The Green Building Certification Institute (GBCI) has launched LEED Proven Provider, a new designation that streamlines the LEED project review process for experienced organizations that demonstrate consistent excellence in administering LEED projects.
“LEED Proven Provider makes the LEED review process faster and more seamless,” said Doug Gatlin, vice president of program delivery, U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) and GBCI. “It allows GBCI to deliver faster reviews of LEED projects while still maintaining the integrity of the LEED certification process.”
LEED Proven Provider is designed to minimize the need for additional work during the project review process. It also creates an opportunity for participants and LEED reviewers to work together to enhance the LEED certification experience and facilitates direct engagement with and support for project teams.
“One of the many things we’ve heard from customers is that the LEED review process can be complex,” added Gatlin. “LEED Proven Provider rewards organizations that are submitting great LEED applications while speeding up the review process, which is a benefit that participants can pass along to their clients.”
Organizations that demonstrate and maintain high-quality project submissions through LEED Proven Provider receive benefits, such as greater access to a LEED reviewer and recognition from USGBC for their sustained track record of high-quality project submissions.
Organizations with significant LEED project administration experience (a minimum of six certified projects in a single rating system family) are eligible to apply.
LEED Proven Provider has been beta tested by several experienced organizations in the marketplace. New organizations looking to participate can learn more here.
Related Stories
| Jul 18, 2014
Engineering firms look to bolster growth through new services, technology [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Following solid revenue growth in 2013, the majority of U.S.-based engineering and engineering/architecture firms expect more of the same this year, according to BD+C’s 2014 Giants 300 report.
| Jul 18, 2014
Top Engineering/Architecture Firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Jacobs, AECOM, Parsons Brinckerhoff top Building Design+Construction's 2014 ranking of the largest engineering/architecture firms in the United States.
| Jul 18, 2014
Top Engineering Firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Fluor, Arup, Day & Zimmermann top Building Design+Construction's 2014 ranking of the largest engineering firms in the United States.
| Jul 18, 2014
Top Architecture Firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Gensler, Perkins+Will, NBBJ top Building Design+Construction's 2014 ranking of the largest architecture firms in the United States.
| Jul 18, 2014
2014 Giants 300 Report
Building Design+Construction magazine's annual ranking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S.
| Jul 7, 2014
7 emerging design trends in brick buildings
From wild architectural shapes to unique color blends and pattern arrangements, these projects demonstrate the design possibilities of brick.
| Jul 2, 2014
Emerging trends in commercial flooring
Rectangular tiles, digital graphic applications, the resurgence of terrazzo, and product transparency headline today’s commercial flooring trends.
| Jun 30, 2014
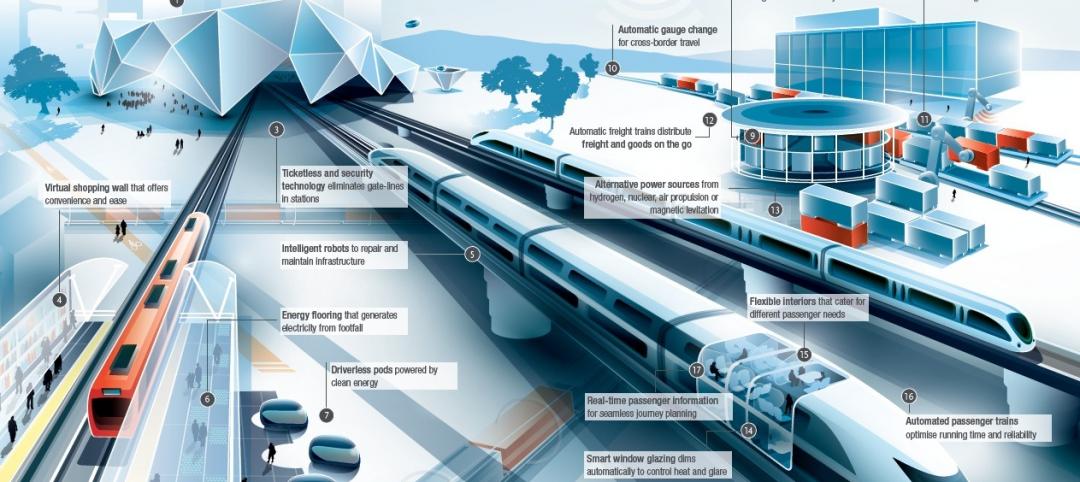
Arup's vision of the future of rail: driverless trains, maintenance drones, and automatic freight delivery
In its Future of Rail 2050 report, Arup reveals a vision of the future of rail travel in light of trends such as urban population growth, climate change, and emerging technologies.
| Jun 18, 2014
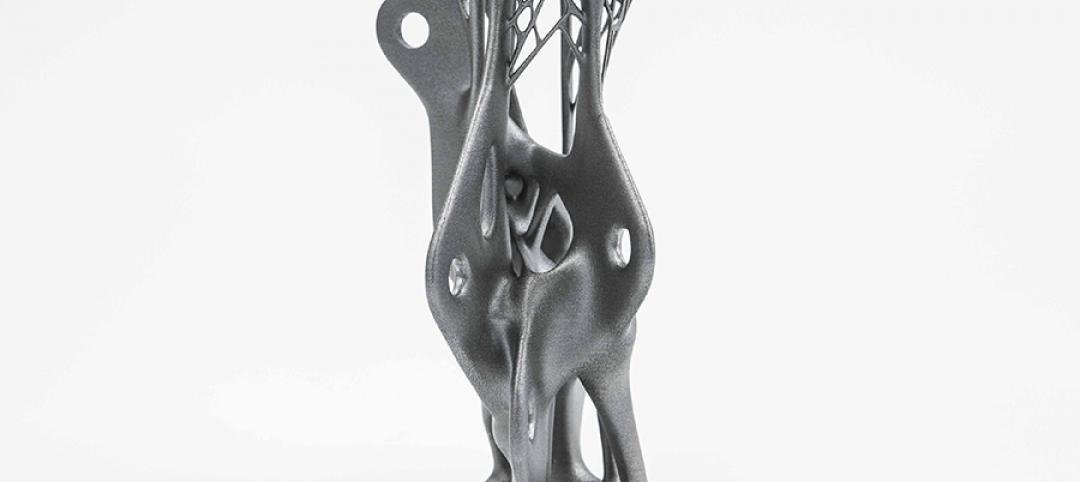
Arup uses 3D printing to fabricate one-of-a-kind structural steel components
The firm's research shows that 3D printing has the potential to reduce costs, cut waste, and slash the carbon footprint of the construction sector.
| Jun 12, 2014
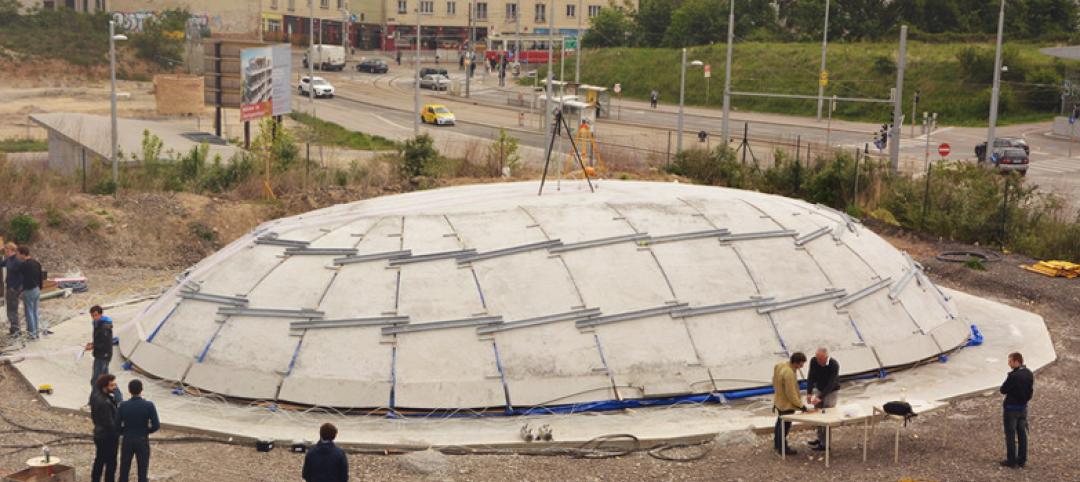
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.