Mace Group is London’s largest contractor, and has been associated with some of that city’s signature projects, including its 95-story skyscraper The Shard; the 443-foot-high cantilevered observation wheel known as London Eye; and Heathrow Terminal 5, which at nearly four million sf on 640 acres is the largest freestanding structure in the United Kingdom.
Since its inception in 1990, Mace has explored where production and construction might intersect. That inquest is suddenly urgent today, as U.K. cities will need 10,500 new homes to be built per month every year through 2038. To meet that demand, the country’s construction industry must rev up its productivity by 30%.
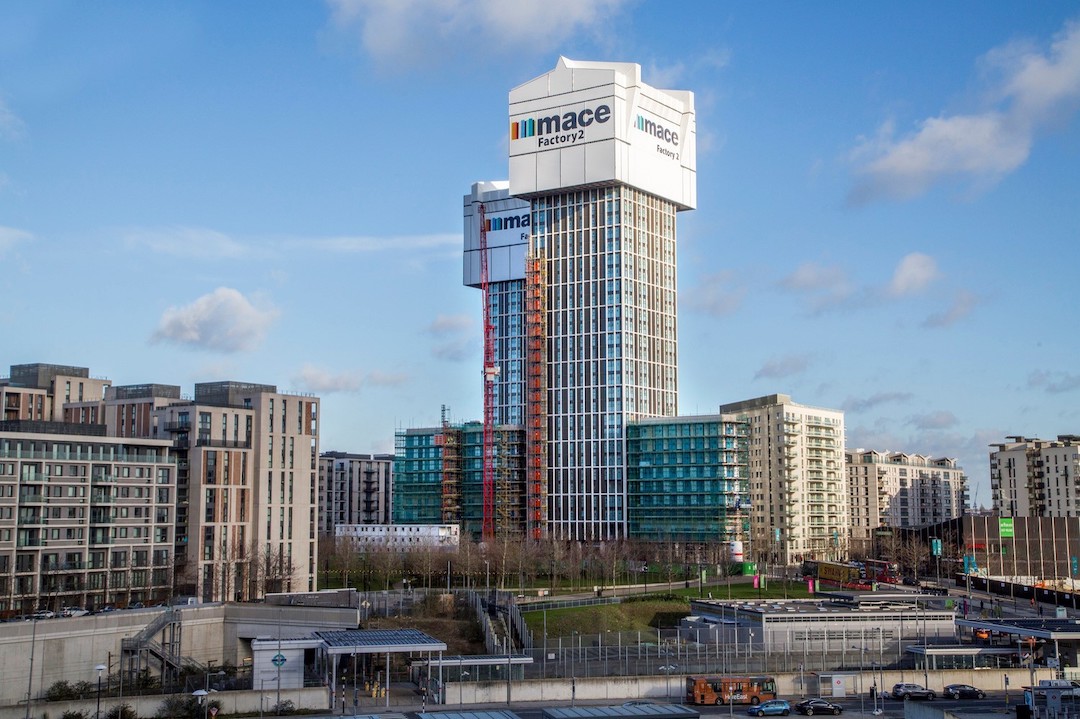
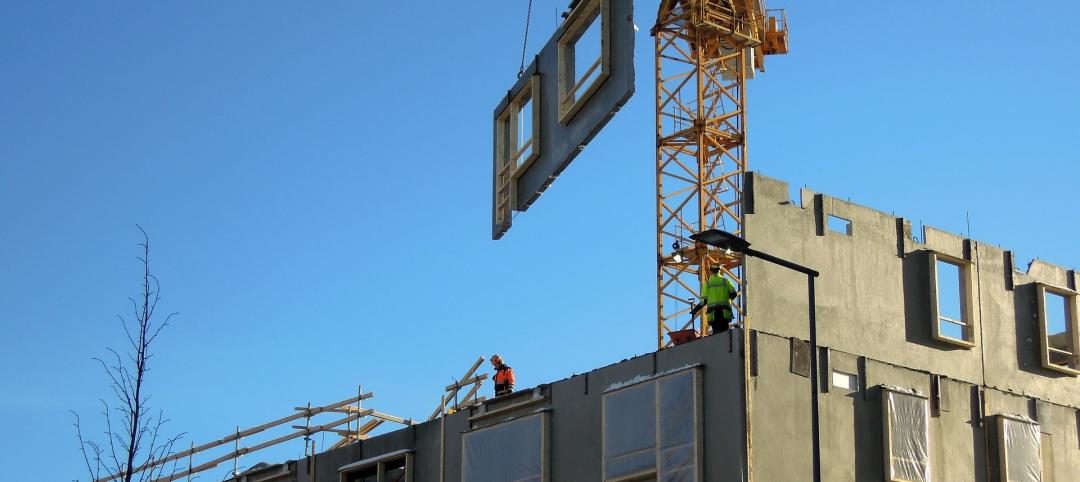
Recently, Mace took a step toward shifting from construction to production when it literally built factories on top of two under-construction residential towers in Stratford. Workers within those factories poured concrete, and assembled and installed prefab MEP systems, bathroom pods, risers, and façade components. The firm showcased its factory during a presentation at Autodesk University in London in June.
Skyscrapers rise with six-story prefab factories
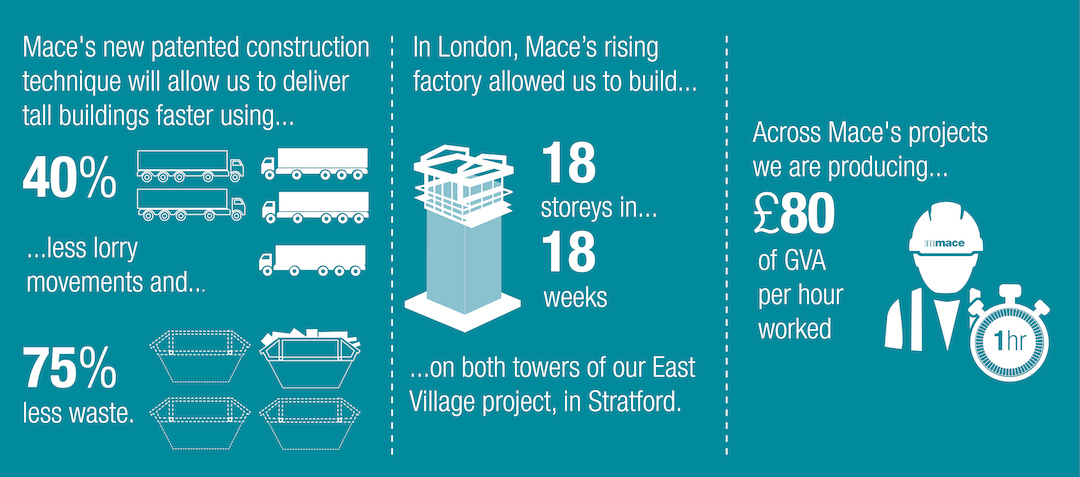
The six-story factories each weighed 510 tons and were 35 meters wide, 41 meters long, and 33 meters high. Some of their spaces were dedicated to materials delivery, façade installation, and assembling sub-assemblies. The structural engineer Davies Maguire helped Mace figure out how the building would manage that weight load.
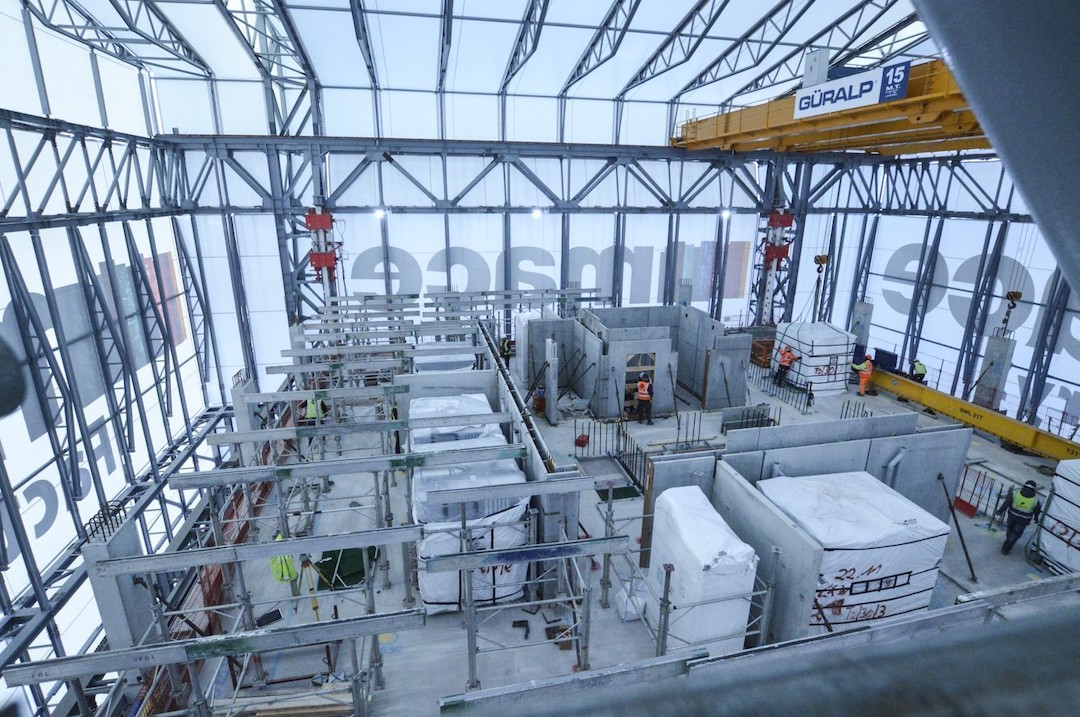 Photo: Mace Group
Photo: Mace Group
Matt Gough, Mace’s Director of Innovation and Work Winning, tells BD+C that the factories were “cost neutral” in that they eliminated the need for tower cranes, and increased productivity to the point where crews could complete 18 floors in 18 weeks. The factories reduced the project’s transportation by 40%, and its waste by 75% compared to a more conventional construction site. This project’s “gross value added” per worker, at £80 ($101.41) per hour worked, was higher than the U.K.’s average for construction and manufacturing.
“We changed the process for delivering high rises,” says Gough, even as it struggled at first to get some trades to work “in a different way.”
In January, Mace handed over the two residential towers to their developer, a joint venture between Qatari Diar and Delancey. Stratford is Mace’s sole project with onsite factories. The contractor is open to doing more projects like it in the U.K. and elsewhere (it has a construction management office in New York). Mace’s goal is to be “manufacturing” 85% of its projects 50% faster by 2022 via just-in-time logistics and sharper site management abetted by technology.
The contractor is doing modular construction on some projects, and intends to rely more on offsite prefabrication, which could result in safer jobsites with fewer workers needed.
How do you construct one floor of a building in just 55 hours? At N08, our project at East Village in Stratford, Mace used the 'rising factories' - an #innovative new #construction method - to deliver a step change in productivity and efficiency. Watch our latest video: pic.twitter.com/evIOsT3GTU
— Mace (@MaceGroup) June 13, 2018
 Infographic: Mace Group
Infographic: Mace Group
Related Stories
Contractors | May 26, 2023
Enhanced use of data is crucial for improving construction job site safety
Executives with major construction companies say new digital tools are allowing them to use data more effectively to reduce serious safety incidents and improve job site safety.
AEC Tech Innovation | May 12, 2023
Meet Diverge, Hensel Phelps' new ConTech investment company
Thai Nguyen, Director of Innovation with Hensel Phelps, discusses the construction giant's new startup investment platform, Diverge.
Sustainability | May 1, 2023
Increased focus on sustainability is good for business and attracting employees
A recent study, 2023 State of Design & Make by software developer Autodesk, contains some interesting takeaways for the design and construction industry. Respondents to a survey of industry leaders from the architecture, engineering, construction, product design, manufacturing, and entertainment spheres strongly support the idea that improving their organization’s sustainability practices is good for business.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
AEC Tech Innovation | Apr 27, 2023
Does your firm use ChatGPT?
Is your firm having success utilizing ChatGPT (or other AI chat tools) on your building projects or as part of your business operations? If so, we want to hear from you.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
Reinforced concrete walls and fins stiffen and shade the National Bank of Kuwait skyscraper
When the National Bank of Kuwait first conceived its new headquarters more than a decade ago, it wanted to make a statement about passive design with a soaring tower that could withstand the extreme heat of Kuwait City, the country’s desert capital.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
Meet The Hithe: A demountable building for transient startups
The Hithe, near London, is designed to be demountable and reusable. The 2,153-sf building provides 12 units of business incubator workspace for startups.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
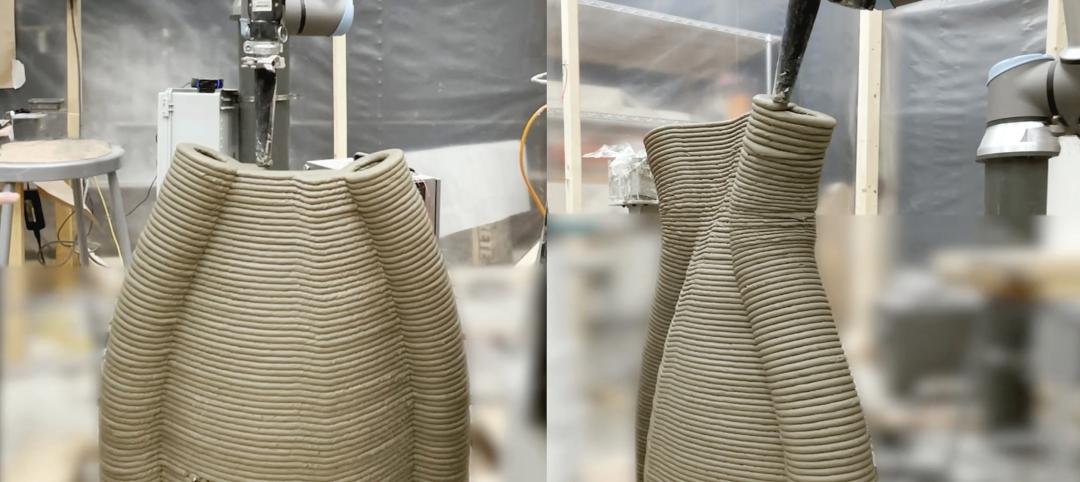
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.