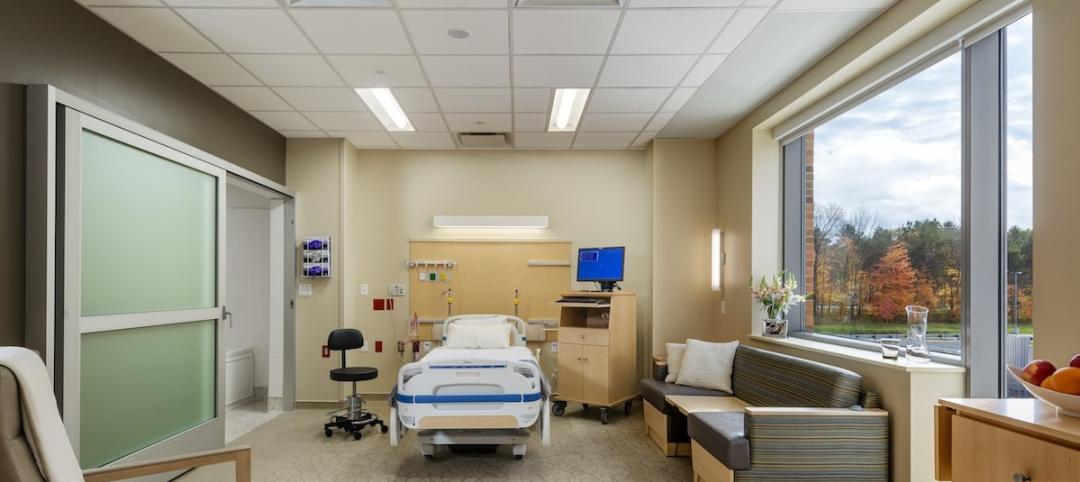
Among the 25 cities in the U.S. with the largest homeless populations, the only city in Florida is Miami, with roughly 3,700 homeless, or 8.1 people per 1,000, according to U.S. News and World Report. Local agencies and programs such as Camillus House’s Lazarus Project and the Miami Permanent Supportive Housing Program target individuals suffering from mental illness that experts identify as one of the root causes of homelessness.
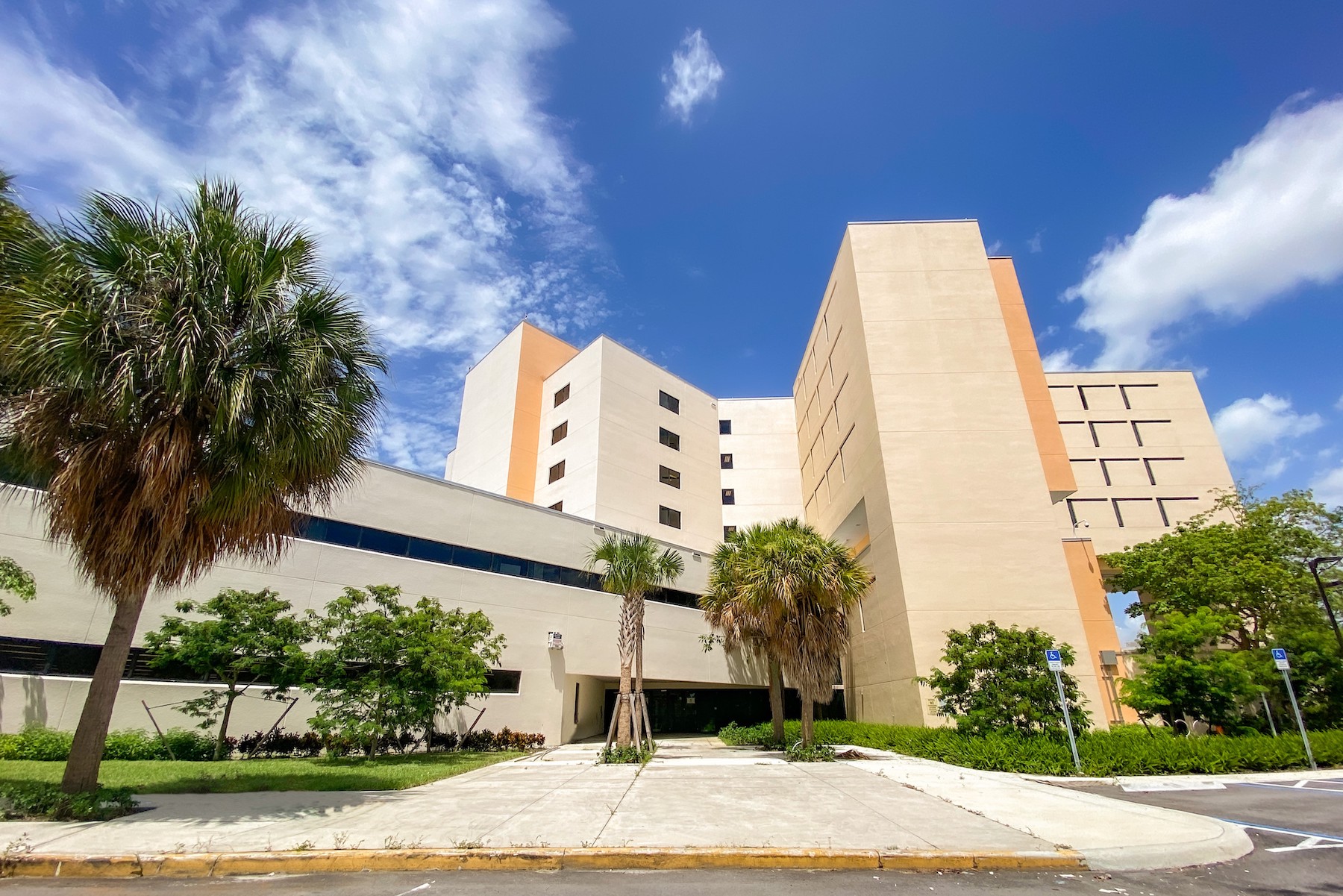
A team that included SBLM Architects recently completed the renovation and conversion of a vacant seven-story, 180,000-sf building—which had previously served as a mental health evaluation and treatment center—into the Miami Center for Mental Health and Recovery, whose goal is to divert individuals with serious mental problems from the criminal justice system to a facility where they can receive proper care and treatment, and possibly transition into more stable housing.
The Miami Center is a response to the Baker Act, a Florida law passed in 1971 that enables families and loved ones to provide emergency mental health services and temporary detention for people who are impaired because of their mental illness, and who are unable to determine their needs for treatment.
The revamped, 208-bed Miami Center, which in late December received its Temporary Certificate of Occupancy, is unique in that its first floor, where detainees are processed and evaluated, includes a Hearing Room with judge and magistrate chambers for related hearings and legal proceedings.
SBLM’s design, in fact, was “conceived” by Judge Steven Leifman, Associate Administrative Judge in the criminal division of Florida’s 11th Circuit Court. “The judge has been the driving force behind this,” confirms Jim Cohen, a Vice President with Miami-based SBLM Architects, who spoke with BD+C yesterday. Judge Leifman was also instrumental is raising funds for this Center.
Bureaucratic snags delay development
Cohen recounts that the “mental health diversion” concept emerged in 2010 after an expose in the mid 2000s revealed that Miami-Dade County's Correctional Department wasn’t equipped to provide the care needed by mentally ill inmates.
At first, the plan was to use only a couple of floors in the building, which was built in 1980. That morphed into a design-build project that at one point had Johnson Controls offering to pay for the entire renovation if its systems were installed. (The county declined that offer.)
The county hired SBLM in 2015, and Cohen says now that the building provided the “backbone and space to realize the judge’s vision.” The building team on this $52 million renovation project included Thornton Construction Company (GC), Bliss & Nyitray (SE) TWR Engineers (MEP), and TLC Engineering for Architecture (technology).
A continuum of care

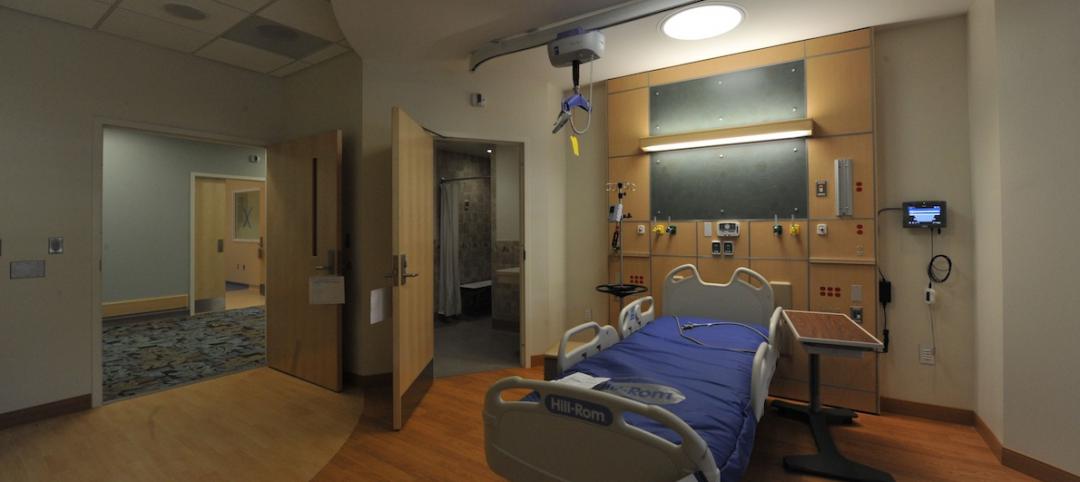
After the intake and evaluation processes, an individual is moved into Crisis Stabilization Unit on the second floor with 16 beds, outpatient clinics, 15 offices for support services, and a conference center for professional and educational training (including law enforcement training specifically for this population). The second floor also has a “respite area” for persons who don’t meet the Center’s crisis criteria but have nowhere else to go.
There’s a secure wing on the second floor for residents that includes a gym, a multipurpose day room, visitation areas, and access to a 33,000-sf outdoor recreation space with landscaping, seating, a walking path, and basketball courts.
Mechanical equipment is on the third floor, which also serves as a physical and acoustical buffer from the resident sleeping areas on floors four through six. (The seventh floor hasn’t been built out yet.) Each resident floor has six to eight sleep pods that allow patient care to be segmented. A maximum of five beds per resident floor may be assigned to that floor’s private bathroom.
Resident floors have dedicated support areas for pharmacies, exam rooms, professional therapy offices, laundries, and dining. As a resident’s condition stabilizes, there can be relocations to higher floors that provide independent living opportunities. As such, Miami Center claims to be the first of its kind in the country that offers a continuum of healthcare for the mentally ill that includes the prospect of reintegrating into society.
Treatment instead of detention
The custodial component, says Cohen, can last up to six months. If the patient shows improvement, he or she is eligible for longer-term houisng on floors five and six. At that stage, a patient can opt to leave the program.
The opening of the Miami Center, which will cost $30 million per year to run, is projected to save Miami-Dade County $100,000 per person annually by providing treatment programs to mentally ill people who otherwise would be held for extended periods in county detention facilities. Cohen says he’s been contacted by the city of Seattle about Miami-Dade’s diversion efforts, and notes that Judge Leifman has toured the facility with representatives from other cities.
Cohen adds that the first floor of the building includes a commercial kitchen that, once operational, could provide patients with training applicable to the food service industry.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Aug 6, 2015
HEALTHCARE AEC GIANTS: Hospital and medical office construction facing a slow but steady recovery
Construction of hospitals and medical offices is expected to shake off its lethargy in 2015 and recover modestly over the next several years, according to BD+C's 2015 Giants 300 report.
Contractors | Jul 29, 2015
Consensus Construction Forecast: Double-digit growth expected for commercial sector in 2015, 2016
Despite the adverse weather conditions that curtailed design and construction activity in the first quarter of the year, the overall construction market has performed extremely well to date, according to AIA's latest Consensus Construction Forecast.
Healthcare Facilities | Jul 23, 2015
David Adjaye unveils design for pediatric cancer treatment center in Rwanda
The metallic, geometric façade is based on the region’s traditional Imigongo art.
Healthcare Facilities | Jul 22, 2015
Best of healthcare design: 8 projects win AIA National Healthcare Design Awards
Montalba Architects' prototype mobile dental unit and Westlake Reed Leskosky's modern addition to the Cleveland Clinic Brunswick Family Health Center highlight the winning projects.
Healthcare Facilities | Jul 8, 2015
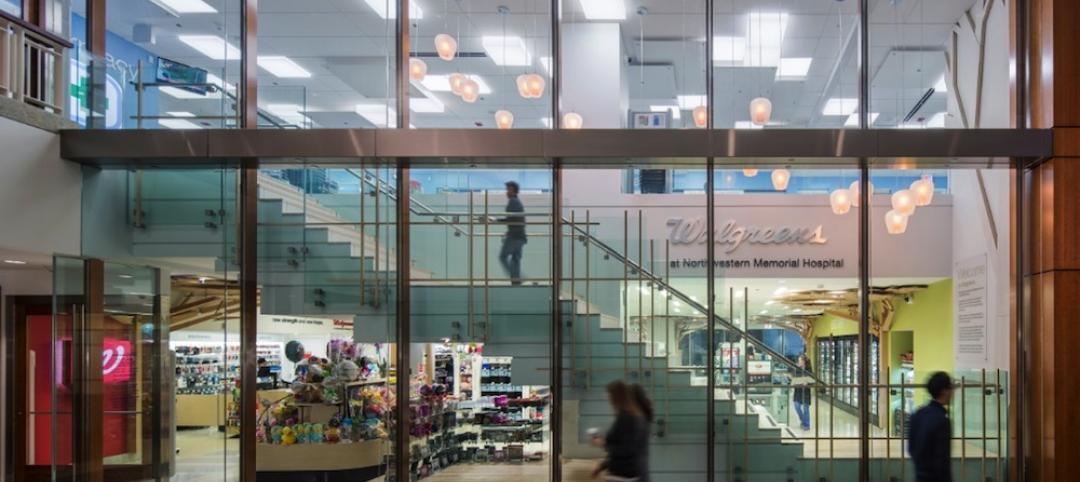
From Subway to Walgreens, healthcare campuses embrace retail chains in the name of patient convenience
Most retail in healthcare discussions today are focused on integrating ambulatory care into traditional retail settings. Another trend that is not as well noted is the migration of retailers onto acute care campuses, writes CBRE Healthcare's Craig Beam.
Healthcare Facilities | Jul 6, 2015
The main noisemakers in healthcare facilities: behavior and technology
Over the past few decades, numerous research studies have concluded that noise in hospitals can have a deleterious effect on patient care and recovery.
University Buildings | Jun 29, 2015
Ensuring today’s medical education facilities fit tomorrow’s healthcare
Through thought-leading design, medical schools have the unique opportunity to meet the needs of today’s medical students and more fully prepare them for their future healthcare careers. Perkins+Will’s Heidi Costello offers five key design factors to improve and influence medical education.
Sponsored | Healthcare Facilities | Jun 23, 2015
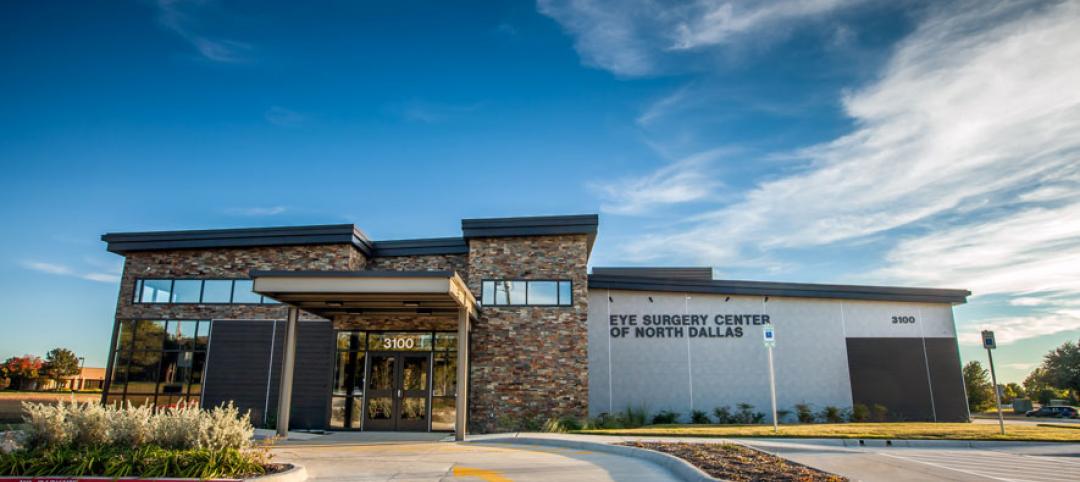
Texas eye surgery center captures attention in commercial neighborhood
The team wanted to build an eye surgery center in an already established area but provide something clean and fresh compared to neighboring buildings.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 16, 2015
Heatherwick’s design for cancer center branch has ‘healing power’
The architect describes it as “a collection of stepped planter elements”
Healthcare Facilities | May 27, 2015
Roadmap for creating an effective sustainability program in healthcare environments
With a constant drive for operational efficiencies and reduction of costs under an outcome-based healthcare environment, there are increasing pressures to ensure that sustainability initiatives are not only cost effective, but socially and environmentally responsible. CBRE's Dyann Hamilton offers tips on establishing a strong program.