Demand for multistory logistics centers is increasing in cities around the country that are looking to provide “last mile” ecommerce delivery to urban populations while using the least amount of costly land possible.
But vertical logistics centers have their own operational complexities that include inventory and fleet management, vehicular parking, and staying abreast of the latest transportation modes and technologies.
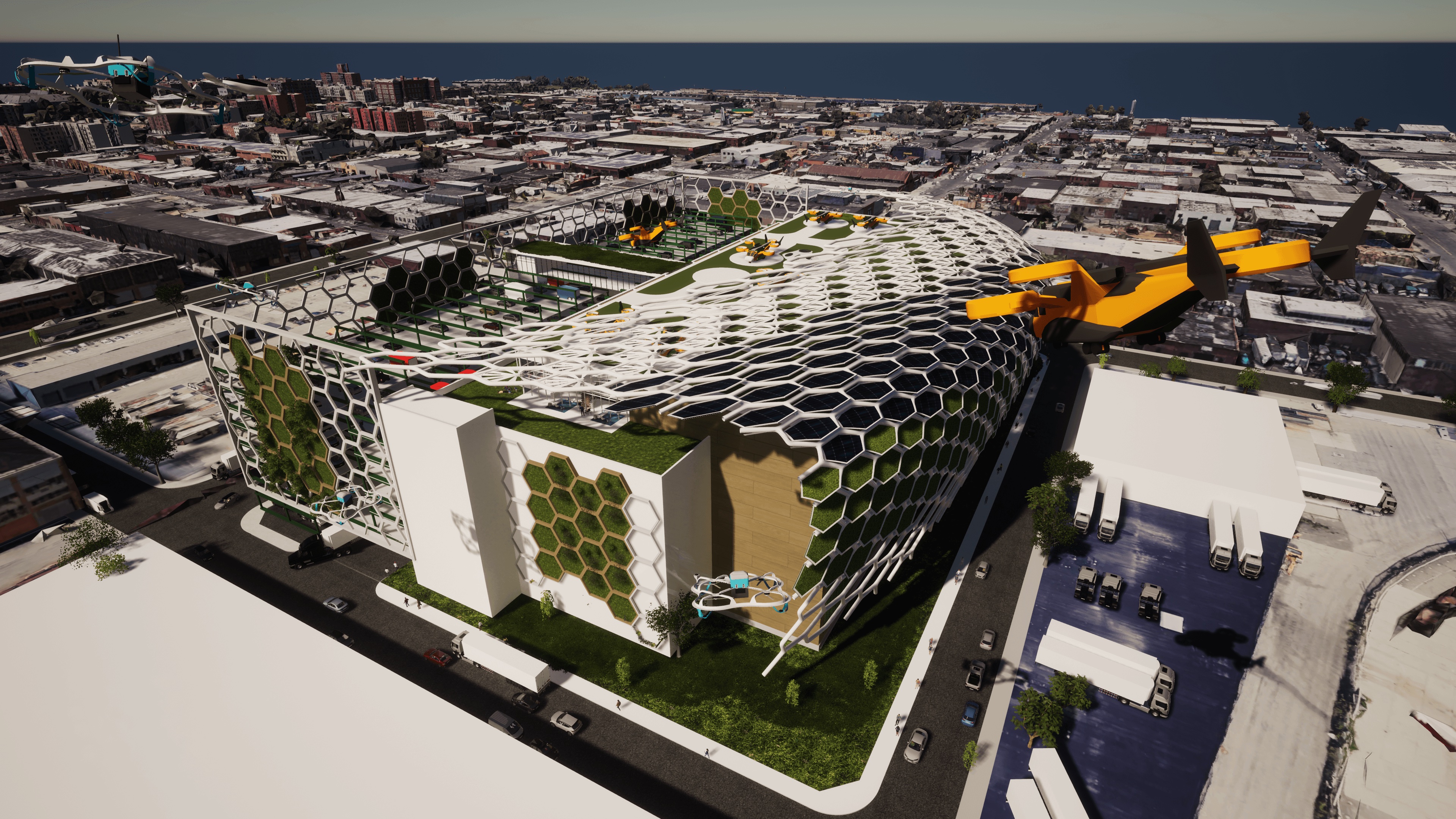
The national design firm Ware Malcomb recently presented a design concept for a Logistics Building of the Future at a conference in Jersey City, N.J., conducted by NAIOP, the Commercial Real Estate Development Association. This concept, which the firm is calling a “thought exercise,” places a premium on technology driven efficiency and coordination. The concept also pays heed to reducing the building’s carbon footprint through a combination of natural and mechanical solutions.
The question being answered by this design concept, says Matt Brady, LEED AP, an Architect and Executive Vice President at Ware Malcomb’s office in Irvine, Calif., is how to fit more products into a facility while realizing the greatest efficiency. “The through-put is the game changer,” he says.
Automation drives efficiency
This hypothetical logistics center is a five-story building (including its roofdeck) that would sit on 4.6. acres in San Francisco. Ware Malcomb collaborated with several industry leaders to devise this concept, including Jones Lang LaSalle, DH Property Holdings (a leading developer of urban infill industrial facilities), Suffolk Construction (for building costs), and Parkmatic, which provides space-controlling automated parking racks.
Brady says computer-driven systems play a big role in the logistics center’s operations: they coordinate arrivals so that trailers can be precision-parked into the facility’s docks; they organize and stage the storage of goods in the building’s tall warehouse so inventory can be retrieved quicker; and in partly automated packing areas, loads of goods are created to be placed into smaller delivery vans, the drivers for which are assigned automatically.
One of the big problems for vertical logistics center in urban settings is finding enough space for parking. Brady notes that in New York, trailer and van drivers sometimes end up parking blocks from existing facilities. Ware Malcomb’s design concept stacks employee vehicles in racks so delivery vans can fit into the center and aren’t idling elsewhere. Brady acknowledges that parking becomes more of a challenge when vehicles are electric and take time to recharge.
Ware Malcomb’s concept is multimodal and assumes electric vehicles and delivery drones. “Flying vehicles aren’t here yet, but warehouses need to be ready for them,” he explains.
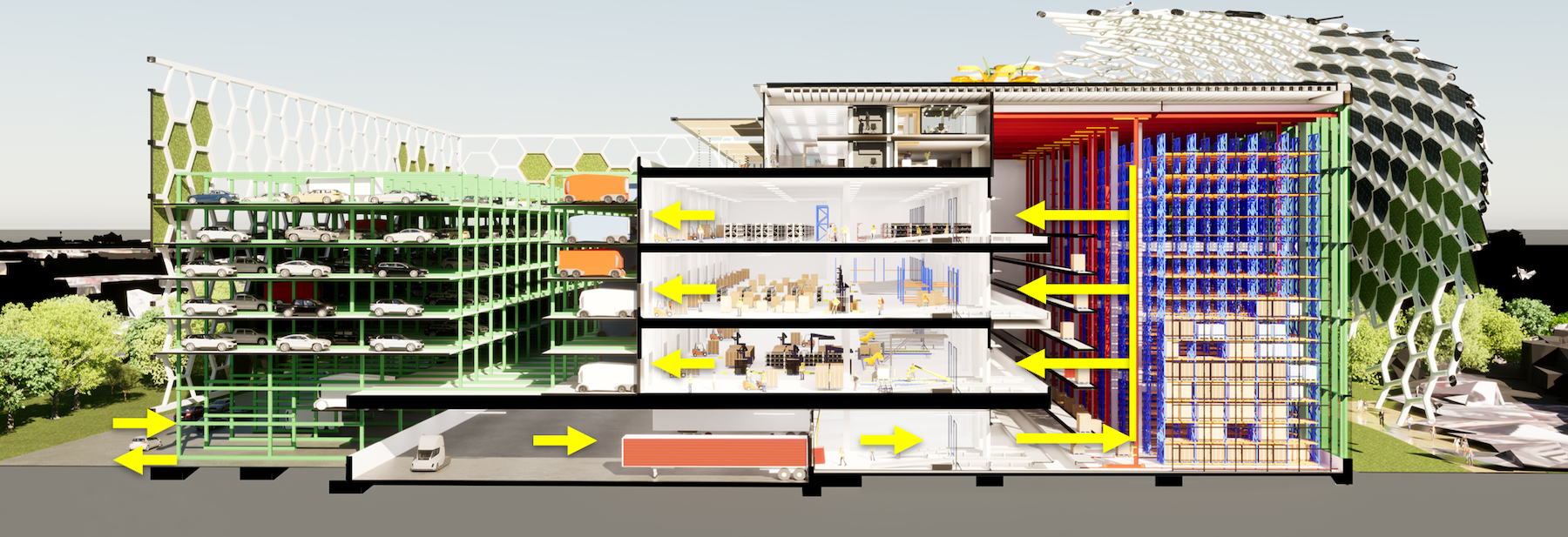
A greener distribution center
The design concept also shows options to reduce the logistics center’s carbon footprint. For example, the concept envisions a honeycombed skin that generates wind and cools the building’s exterior surface. The concept also incorporates sustainable features such as agricultural air filtration, wind turbines, angled solar cells, photoreactor algae-filled glass, rainwater collection, and 3D-printed flexible infrastructure.
Brady says the feedback from developers so far has been positive, and at least one developer is interested “in doing something like this.” An ecommerce company has expressed interest in using Ware Malcomb’s design concept as part of a charrette about industrial buildings in general.
Ware Malcomb sees its concept as leading to speculative development, ideally for a single tenant per building so that there’s just one systems operator. Brady says that the point of this exercise is not to get developers to copy the concept as much as it is to prepare them for what might be coming. “Occupiers are evolving fast, and developers need to keep up,” he says.
Brady also believes that while new construction of industrial buildings has been leveling off, demand is a function of the economy. “Based on people we talk to, there’s still a lot of room for ecommerce growth.”
Related Stories
Movers+Shapers | Jun 16, 2016
THE PANAMAX EFFECT: Panama Canal expansion could trigger an East Coast construction boom
Cities lining the East Coast and Gulf Coast, from New York City to New Orleans, are spending big bucks to accommodate the larger vessels that will now be able to cross a wider and deeper Panama Canal.
Self-Storage Facilities | Apr 20, 2016
Design is now a factor in storage wars
Self-storage facilities are blending into neighborhoods better, and competing for rentals from women, their primary customers.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 13, 2016
Ford begins 10-year plan to centralize Dearborn, Mich., campus
The company said that it will rebuild 7.5 million sf of work space over a 10-year period, which will shift 30,000 employees from 70 buildings now into two primary locations.
Game Changers | Feb 5, 2016
Tesla: Battery storage is not just about electric vehicles
With his $5 billion, 13.6 million-sf Gigafactory, Tesla’s Elon Musk seeks to change the economics of battery energy storage, forever.
Game Changers | Feb 4, 2016
GAME CHANGERS: 6 projects that rewrite the rules of commercial design and construction
BD+C’s inaugural Game Changers report highlights today’s pacesetting projects, from a prefab high-rise in China to a breakthrough research lab in the Midwest.
| Jan 14, 2016
How to succeed with EIFS: exterior insulation and finish systems
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
Giants 400 | Sep 10, 2015
INDUSTRIAL SECTOR GIANTS: Stantec, Turner, Jacobs among top industrial AEC firms
BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest industrial sector design and construction firms, as reported in the 2015 Giants 300 Report
Industrial Facilities | Sep 3, 2015
DATA CENTER SECTOR GIANTS: Fluor, Gensler, Holder Construction among top data center AEC firms
BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest data center sector design and construction firms, as reported in the 2015 Giants 300 Report
Industrial Facilities | Aug 18, 2015
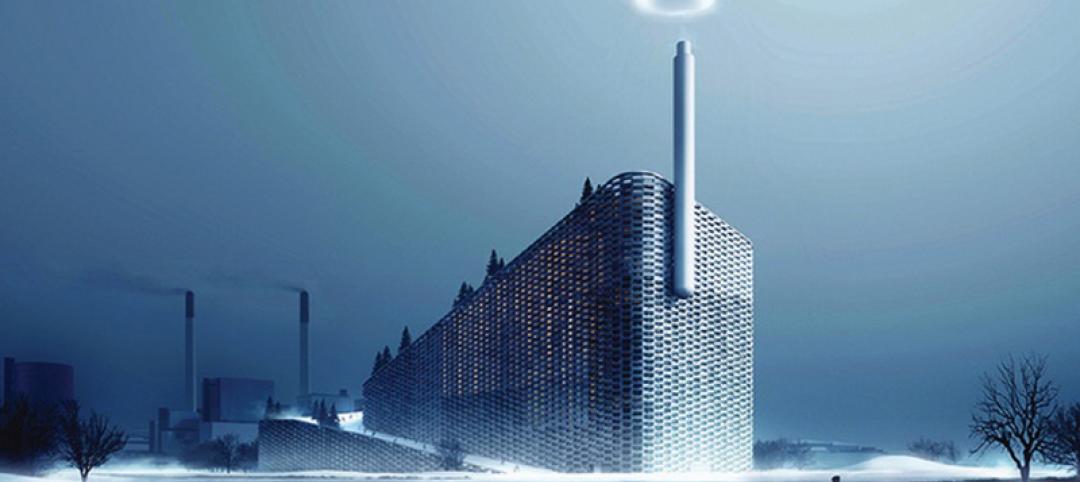
BIG crowdfunds steam ring prototype for Amager Bakke power plant project
The unusual power plant/ski slope project in Copenhagen will feature a smokestack that will release a ring-shaped puff for every ton of CO2 emitted.
Sponsored | Industrial Facilities | Aug 17, 2015
California wastewater agency wins with radiant technology
The Big Bear Area Regional Wstewater Agency tried several different methods to dry the sludge with only marginal success, so they decided to devise a new system that would be more effective, more efficient and would reduce the odor complaints.