In 1995, the city of New Haven, Conn., launched a program to build five new schools and renovate and upgrade seven others. At the time, city officials could not have envisioned their program morphing into a 17-year, 44-school, $1.5 billion project to completely overhaul its entire portfolio of K-12 facilities for nearly 23,000 students.
New Haven's massive undertaking is being handled by the Glastonbury, Conn., office of program manager Gilbane Building Companies (ranked #7 for CMs on BD+C's 2006 Giants 300 list), whose responsibilities on the project evolved along with the project itself.
Gilbane was originally hired as one of three construction managers who were to divvy up work on an 11-school, $23 million program. It didn't take long, however, for New Haven school officials to realize that they lacked the skills and resources to oversee the project, so Gilbane found itself competing for—and winning—the role of program manager. In 1998, the firm was asked to review the district's master plan; two years later, they unveiled a new multiphase plan that involved construction and renovation of 46 schools (later trimmed to 44), with a budget exceeding 10 figures.
Gilbane VP Tom Rogér says it took some time for the firm to gain the city's trust. “The first couple of years, there was a real learning curve on both our parts,” says Rogér. “What helped us a lot was that when we said something was going to happen, it happened. That was something they weren't used to. It was a revelation!”
Those hallelujah moments led to the city's approval of the dramatically expanded construction program. “After things started happening and they believed that our project work wasn't b.s., the city's board of aldermen asked why we weren't doing every single school,” says Rogér. The city even used the construction program as an opportunity to realign its grade structure, eliminating middle schools (which had performance, staffing, and safety problems) and creating K-8 facilities and 9-12 high schools.
Funding the original 11-school program involved a “stroke of genius” by the city's finance director, according to Rogér. The finance director bundled 300-400 tax-delinquent properties and sold them to a developer for $23 million, all of which went into a school construction trust fund. Later, the city relied on its bonding authority to fund the projects without having to rely on voter referendums.
One early decision rested on the design of the schools. “From a cost and schedule standpoint, I suggested using templates, and I got an emphatic no,” says Rogér. “They wanted each project to have its own architectural identity.” As a result, each school has a program appropriate to its neighborhood and academic focus. To maintain consistency and continuity, however, Gilbane authored a set of building standards (now in its ninth edition) that Building Teams are required to follow.
Working with 20 different architects and 10 different construction management firms proved wearying at times, but Rogér says that Gilbane made it clear that their firm was running the program and that they would manage it to everyone's advantage. “That added a lot of trust and credibility,” says Rogér. While Gilbane manages the RFQ process, however, the city makes the ultimate decision on which firms get the jobs.
Currently, there are 22 completed school projects and 10 active projects: five under construction and five in the design phase. The first was completed in 1998 and the last school is expected to be finished in 2012, at which time the program will have constructed 4.5 million sf. At its peak in 2006, Gilbane had a dedicated full-time staff of 22 on the projects; current staff totals 17. About 80-90% of the staff came from within Gilbane.
“One of the biggest benefits to New Haven—or any school district—is that hiring an outside program manager lets you hit the ground running with experienced people, systems, and relationships to make things happen,” says Rogér. “A public entity has to staff up or convert existing in-house staff to run a program of this size. Your building engineer who's been doing sidewalks for the past few years should never be put in the position to oversee a $1.5 billion program.”
On the other hand, Roger acknowledges, “there are some programs where the in-house people hate you because they think they could do a better job. We were lucky, in that the city tried to do the work themselves for a couple of years and they saw how hard it was. New Haven is happy to have us.”
|
Related Stories
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| Apr 29, 2014
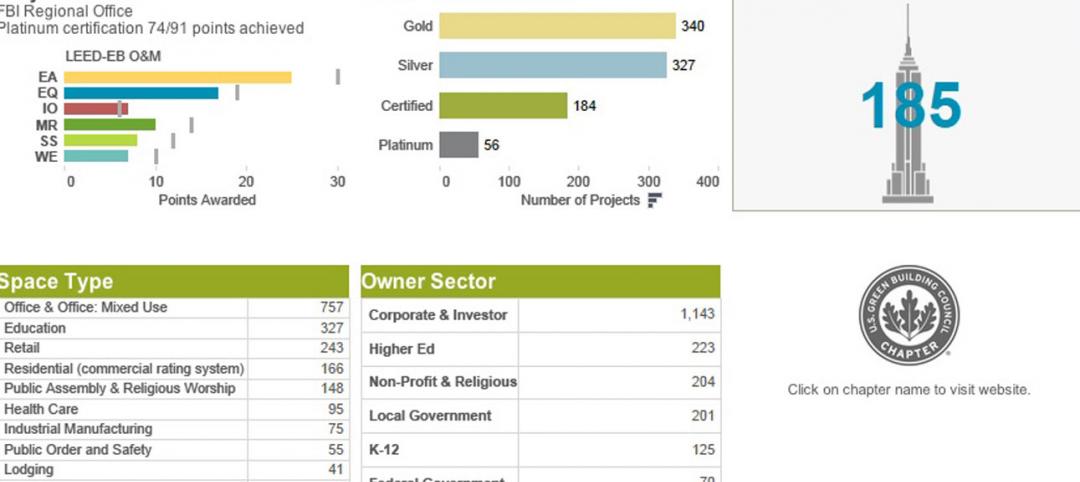
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
Sponsored | | Apr 23, 2014
Ridgewood High satisfies privacy, daylight and code requirements with fire rated glass
For a recent renovation of a stairwell and exit corridors at Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Ill., the design team specified SuperLite II-XL 60 in GPX Framing for its optical clarity, storefront-like appearance, and high STC ratings.
| Apr 16, 2014
Upgrading windows: repair, refurbish, or retrofit [AIA course]
Building Teams must focus on a number of key decisions in order to arrive at the optimal solution: repair the windows in place, remove and refurbish them, or opt for full replacement.
| Apr 9, 2014
Steel decks: 11 tips for their proper use | BD+C
Building Teams have been using steel decks with proven success for 75 years. Building Design+Construction consulted with technical experts from the Steel Deck Institute and the deck manufacturing industry for their advice on how best to use steel decking.
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
| Apr 1, 2014
Hawaiian performing arts center named nation's best new theater
Seabury Hall Creative Arts Center, a prep-school performing arts center on Maui in Hawaii, received the United States Institute for Theatre Technology's (USITT) highest architecture award—the Honor Award.
| Mar 26, 2014
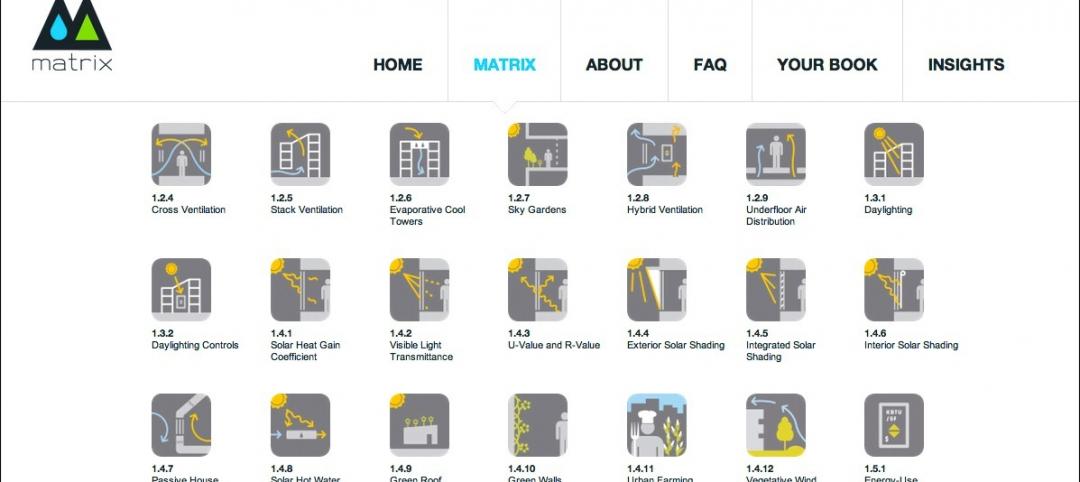
Callison launches sustainable design tool with 84 proven strategies
Hybrid ventilation, nighttime cooling, and fuel cell technology are among the dozens of sustainable design techniques profiled by Callison on its new website, Matrix.Callison.com.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 17, 2014
Rem Koolhaas explains China's plans for its 'ghost cities'
China's goal, according to Koolhaas, is to de-incentivize migration into already overcrowded cities.