacoma, Wash., some of the concerns addressed were: Whose responsibility is it to input all model information into a system to hand off to facilities managers? What system is to be used if not specified by the owner? What would be the best system to recommend to an owner? Is highly detailed information such as structural tolerances of each beam really necessary for FM? Is it one system that catalogs all products in the entire building, or several different systems for different parts of the building?
“Level 500 is really about pure information, not graphical representations,” says David Francis, BIM Division Leader at Southland Industries (www.southlandind.com) and a member of BIMForum’s LOD committee. “The problem is there are software people trying to tell FM people how to run their business. If you’re an FM person, you’ll be using your FM or BMS software interface, but pulling the information from the BIM model and documents associated with the model. An FM guy is not going to open a Navisworks model and fly through it to find out what’s wrong with his building. He just wants the information.”
“One of the things we all agreed to was that level 500 needed to be the field-verification aspect of the data accompanying the model geometry,” explains Ron Dellaria, Chief Compliance Officer at Astorino and a member of the LOD committee. “We asked, ‘If it really is the as-built model, does it necessarily need that level of granularity for FM?’ You can’t equate an as-built model to an FM model. Not yet, at least. This will take more research. We felt it was best to tackle it in a later version.”
“The benefit of this setup was that, as we were developing the LODs, we were passing them off to each other,” says Ron Dellaria, Chief Compliance Officer at Astorino (www.astorino.com), who served on the LOD committee’s interior construction group. “It was of utmost importance to get a view of what the end user, in this case the contractor, wanted to see in terms of data. We could preserve design intent and they could tell us what they needed. If this really is the new deliverable, what we’re issuing needs to be acceptable by those using it next.”
What quickly became apparent to the committee was that different disciplines would need to continue to work at different levels of modeling as projects progressed. For example, structural engineering would always be ahead of MEP engineering.
“No two buildings are alike and no two workflows of element development will be the same,” says Will Ikerd, Principal at Ikerd Consulting (www.ikerd.com), who served on the LOD committee’s structural group. “There will be similarities, just like every building has a foundation, but how that comes together will differ, as well as how the LOD in each discipline comes together at different times in the project.
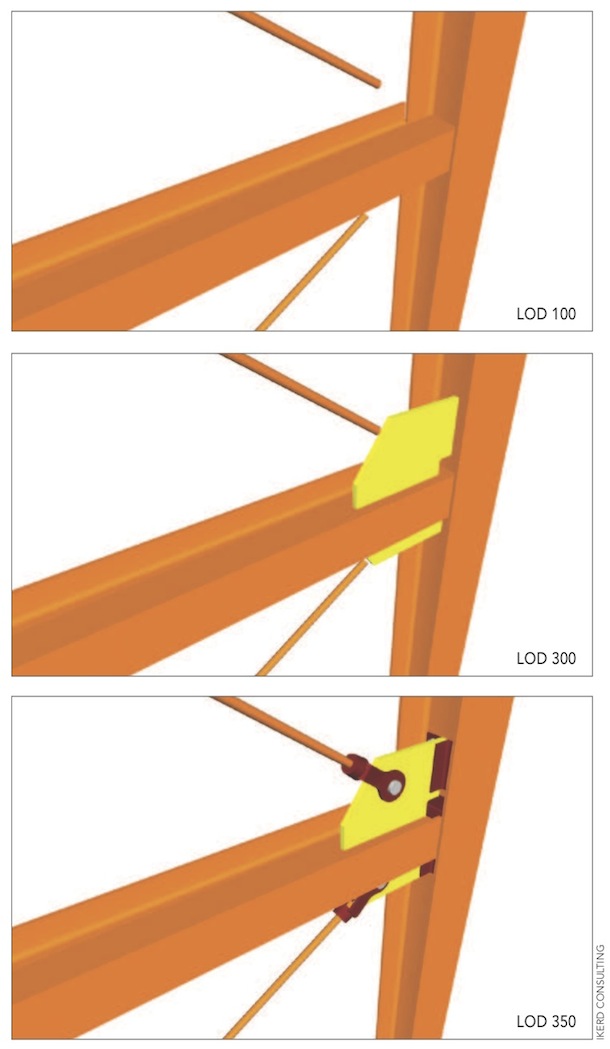
Ikerd, a BD+C “40 Under 40” honoree (class of 2011), also saw a need for sequential LOD graphics for the specification document, providing a set of common images that define the model elements. “Until now, the AECO industry has been using thousands of words for LOD with no common images,” he says.
The LOD Specification document was published on July 3. The document has a high level of instruction and detail for all of its elements, and software manufacturers will have enough information to give proper detail for specification for 3D elements created in-house and by third-party software vendors just from reading the LOD definitions.
For more, visit: http://bimforum.org/lod.
As part of its work on the LOD Specification, the BIMForum LOD committee created sequential graphics for each level of development definition. The examples above depict a connection detail modeled at LOD 100 (top), 300 (middle), and 350 (bottom).
Related Stories
Sustainability | Sep 18, 2024
3 living buildings made by a living practice
Prompting humans to reexamine our relationship to the environment, architecture creates the opportunity for us to physically experience ideas of beauty, performance, and structure through the distinct lens of place.
3D Printing | Sep 17, 2024
Alquist 3D and Walmart complete one of the nation’s largest free-standing, 3D-printed commercial structures
Walmart has completed one of the largest free-standing, 3D-printed commercial structures in the US. Alquist 3D printed the almost 8,000-sf, 20-foot-high addition to a Walmart store in Athens, Tenn. The expansion, which will be used for online pickup and delivery, is the first time Walmart has applied 3D printing technology at this scale.
Retail Centers | Sep 17, 2024
Thinking outside the big box (store)
For over a decade now, the talk of the mall industry has been largely focused on what developers can do to fill the voids left by a steady number of big box store closures. But what do you do when big box tenants stay put?
Government Buildings | Sep 17, 2024
OSHA’s proposed heat standard published in Federal Register
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has published a proposed standard addressing heat illness in outdoor and indoor settings in the Federal Register. The proposed rule would require employers to evaluate workplaces and implement controls to mitigate exposure to heat through engineering and administrative controls, training, effective communication, and other measures.
Codes and Standards | Sep 17, 2024
New California building code encourages, but does not mandate heat pumps
New California homes are more likely to have all-electric appliances starting in 2026 after the state’s energy regulators approved new state building standards. The new building code will encourage installation of heat pumps without actually banning gas heating.
Mass Timber | Sep 17, 2024
Marina del Rey mixed-use development is L.A.’s largest mass timber project
An office-retail project in Marina del Rey is Los Angeles’ largest mass timber project to date. Encompassing about 3 acres, the 42XX campus consists of three low-rise buildings that seamlessly connect with exterior walkways and stairways. The development provides 151,000 sf of office space and 1,500 sf of retail space.
Education Facilities | Sep 16, 2024
Hot classrooms, playgrounds spur K-12 school districts to go beyond AC for cooling
With hotter weather occurring during the school year, school districts are turning to cooling strategies to complement air conditioning. Reflective playgrounds and roads, cool roofs and window films, shade structures and conversion of asphalt surfaces to a natural state are all being tried in various regions of the country.
Office Buildings | Sep 16, 2024
Maximizing office square footage through ‘agile planning’
Lauren Elliott, RID, NCIDQ, Director of Interior Design, Design Collaborative, shares tips for a designing with a popular and flexible workspace model: Agile planning.
3D Printing | Sep 13, 2024
Swiss researchers develop robotic additive manufacturing method that uses earth-based materials—and not cement
Researchers at ETH Zurich, a university in Switzerland, have developed a new robotic additive manufacturing method to help make the construction industry more sustainable. Unlike concrete 3D printing, the process does not require cement.
Libraries | Sep 12, 2024
How space supports programming changes at university libraries
GBBN Associate Sarah Kusuma Rubritz, AIA, uses the University of Pittsburgh's Hillman Library to showcase how libraries are transforming to support students’ needs.