Digital design tools are making the once impossible, possible. From Frank Gehry’s wild, CATIA-generated geometries to the algorithm-driven healthcare planning techniques employed by Silicon Valley design firm Aditazz, architecture and engineering professionals continue to push the limits of BIM/VDC and 3D modeling tools.
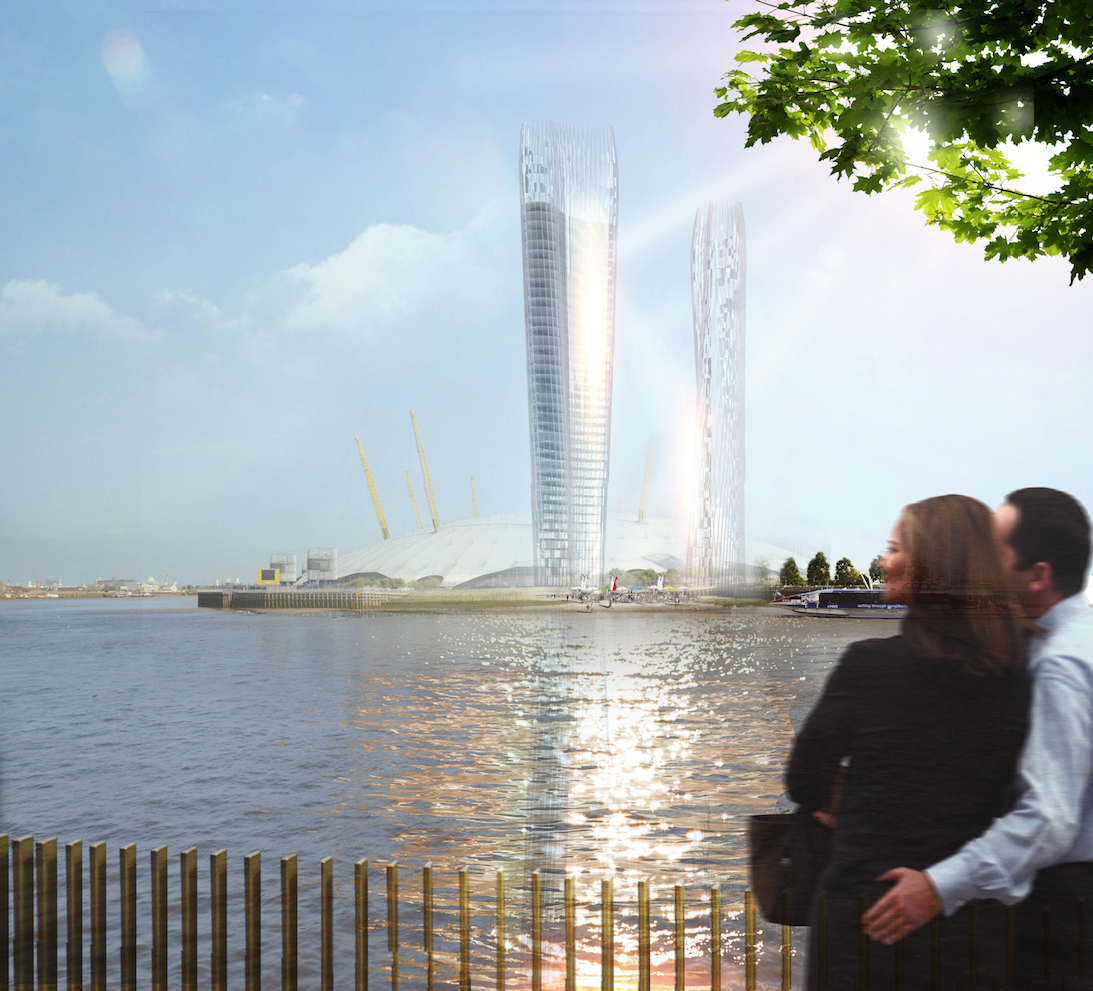
The latest case comes from NBBJ’s London office. Last March, a team led by NBBJ Design Director Christian Coop unveiled an inventive dual-tower scheme that, through the optimization of the buildings’ orientation, form, footprint, and glass exterior, effectively “erases” the shadows that would otherwise darken the public plaza between the buildings. The concept, dubbed the No-Shadow Tower, was developed for an ideas competition organized by New London Architecture. It uses a site in North Greenwich, London, as a testing ground, but Coop says the technique can be adapted to any location in the world.
The towers are designed to work in tandem: the northernmost building doubles as a massive light reflector, casting sunlight at precise angles throughout the day to blot out the shadows created by the south tower. The result: shadows cast at street level are reduced by up to 60%.
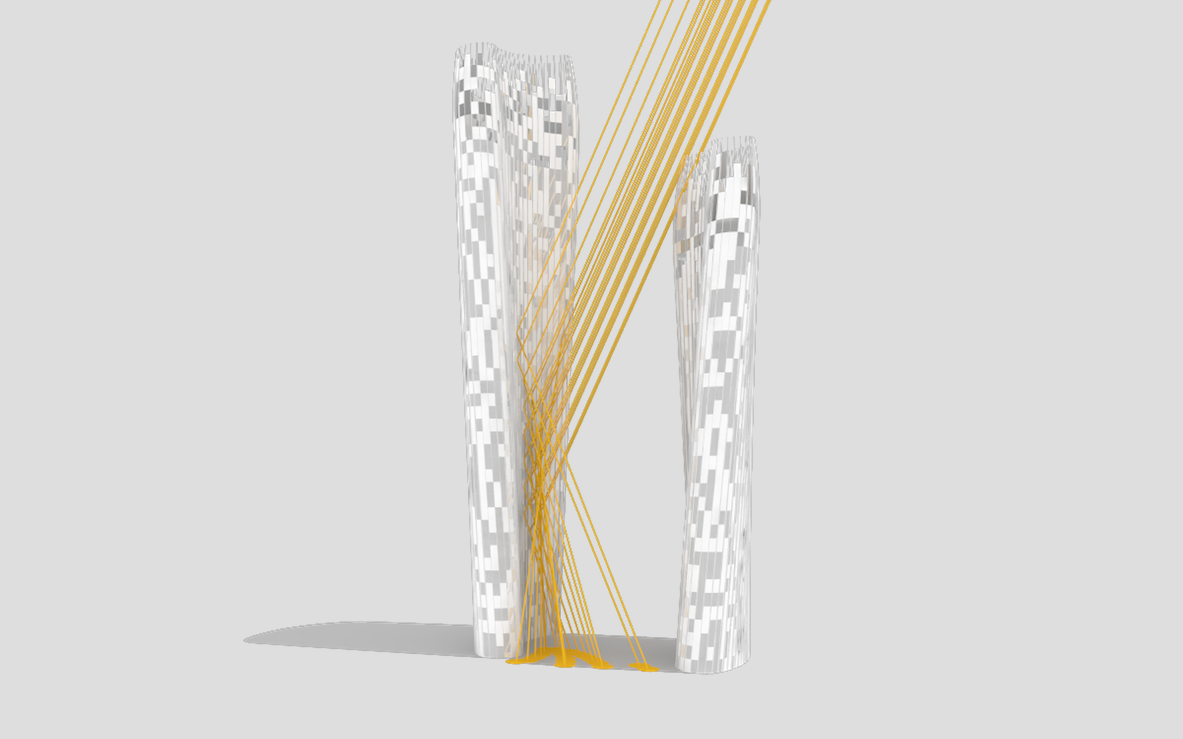
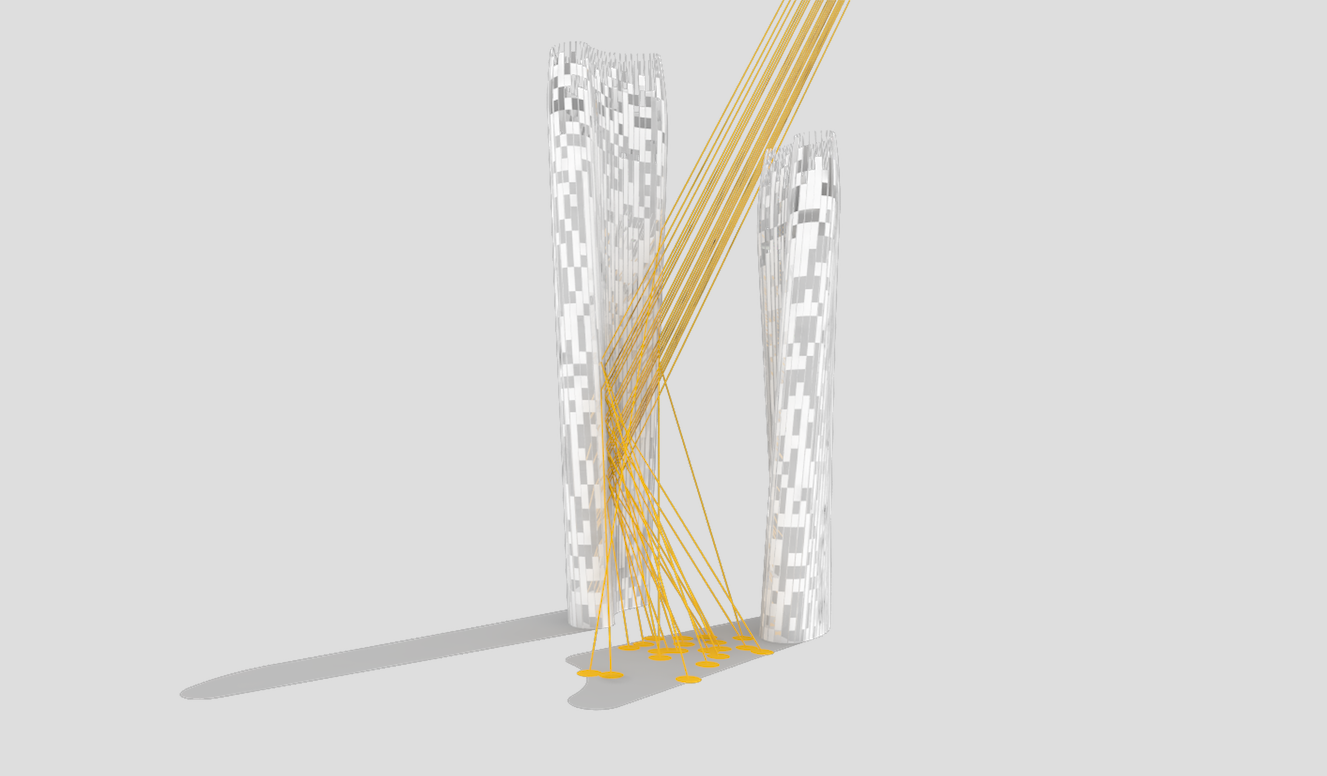
Leveraging the 3D surface modeling tool Rhinoceros and the graphical algorithm editor Grasshopper, the team first inputted the project’s key program requirements—height, total gross square footage, GSF of office, living, retail, etc. It then created an algorithm that records the sun’s angle during each moment of the year, as well as the resulting shadows cast by the towers, and translates the results into the shape of the towers.
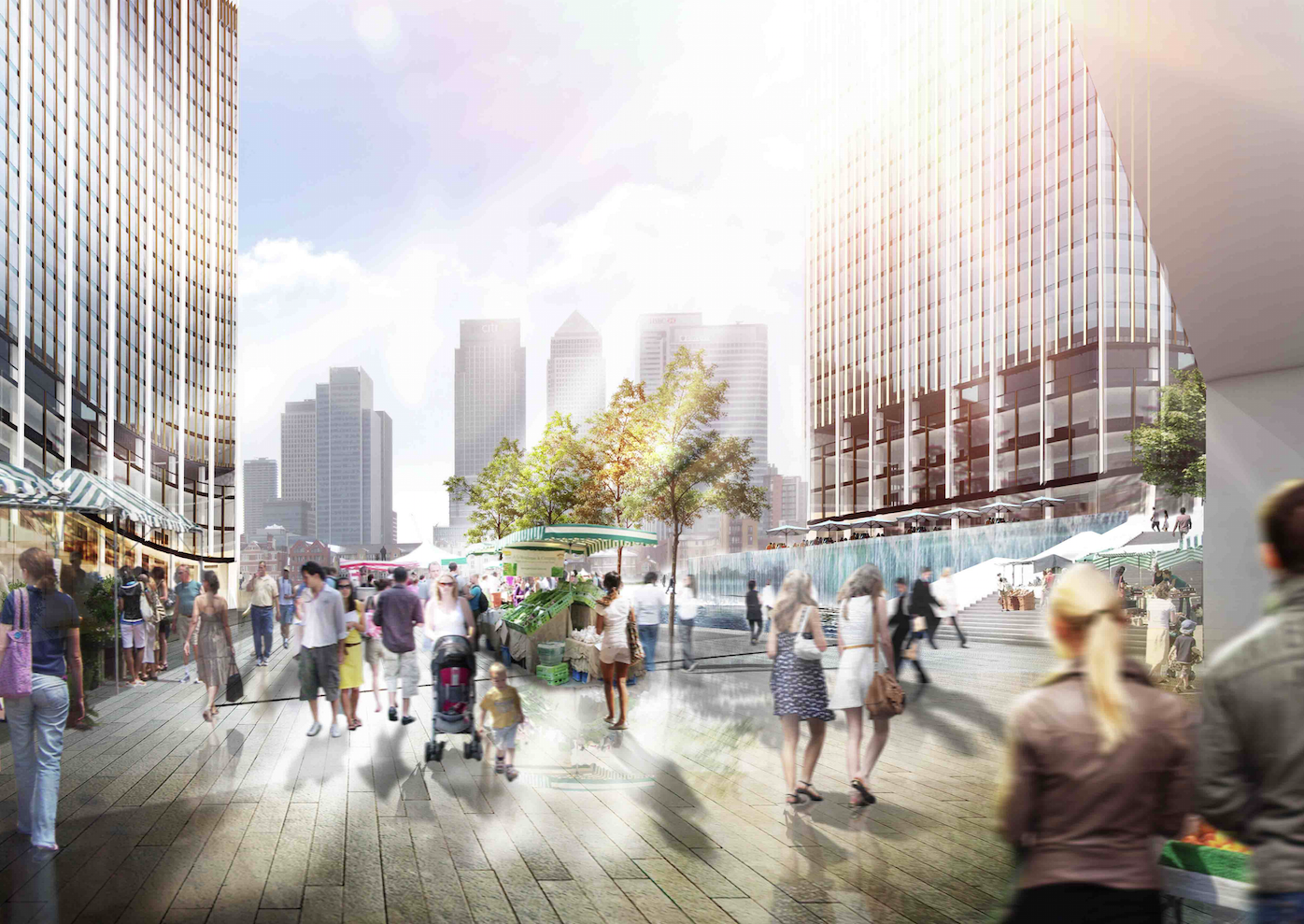 Once the design team settled on the shape of the towers, the glass exteriors were fine-tuned to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to spread light evenly across the plaza.
Once the design team settled on the shape of the towers, the glass exteriors were fine-tuned to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to spread light evenly across the plaza.
Coop’s team then instructed the program to create building forms that would redirect the maximum amount of daylight onto the plaza. It kicked out scads of shapes. Some were “bonkers,” Coop told Wired. After several iterations, the team settled on a pair of gently curved forms that taper at the base. The towers were further optimized to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to distribute light evenly across the plaza.
“We found that reflecting the sunlight pane by pane, rather than on a concave surface, creates pools of light on the ground below rather than one area of concentrated light reflection,” said Coop.
While just a concept—and one with fairly limited application opportunities across the globe, as dual-tower schemes are relatively rare—the No-Shadow Tower is a powerful demonstration of the potential of design computation. The process involves the use of software applications—Grasshopper, Dynamo, etc.—that leverage algorithms to link geometry with data to address specific issues, or, more accurately, predict outcomes.
Beyond basic applications like predicting the energy performance or cost of a given design iteration, firms like NBBJ are exploring how these tools can be used to optimize an office tower to maximize views from every space or design an inpatient wing to minimize steps for the nurses. Erase shadows? That’s the most imaginative application yet.
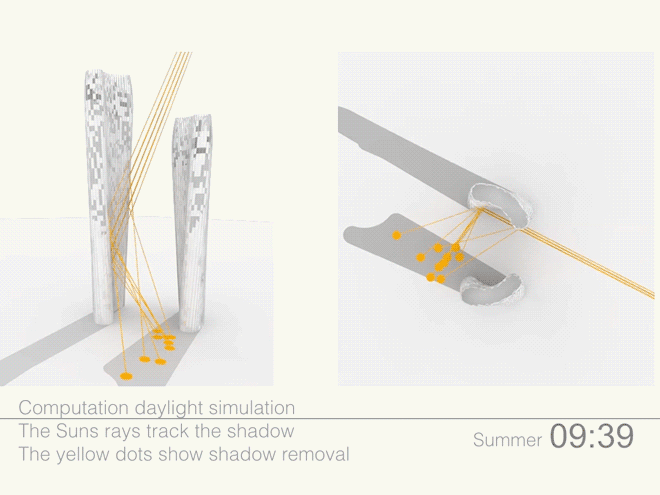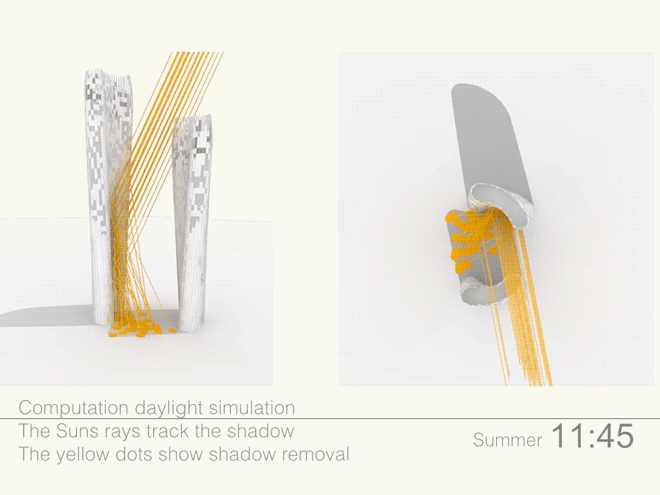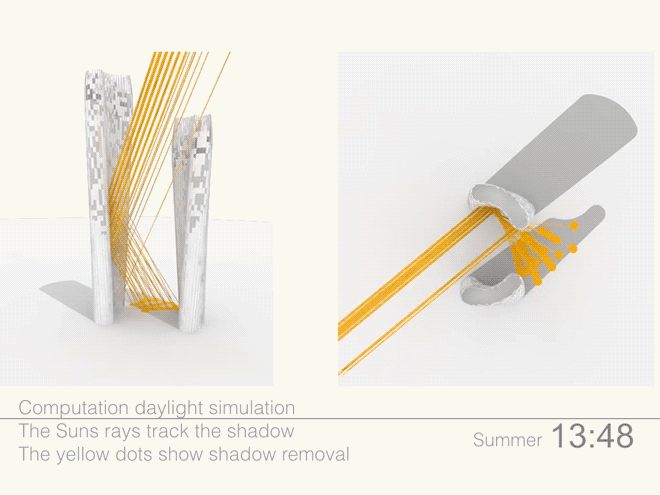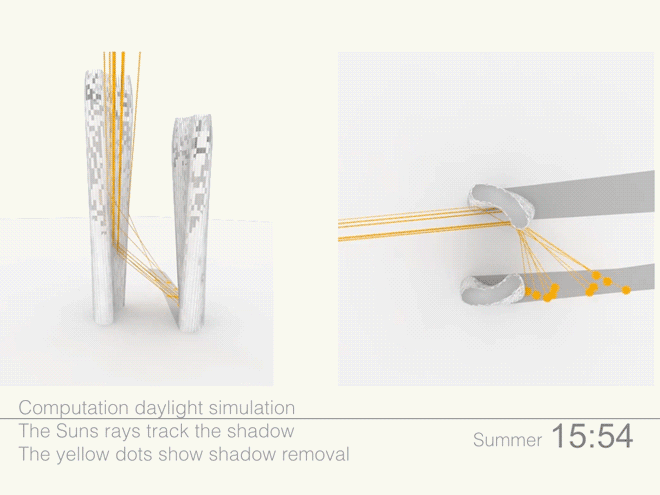
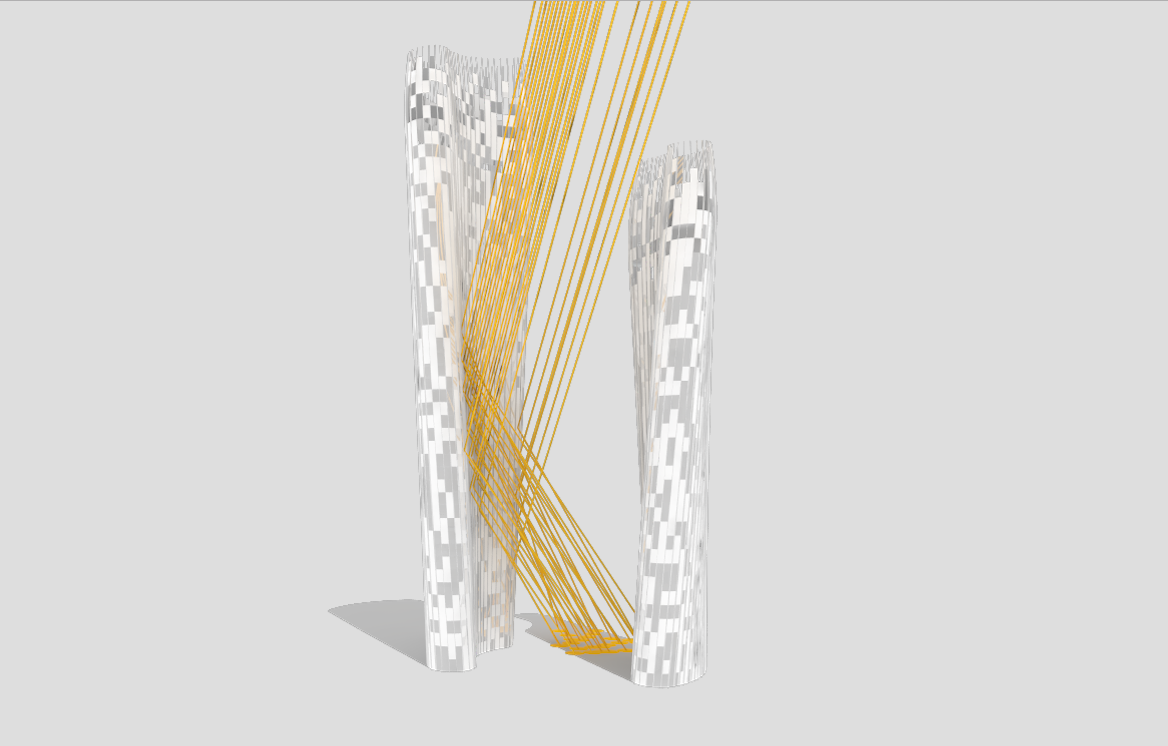 Illustrations above depict how the towers’ forms were optimized to redirect sunlight onto the plaza throughout the day.
Illustrations above depict how the towers’ forms were optimized to redirect sunlight onto the plaza throughout the day.
Related Stories
Sustainability | May 1, 2023
Increased focus on sustainability is good for business and attracting employees
A recent study, 2023 State of Design & Make by software developer Autodesk, contains some interesting takeaways for the design and construction industry. Respondents to a survey of industry leaders from the architecture, engineering, construction, product design, manufacturing, and entertainment spheres strongly support the idea that improving their organization’s sustainability practices is good for business.
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
AEC Tech Innovation | Apr 27, 2023
Does your firm use ChatGPT?
Is your firm having success utilizing ChatGPT (or other AI chat tools) on your building projects or as part of your business operations? If so, we want to hear from you.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Resiliency | Apr 18, 2023
AI-simulated hurricanes could aid in designing more resilient buildings
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have devised a new method of digitally simulating hurricanes in an effort to create more resilient buildings. A recent study asserts that the simulations can accurately represent the trajectory and wind speeds of a collection of actual storms.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
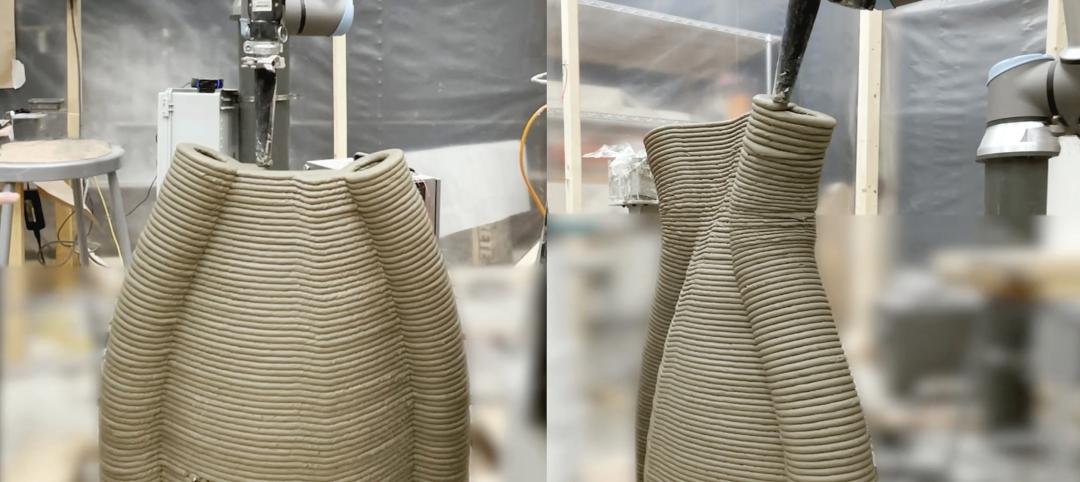
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.
AEC Tech | Mar 14, 2023
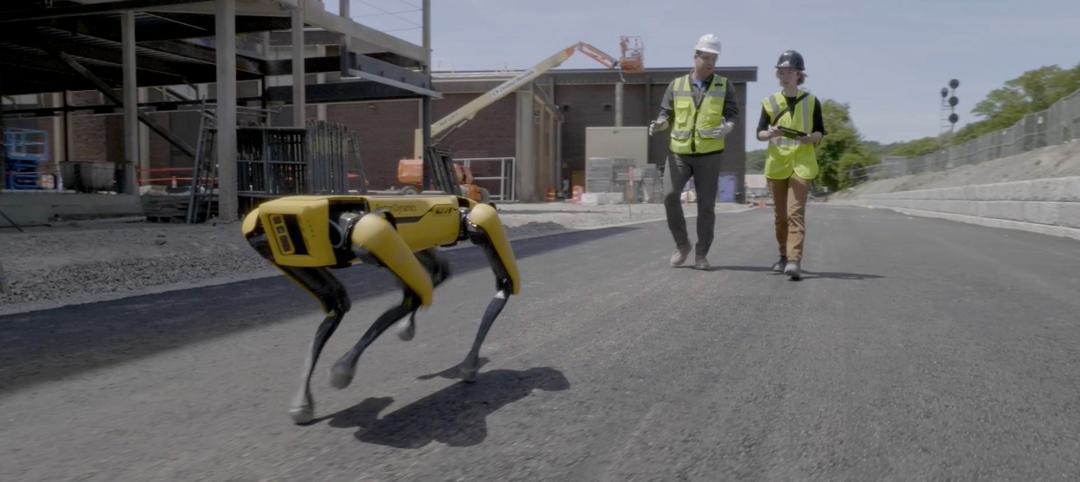
Skanska tests robots to keep construction sites clean
What if we could increase consistency and efficiency with housekeeping by automating this process with a robot? Introducing: Spot.
Modular Building | Mar 3, 2023
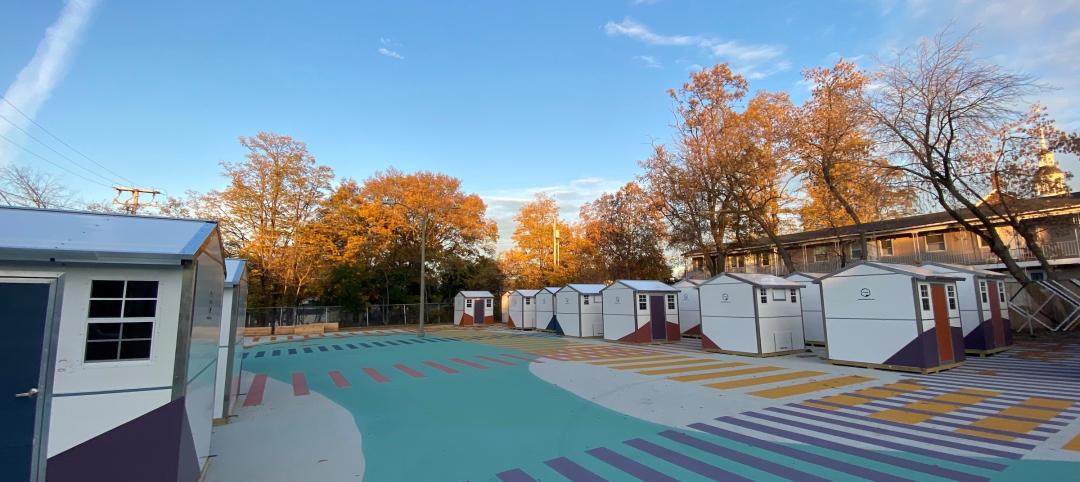
Pallet Shelter is fighting homelessness, one person and modular pod at a time
Everett, Wash.-based Pallet Inc. helped the City of Burlington, Vt., turn a municipal parking lot into an emergency shelter community, complete with 30 modular “sleeping cabins” for the homeless.