The mushrooming global demand for lab space has prompted AEC firms and their developer clients to rethink how science buildings can be designed and constructed quicker and efficiently.
These buildings need “to be optimized for a tenant; concerns about vibration, ventilation, containment, and specialized equipment go beyond the scope of traditional workplaces,” wrote Chad Yoshinobu, AIA, LEED BD+C, Design Director, and a global leader in Gensler’s science practice in Seattle.
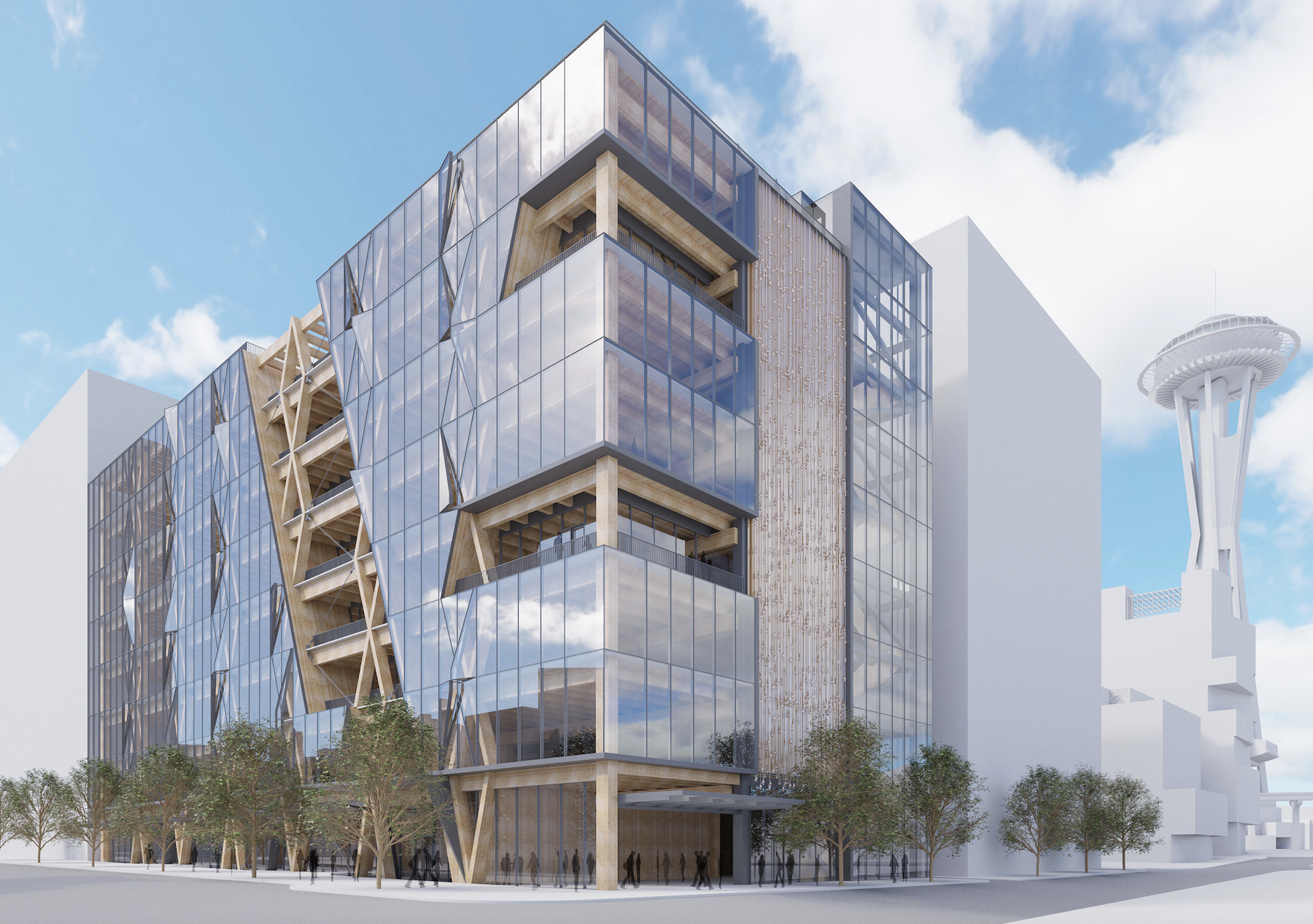
Enter NEXT, a prototype that Gensler and the engineering firms Buro Happold and KPFF have developed, with performance metrics backed up by data.
The research project was funded by Gensler Research Institute, and was designed on the specific site within Seattle’s Uptown Arts District to be 250,000 sf and eight stories tall. The project had three goals: to make this space more than just a container for people, to increase product differentiation for competitive marketing, and to offer solutions that prioritize decarbonization as a method of resilience.
Mass timber was a seminal building material for this project, mainly because it is well-suited to off-site modular construction at a nearby factory and can be delivered as a kit of parts, explained Yoshinobu.
“This approach would be 30 percent faster and 10 percent cheaper to construct than a conventional concrete building,” he estimated. With 85 percent fewer deliveries to the site and a 75 percent reduction in construction waste, NEXT emits 80 percent less carbon to build than a conventional concrete lab building. This amounts to a savings of approximately 5,200 total metric tons of CO2.
NEXT deploys an all-electric heat pump chiller (EL1) system that Gensler stated is more efficient than a natural gas system in all locations and sectors. All-electric systems result in lower building Energy Use Intensity (EUI) in all markets and achieve zero carbon emissions on a clean grid. In total, NEXT produces 50 percent less greenhouse gas emissions and uses 30 percent less energy annually than a conventional lab building.
FLEXIBLE LAYOUT
Lab benches and vibrations in the floor plate typically determine a lab space’s layout. The NEXT team created a grid at 33 by 33 ft, which Yoshinobu contended is “optimal” for a lab bench layout because of the flexibility it affords tenants to orient the benches as they see fit. The building core is moved from the center to the side of the building, allowing tenants more layout flexibility with far fewer obstructions.
The size of this grid in mass timber doesn’t work well with vibration. “So we partnered with our engineering partner KPFF to make it work,” said Yoshinobu, to achieve a vibration of 6,000 MIPS, a go-to standard for most lab buildings, by implementing a structural frame that acts as an ecosystem between the size of the columns, girders, beams, CLT floors, and concrete topping slab.
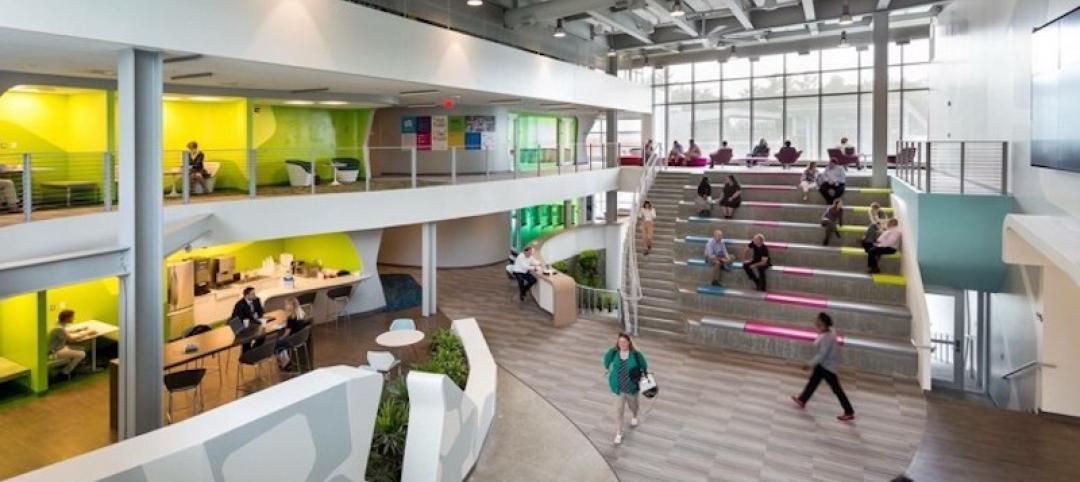
CONNECTING WITH OUTDOORS AND COMMUNITY
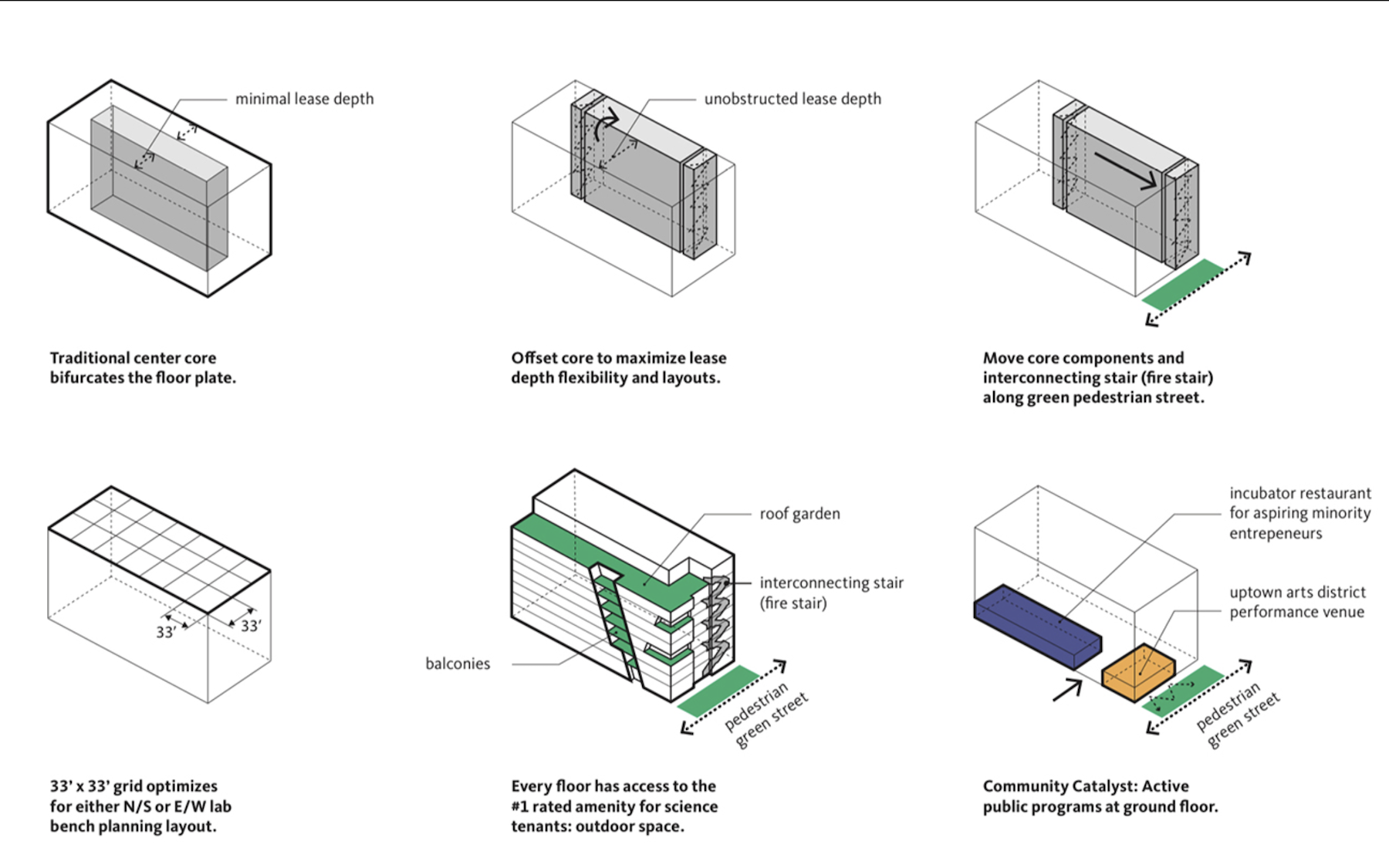
NEXT also places a premium on natural ventilation and outdoor spaces. Multiple operable windows give the workplace more access to fresh air. Seattle’s temperate climate is conducive to natural ventilation, and NEXT is designed so more than one-third of total occupied work hours can be in natural ventilation mode. That leads to energy savings of 30 percent compared to a conventional lab building.
According to the latest Gensler U.S. Workplace Survey, science workers ranked outdoor space as their top workplace amenity. Each floor of the NEXT concept has direct access to outdoor spaces. The building’s fire stair has been turned into a wellness amenity, too, by moving it to the perimeter, and flooding the stairwell with daylight and views. The stair is also an alternative to using elevators.
This multipurpose venue was created in partnership with the Uptown Arts and Cultural Coalition to provide flexible spaces for young musicians, art education, theater, and practice/performance space. The restaurant incubator gives minority entrepreneurs the opportunity to launch their businesses, while a shared kitchen space allows for multiple food venues to enhance the neighborhood food scene. “These efforts will create more cultural diversity within the Uptown District,” wrote Yoshinobu.
He told BD+C that since releasing its research findings, Gensler has received calls from clients and developers “asking us to explore the attributes of this idea on their particular sites.”
Related Stories
Laboratories | Jun 18, 2018
A Massachusetts research building is the first to meet WELL’s Gold standard
Design changes in lighting and HVAC systems were required to meet compliance criteria.
Laboratories | May 21, 2018
Virtual Design and Construction Technology helped design MIT’s new accelerator facility
SGA designed the incubator space.
Laboratories | Feb 26, 2018
Three trends shaping labs of the future
It’s all about flexibility and talent for the future of life sciences.
University Buildings | Feb 16, 2018
The University of Washington receives a new Nanoengineering and Sciences Building
The building marks the second phase of a 168,000-sf complex.
Laboratories | Feb 15, 2018
Mass science: Superlab design best practices
What are superlabs? And what makes for a superbly designed superlab?
Reconstruction & Renovation | Feb 7, 2018
Renovations begin on an underground facility that is investigating the nature of dark matter
This LEO A DALY-designed project makes way to produce the world’s most sensitive detector to this point.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 6, 2018
A new precision dental center embodies Columbia University’s latest direction for oral medicine education
The facility, which nests at “the core” of the university’s Medical Center, relies heavily on technology and big data.
Giants 400 | Dec 13, 2017
Top 45 science + technology architecture firms
HDR, HOK, and Interior Architects top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest science + technology sector architecture and AE firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
Healthcare Facilities | Nov 6, 2017
Design isn’t enough to foster collaboration in healthcare and research spaces
A new Perkins Eastman white paper finds limited employee interaction at NYU Winthrop Hospital, a year after it opened.
Laboratories | Sep 22, 2017
Designing for how we learn: Maker spaces and instructional laboratories
Here is how the See + Hear + Do = Remember mantra can be applied to maker spaces and instructional labs.