It has been estimated that more than half of U.S. public schools need renovations or modernizations to be considered in good overall condition. The cost of bringing those schools up to par, though, could total nearly $200 billion.
Cash-strapped school districts that don’t have the funds to fix everything are searching for answers about where infrastructure improvements will have the greatest positive impact on students’ ability to learn and faculty’s ability to teach.
Earlier this year, Perkins Eastman partnered with the District of Columbia Public Schools on a study, cosponsored by J+J Flooring, to quantify the District’s modernization efforts. Since 2007, the District of Columbia Public Schools has invested more than $3 billion in school modernizations and improvements. Over the next six years, the District is committed to invest over $1 billion as part of its Capital Improvement Plan to modernize more school facilities.
During four consecutive weeks in February 2018, the Perkins Eastman study evaluated the level of satisfaction with Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ)—daylight, thermal comfort, acoustics, and air quality—among occupants of nine elementary and middle public schools in the District: four that have been modernized within the last decade, and five that have had only minor improvements in the last 30 years.
The study intentionally excluded newly construction schools, and focused on younger students who are more vulnerable to environmental impacts because of their continued physical development and elevated respiratory rates.
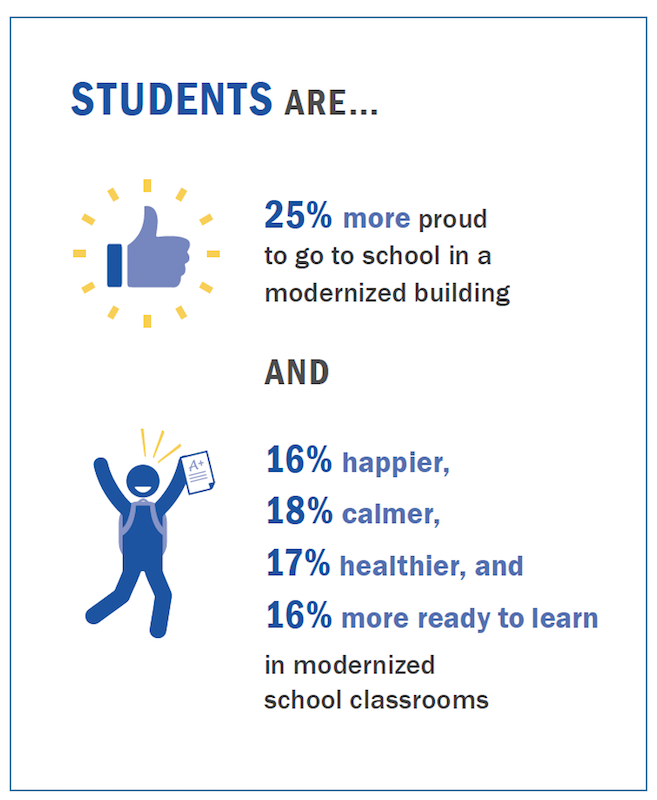
Based on responses from four separate occupant questionnaires (whose response rate was 62% for students, 76% for faculty); on-site IEQ data collection using sensors, and school archival data on social influences, the paper reports that, in almost all IEQ factors, modernized schools saw improvements in both measured conditions and occupants’ satisfaction over non-modernized schools.
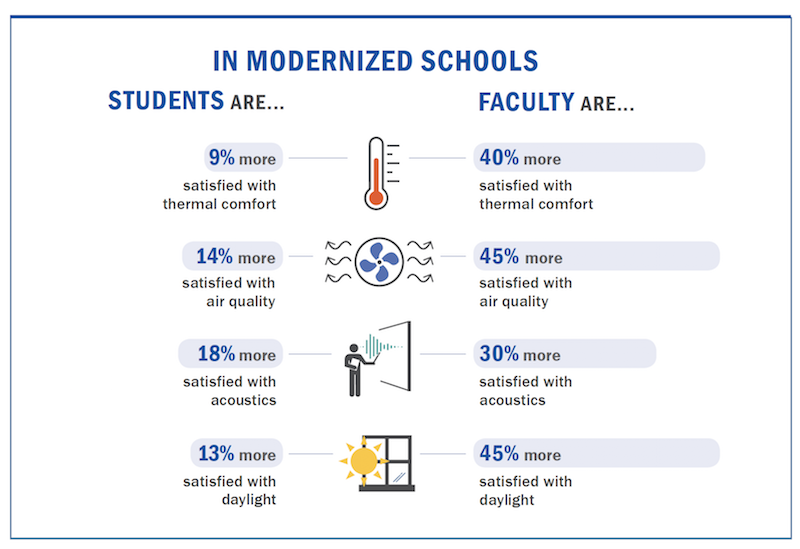
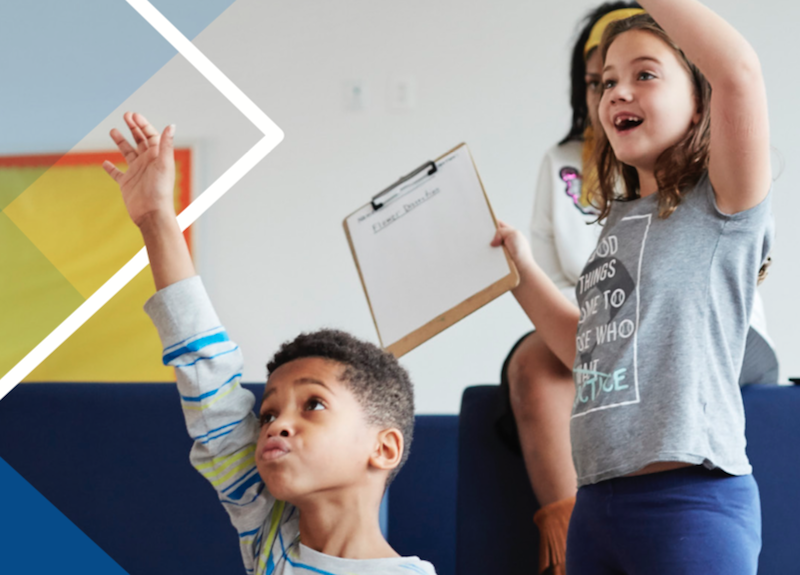
Perkins Eastman questioned students from Kindergarten to through 8th Grade, as well as faculty, and found significantly higher satisfaction levels with indoor environmental quality in modernized schools. Image: Perkins Eastman
Not surprisingly, daylight figures prominently on occupants’ satisfaction ratings. Various past surveys have found that students in classrooms with windows perform 20% faster on math tests and 26% faster on reading tests than students in windowless classroom.
For the Perkins Eastman study, two measures of daylight quality were examined in each room in both the morning and the afternoon: First, how well the daylight gets distributed throughout the entire classroom was studied using a light meter; and, second, the presence of glare or overlit conditions within classrooms was analyzed using calibrated cameras.
The results showed that the evaluated schools were generally more likely to be underlit (35%) than overlit (5%). However, schools across the study were well lit on average, with about 60% of the studied floor area meeting but not exceeding the LEED requirements for daylight autonomy and glare. The evaluated modernized schools were found to have marginally more well-lit areas than non-modernized schools
To evaluate the impact of acoustics, the study used a decibel meter to measure ambient noise levels over time. Readings showed that sound levels were 11% lower in modernized schools than in non-modernized ones. These readings likely indicate that modernizations lead to lower background noise levels due to improvements made to the mechanical systems and the building envelope to prevent infiltration of exterior noise.
However, when studying noise levels in occupied classrooms, the results showed high levels in all schools studied, regardless of whether they were recently modernized or not. These data reflect the dissatisfaction in the questionnaire responses that was found across the board with acoustics, and might indicate an issue that needs to be better addressed in modernization projects.

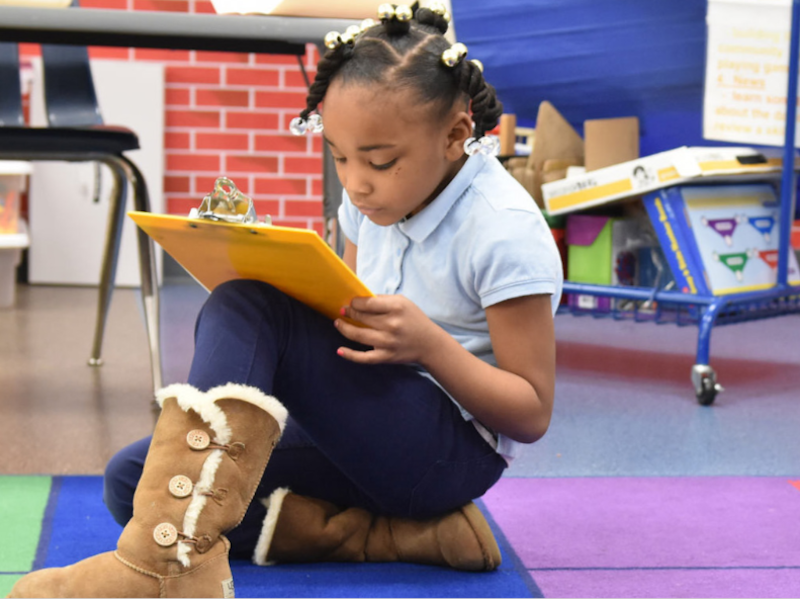
The amount of light in classrooms has a measurable impact on occupants' perceptions of their environment and ability to learn. Image: Perkins Eastman
To assess air quality, the study used a CO2 sensor to measure the effectiveness of ventilation. In the modernized schools, the results indicate that the median CO2 levels when occupied were 25% lower than in non-modernized schools.
The data show that modernized schools, on average, hit peak CO2 levels that were 41% lower than peak levels found in the non-modernized schools. This finding further reinforces the fact that modernized schools have improvements in ventilation effectiveness within classrooms, leading to better air quality for both students and teachers.
Lastly, this study used sensors and thermal cameras to track two aspects impacting thermal comfort: temperature of the classroom environments and thermal bridging of the building envelope. Temperatures within the evaluated modernized schools fell within ASHRAE’s comfort zone range of 68 to 75 degrees F 84% of the time. Non-modernized school fell within that range only 42% of the time
The peak temperatures of modernized schools were 4 degrees F lower than non-modernized schools, which the study found were overheated during winter months, peaking at 81 degrees F. “The non-modernized buildings may have less ability to control or deliver the appropriate amount of heat to an individual classroom space, resulting in overheating during the winter,” the paper suggests.
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Aug 13, 2021
A new P3 guide for K-12 school construction is released
This alternative financing isn’t a silver bullet, but it does provide options to cash-strapped districts.
Contractors | Jul 23, 2021
The aggressive growth of Salas O'Brien, with CEO Darin Anderson
Engineering firm Salas O'Brien has made multiple acquisitions over the past two years to achieve its Be Local Everywhere business model. In this exclusive interview for HorizonTV, BD+C's John Caulfield sits down with the firm's Chairman and CEO, Darin Anderson, to discuss its business model.
K-12 Schools | Jul 9, 2021
LPA Architects' STEM high school post-occupancy evaluation
LPA Architects conducted a post-occupancy evaluation, or POE, of the eSTEM Academy, a new high school specializing in health/medical and design/engineering Career Technical Education, in Eastvale, Calif. The POE helped LPA, the Riverside County Office of Education, and the Corona-Norco Unified School District gain a better understanding of which design innovations—such as movable walls, flex furniture, collaborative spaces, indoor-outdoor activity areas, and a student union—enhanced the education program, and how well students and teachers used these innovations.
K-12 Schools | Jun 29, 2021
A Maryland school system launches a P3 program to speed up K-12 school design, financing, and construction
Gilbane and Stantec are part of a consortium that breaks ground on six new schools this week.
Resiliency | Jun 24, 2021
Oceanographer John Englander talks resiliency and buildings [new on HorizonTV]
New on HorizonTV, oceanographer John Englander discusses his latest book, which warns that, regardless of resilience efforts, sea levels will rise by meters in the coming decades. Adaptation, he says, is the key to future building design and construction.
K-12 Schools | Jun 20, 2021
Los Angeles County issues design guidelines for extending PreK-12 learning to the outdoors
The report covers everything from funding and site prep recommendations to whether large rocks can be used as seating.
Wood | Jun 10, 2021
Three AEC firms launch a mass timber product for quicker school construction
TimberQuest brand seeks to avoid overinvestment in production that has plagued other CLT providers.
Digital Twin | May 24, 2021
Digital twin’s value propositions for the built environment, explained
Ernst & Young’s white paper makes its cases for the technology’s myriad benefits.
Daylighting | Mar 7, 2021
Texas intermediate school lets the sun really shine in
Solatube tubular daylighting devices bring sunlight into the two-story commons/media space for 600 students in grades 3-5 at Sunnyvale Intermediate School.
Market Data | Feb 24, 2021
2021 won’t be a growth year for construction spending, says latest JLL forecast
Predicts second-half improvement toward normalization next year.







![Oceanographer John Englander talks resiliency and buildings [new on HorizonTV] Oceanographer John Englander talks resiliency and buildings [new on HorizonTV]](/sites/default/files/styles/list_big/public/Oceanographer%20John%20Englander%20Talks%20Resiliency%20and%20Buildings%20YT%20new_0.jpg?itok=enJ1TWJ8)









