Digital design tools are making the once impossible, possible. From Frank Gehry’s wild, CATIA-generated geometries to the algorithm-driven healthcare planning techniques employed by Silicon Valley design firm Aditazz, architecture and engineering professionals continue to push the limits of BIM/VDC and 3D modeling tools.
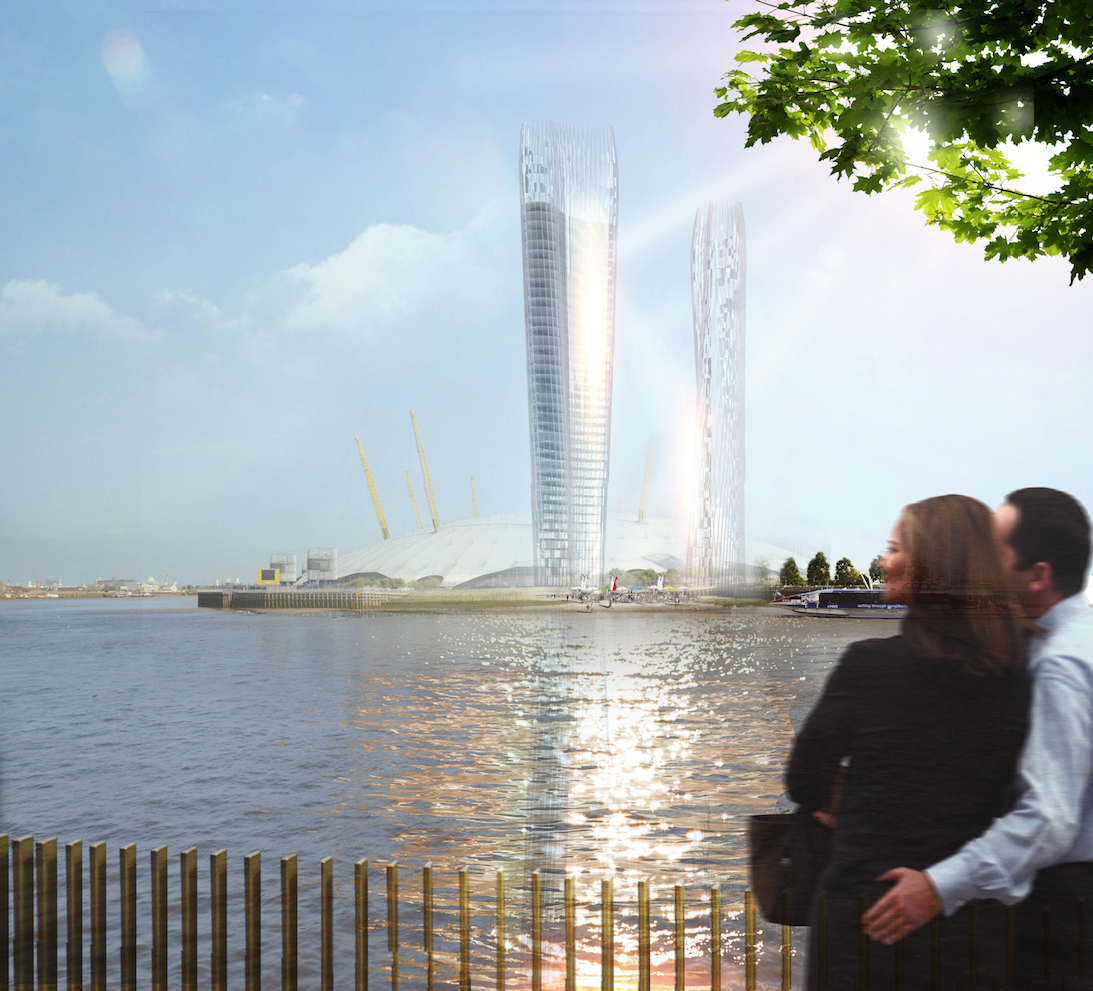
The latest case comes from NBBJ’s London office. Last March, a team led by NBBJ Design Director Christian Coop unveiled an inventive dual-tower scheme that, through the optimization of the buildings’ orientation, form, footprint, and glass exterior, effectively “erases” the shadows that would otherwise darken the public plaza between the buildings. The concept, dubbed the No-Shadow Tower, was developed for an ideas competition organized by New London Architecture. It uses a site in North Greenwich, London, as a testing ground, but Coop says the technique can be adapted to any location in the world.
The towers are designed to work in tandem: the northernmost building doubles as a massive light reflector, casting sunlight at precise angles throughout the day to blot out the shadows created by the south tower. The result: shadows cast at street level are reduced by up to 60%.
Leveraging the 3D surface modeling tool Rhinoceros and the graphical algorithm editor Grasshopper, the team first inputted the project’s key program requirements—height, total gross square footage, GSF of office, living, retail, etc. It then created an algorithm that records the sun’s angle during each moment of the year, as well as the resulting shadows cast by the towers, and translates the results into the shape of the towers.
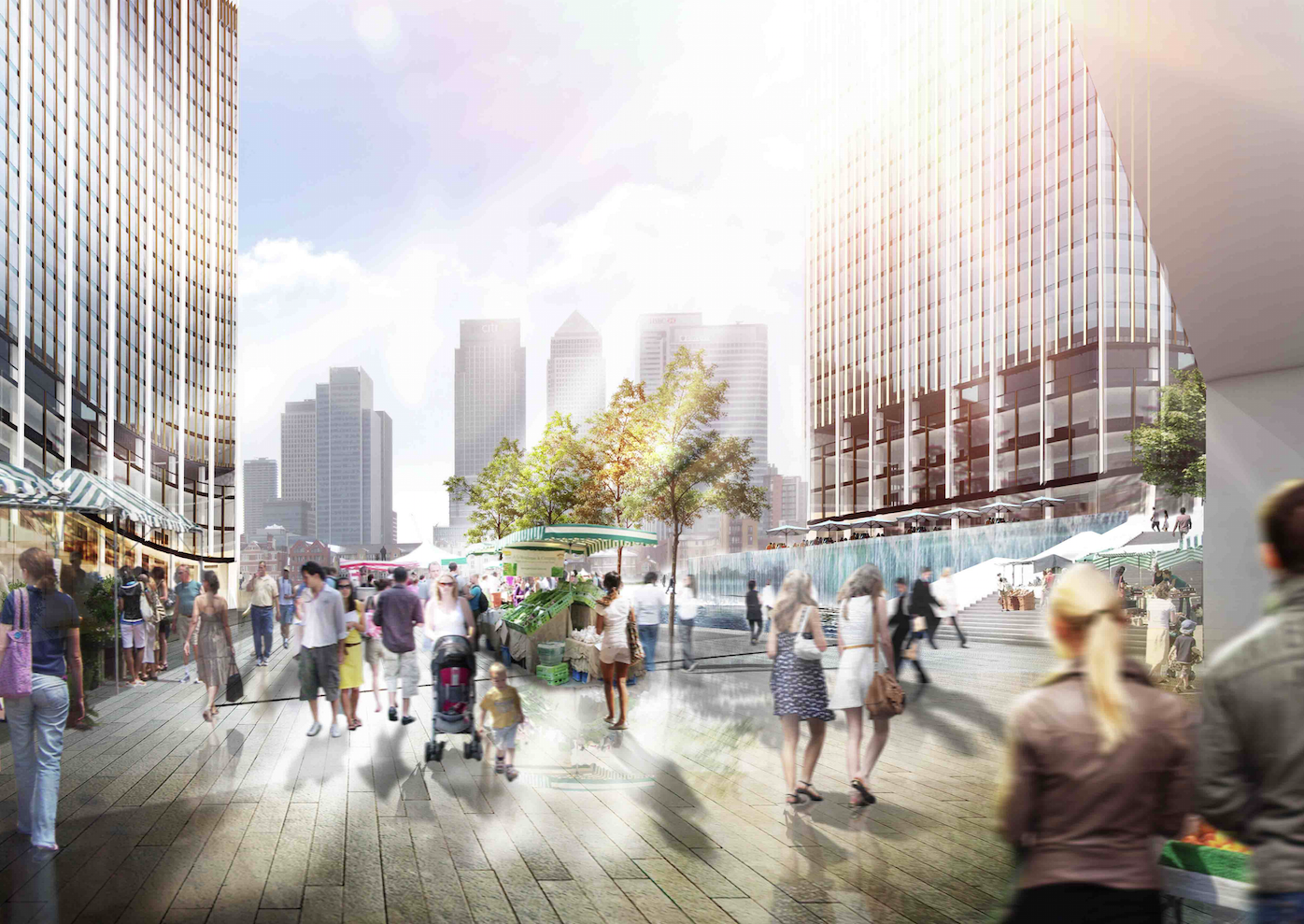 Once the design team settled on the shape of the towers, the glass exteriors were fine-tuned to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to spread light evenly across the plaza.
Once the design team settled on the shape of the towers, the glass exteriors were fine-tuned to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to spread light evenly across the plaza.
Coop’s team then instructed the program to create building forms that would redirect the maximum amount of daylight onto the plaza. It kicked out scads of shapes. Some were “bonkers,” Coop told Wired. After several iterations, the team settled on a pair of gently curved forms that taper at the base. The towers were further optimized to diffuse the sunlight to avoid intense heat and glare, and to distribute light evenly across the plaza.
“We found that reflecting the sunlight pane by pane, rather than on a concave surface, creates pools of light on the ground below rather than one area of concentrated light reflection,” said Coop.
While just a concept—and one with fairly limited application opportunities across the globe, as dual-tower schemes are relatively rare—the No-Shadow Tower is a powerful demonstration of the potential of design computation. The process involves the use of software applications—Grasshopper, Dynamo, etc.—that leverage algorithms to link geometry with data to address specific issues, or, more accurately, predict outcomes.
Beyond basic applications like predicting the energy performance or cost of a given design iteration, firms like NBBJ are exploring how these tools can be used to optimize an office tower to maximize views from every space or design an inpatient wing to minimize steps for the nurses. Erase shadows? That’s the most imaginative application yet.
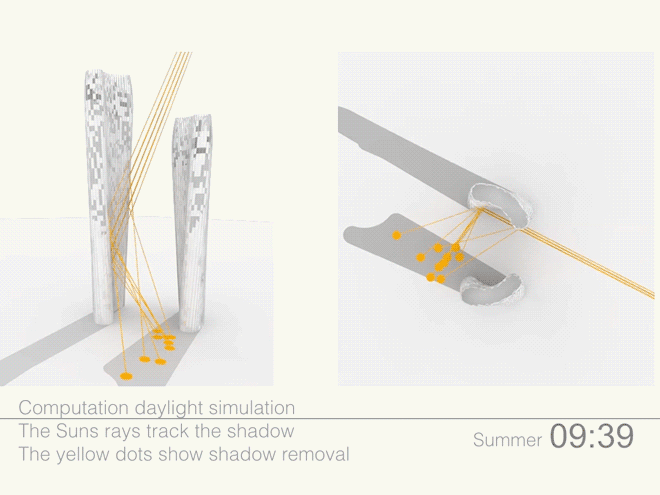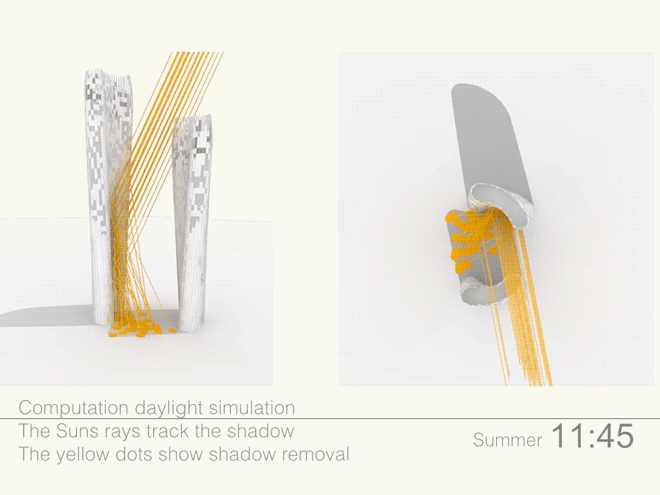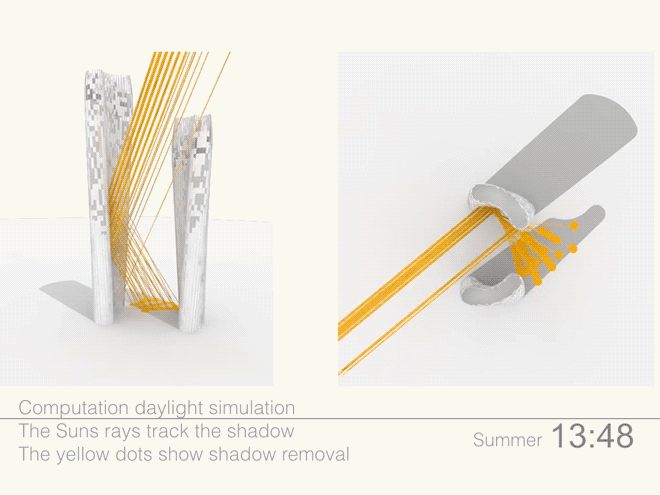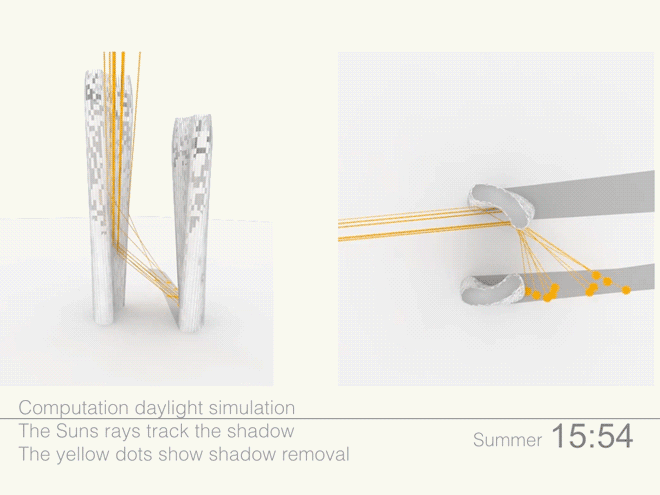
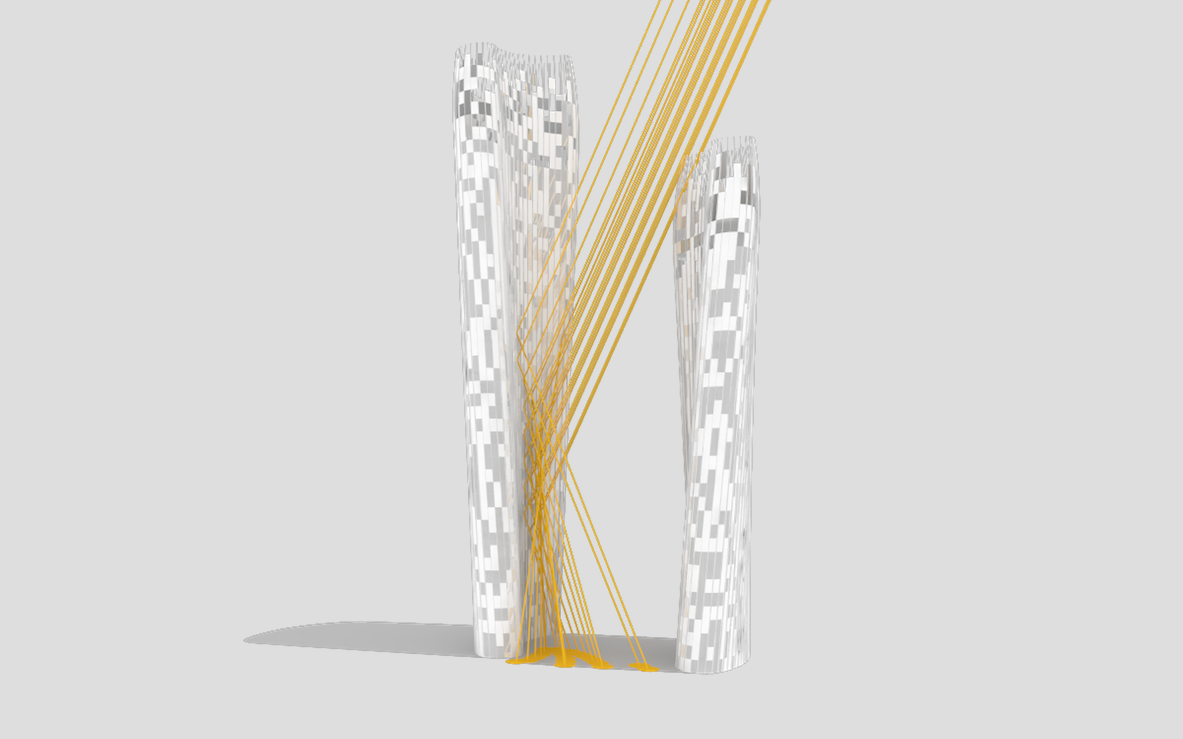
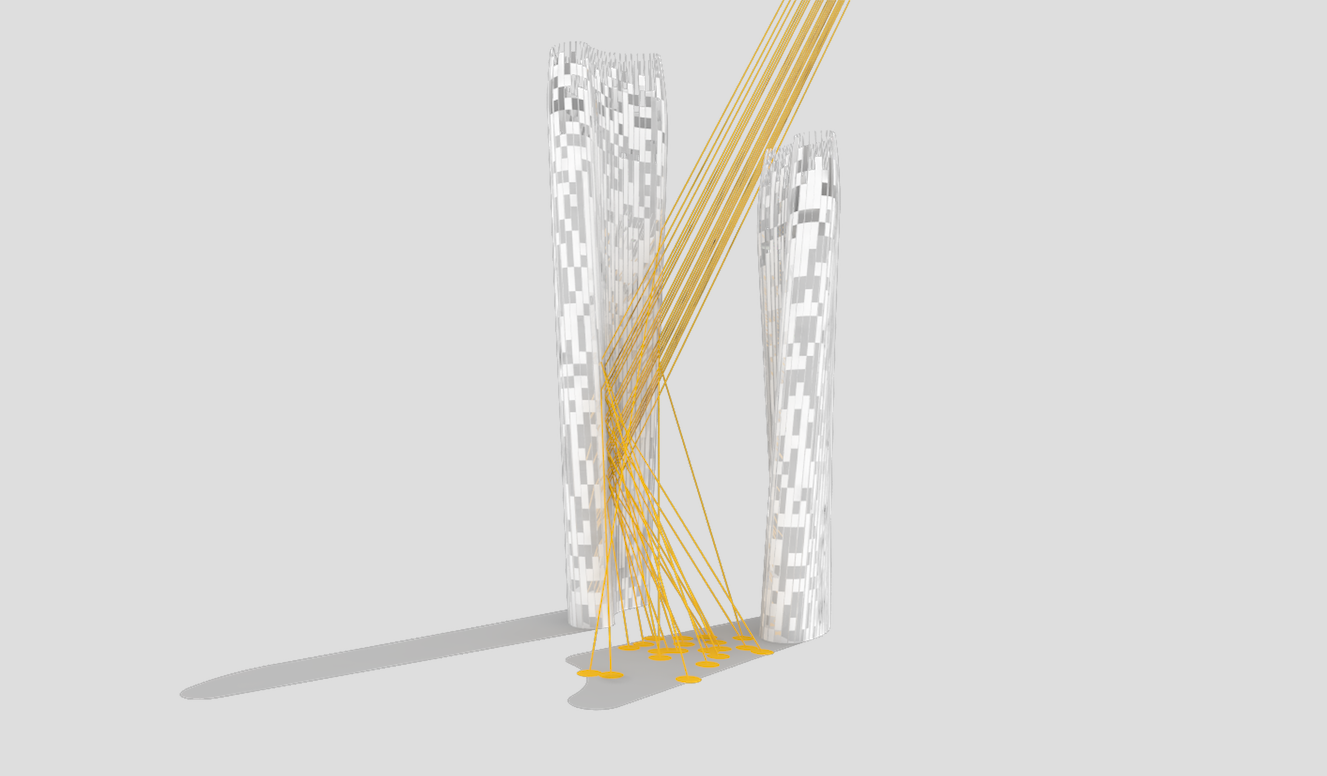
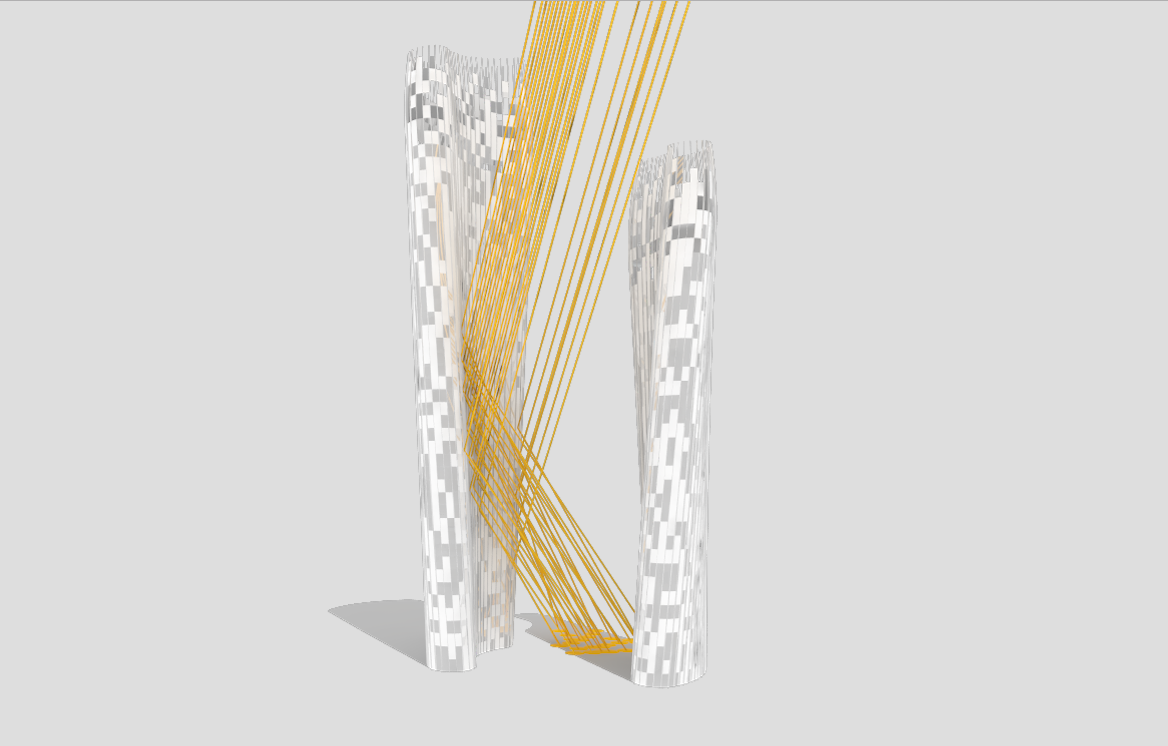 Illustrations above depict how the towers’ forms were optimized to redirect sunlight onto the plaza throughout the day.
Illustrations above depict how the towers’ forms were optimized to redirect sunlight onto the plaza throughout the day.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Dec 15, 2021
EV is the bridge to transit’s AV revolution—and now is the time to start building it
Thinking holistically about a technology-enabled customer experience will make transit a mode of choice for more people.
Designers / Specifiers / Landscape Architects | Nov 16, 2021
‘Desire paths’ and college campus design
If a campus is not as efficient as it could be, end users will use their feet to let designers know about it.
AEC Tech | Oct 25, 2021
Token Future: Will NFTs revolutionize the design industry?
How could non-fungible tokens (NFTs) change the way we value design? Woods Bagot architect Jet Geaghan weighs risk vs. reward in six compelling outcomes.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Oct 15, 2021
7 game-changing trends in structural engineering
Here are seven key areas where innovation in structural engineering is driving evolution.
AEC Tech Innovation | Oct 7, 2021
How tech informs design: A conversation with Mancini's Christian Giordano
Mancini's growth strategy includes developing tech tools that help clients appreciate its work.
AEC Tech | Oct 5, 2021
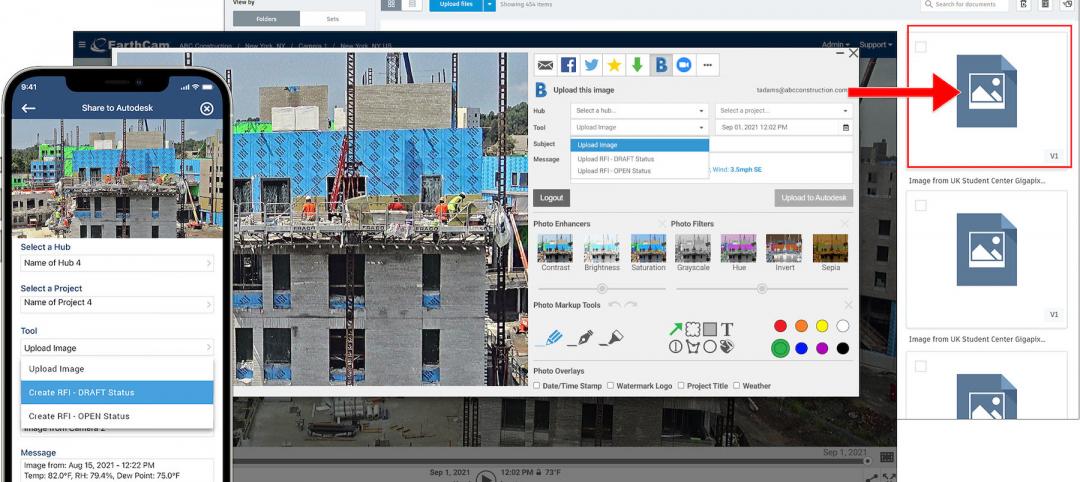
EarthCam Builds On its Connectivity with Autodesk Construction Cloud
Premiering new visual verification features for Autodesk Build and BIM 360
AEC Tech | Sep 21, 2021
A new webtool follows ConTech from incubation to application and beyond
MIT and JLL have created Tech Tracker to help real estate professionals see what’s hot now and what might be.
Architects | Aug 5, 2021
Lord Aeck Sargent's post-Katerra future, with LAS President Joe Greco
After three years under the ownership of Katerra, which closed its North American operations last May, the architecture firm Lord Aeck Sargent is re-establishing itself as an independent company, with an eye toward strengthening its eight practices and regional presence in the U.S.
Architects | Aug 5, 2021
Lord Aeck Sargent's post-Katerra future, with LAS President Joe Greco
After three years under the ownership of Katerra, which closed its North American operations last May, the architecture firm Lord Aeck Sargent is re-establishing itself as an independent company, with an eye toward strengthening its eight practices and regional presence in the U.S.
AEC Tech | Jul 14, 2021
Bjarke Ingels Group and UNStudio invest in SpaceForm, a virtual workspace for architects
Squint/Opera developed the platform in 2018.