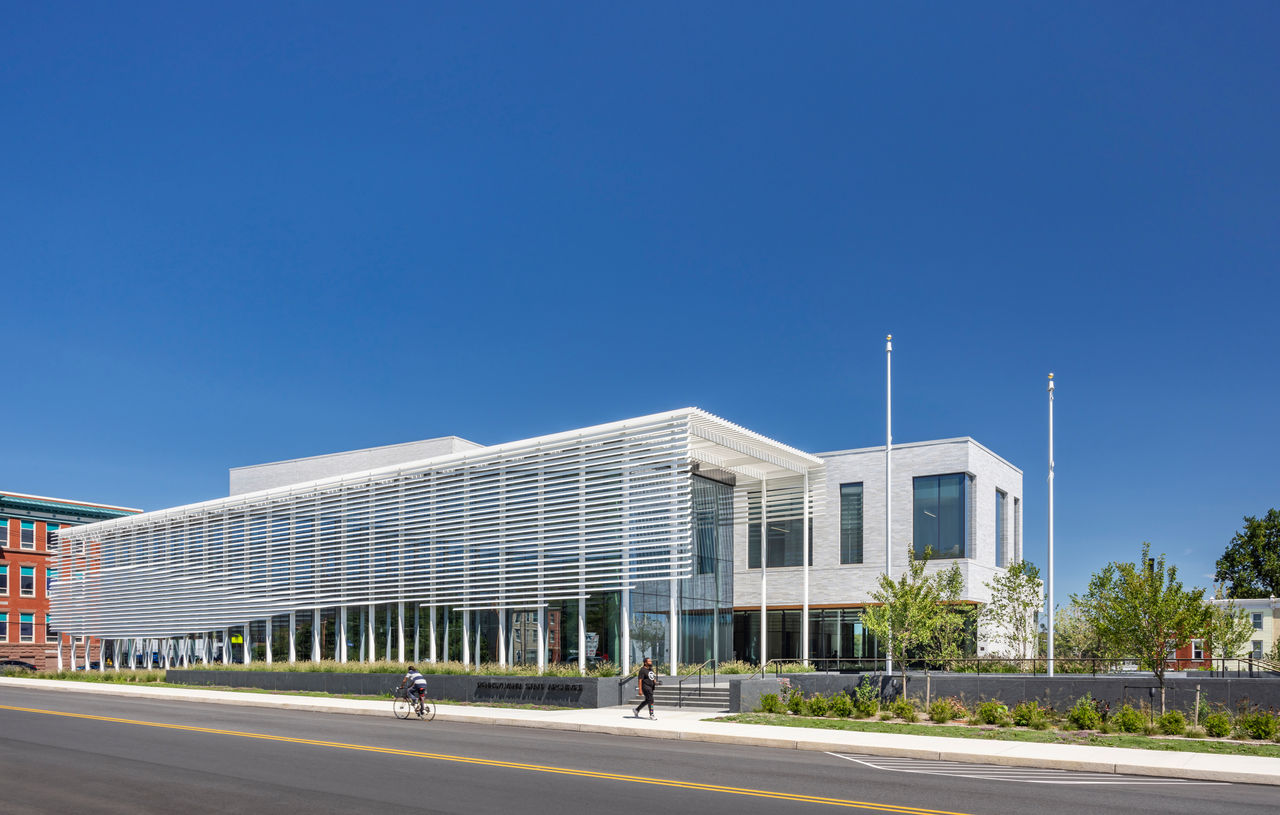
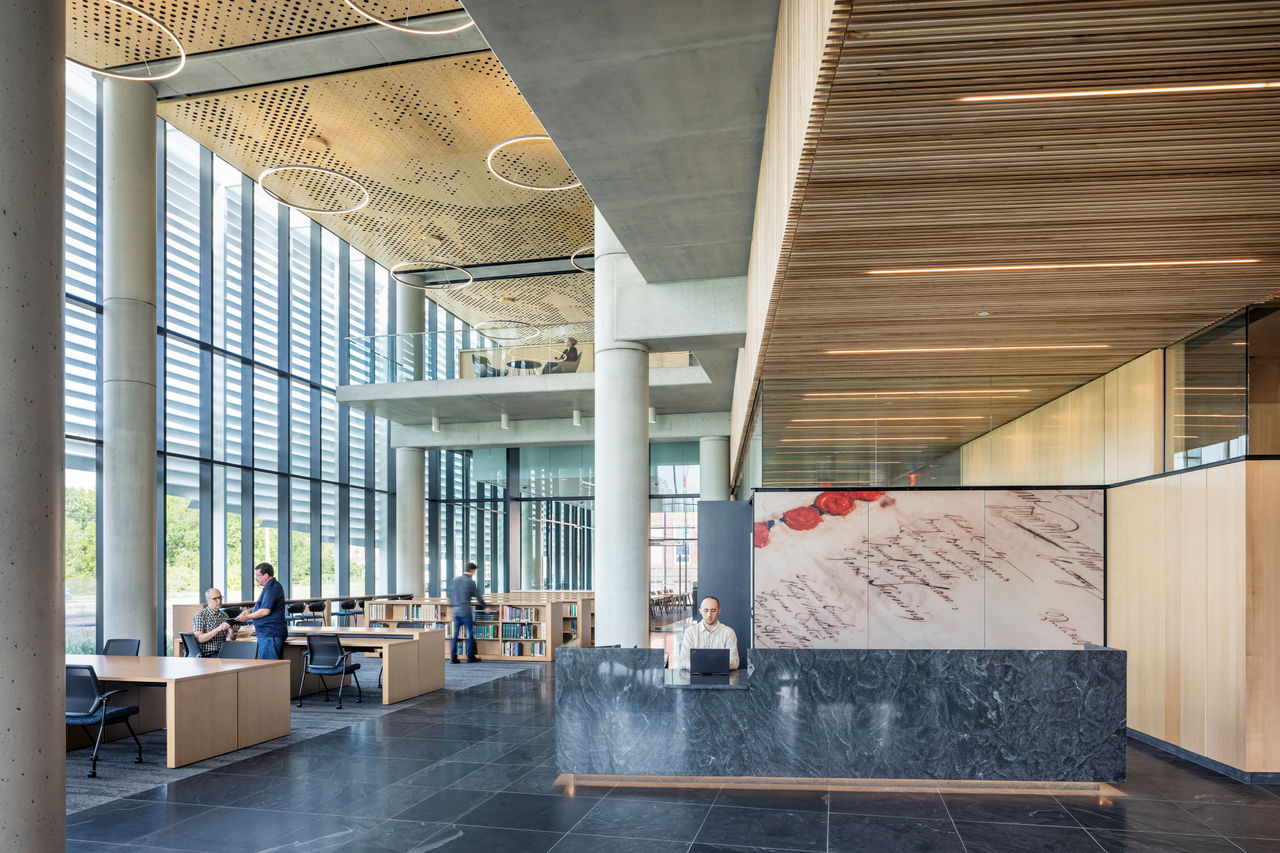
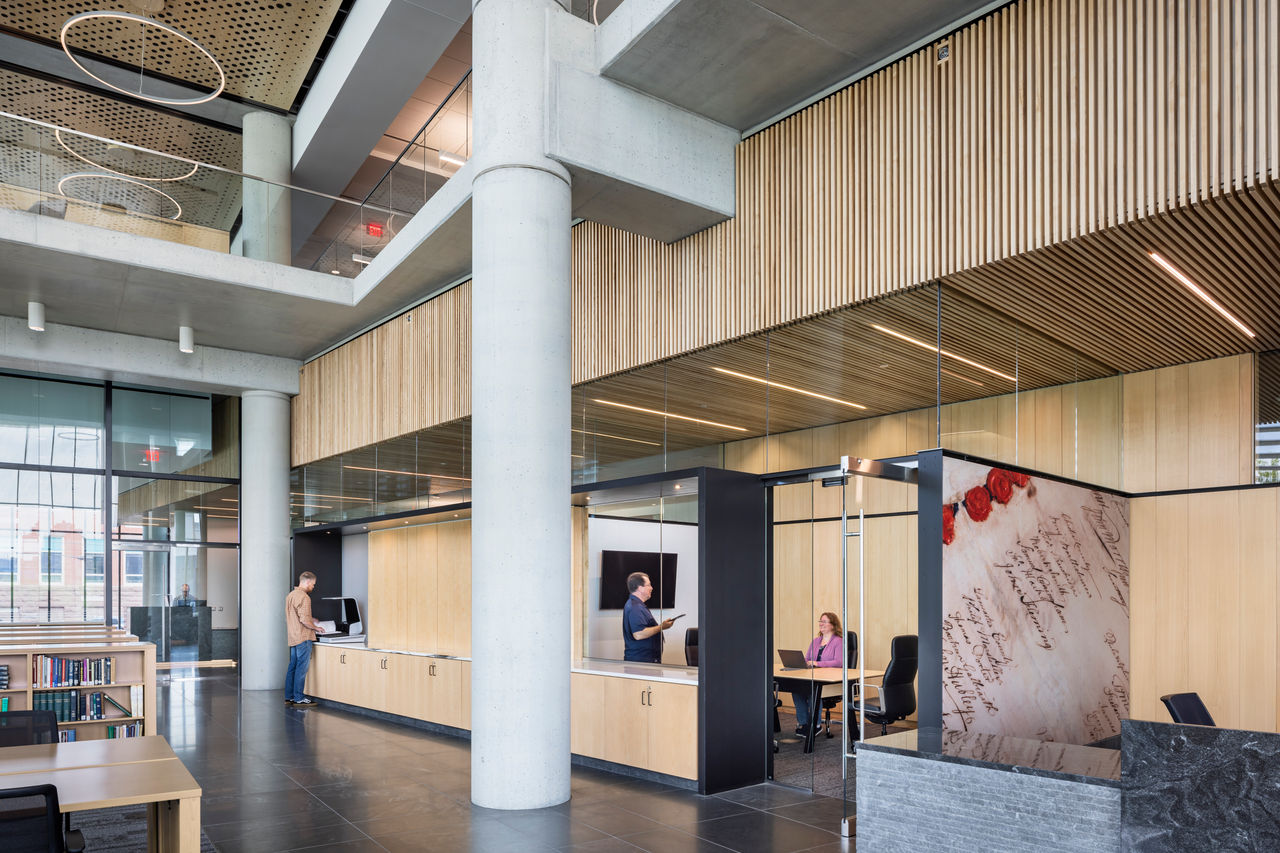
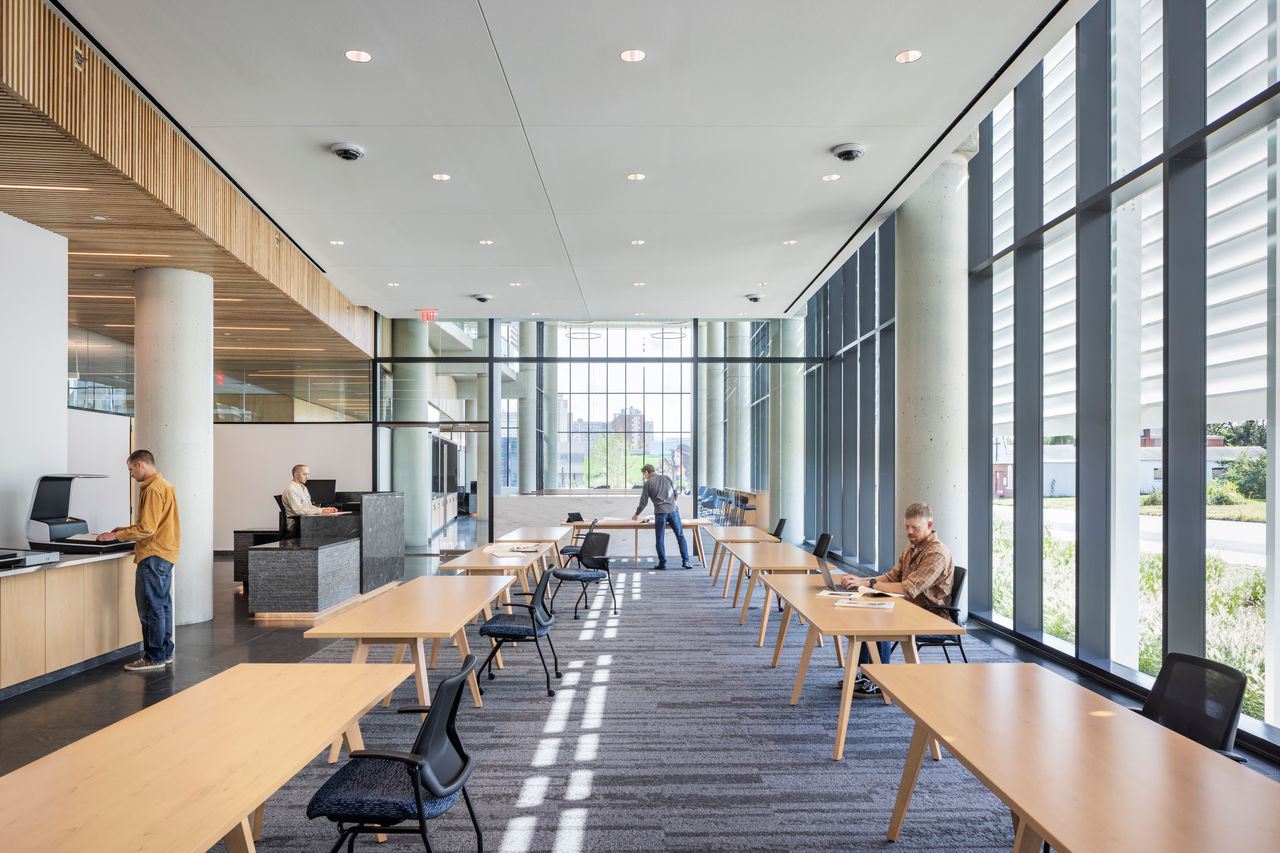
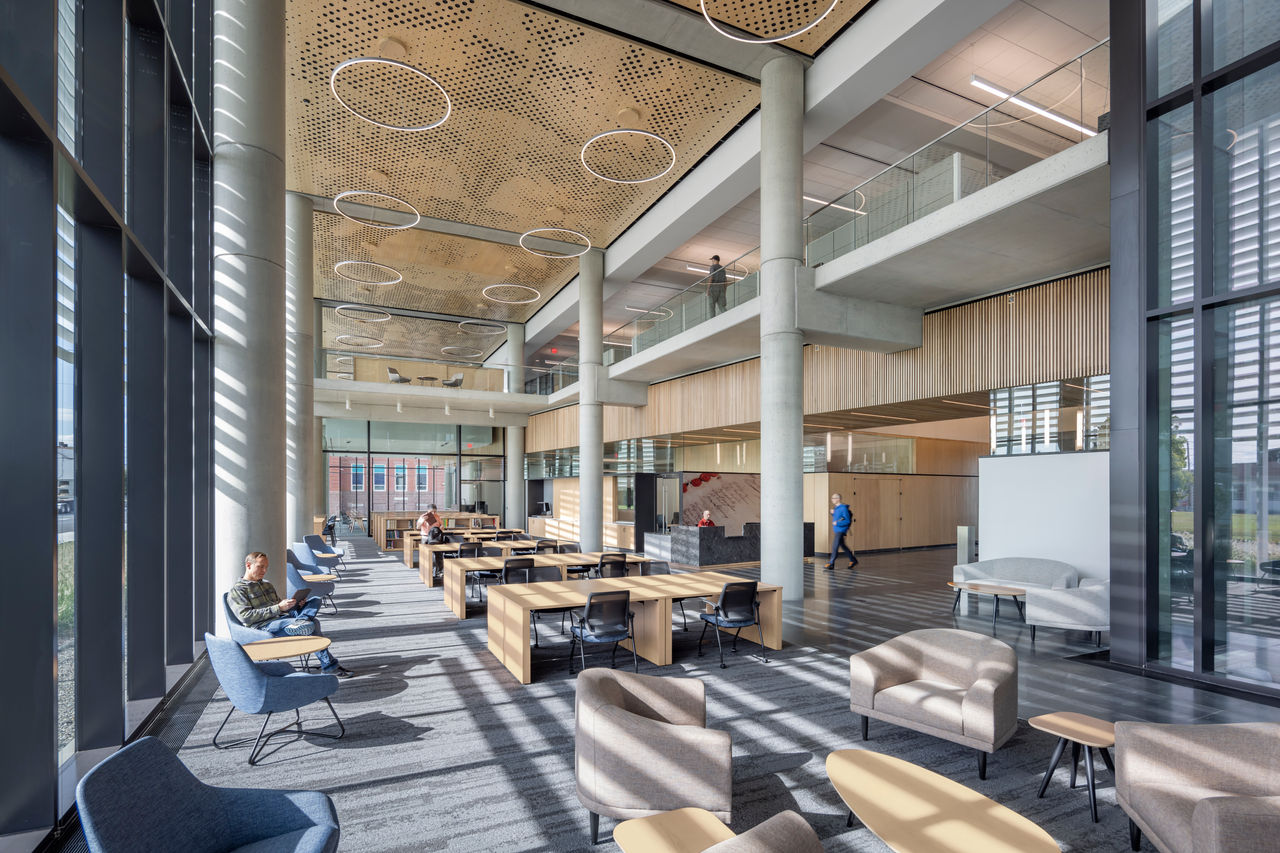
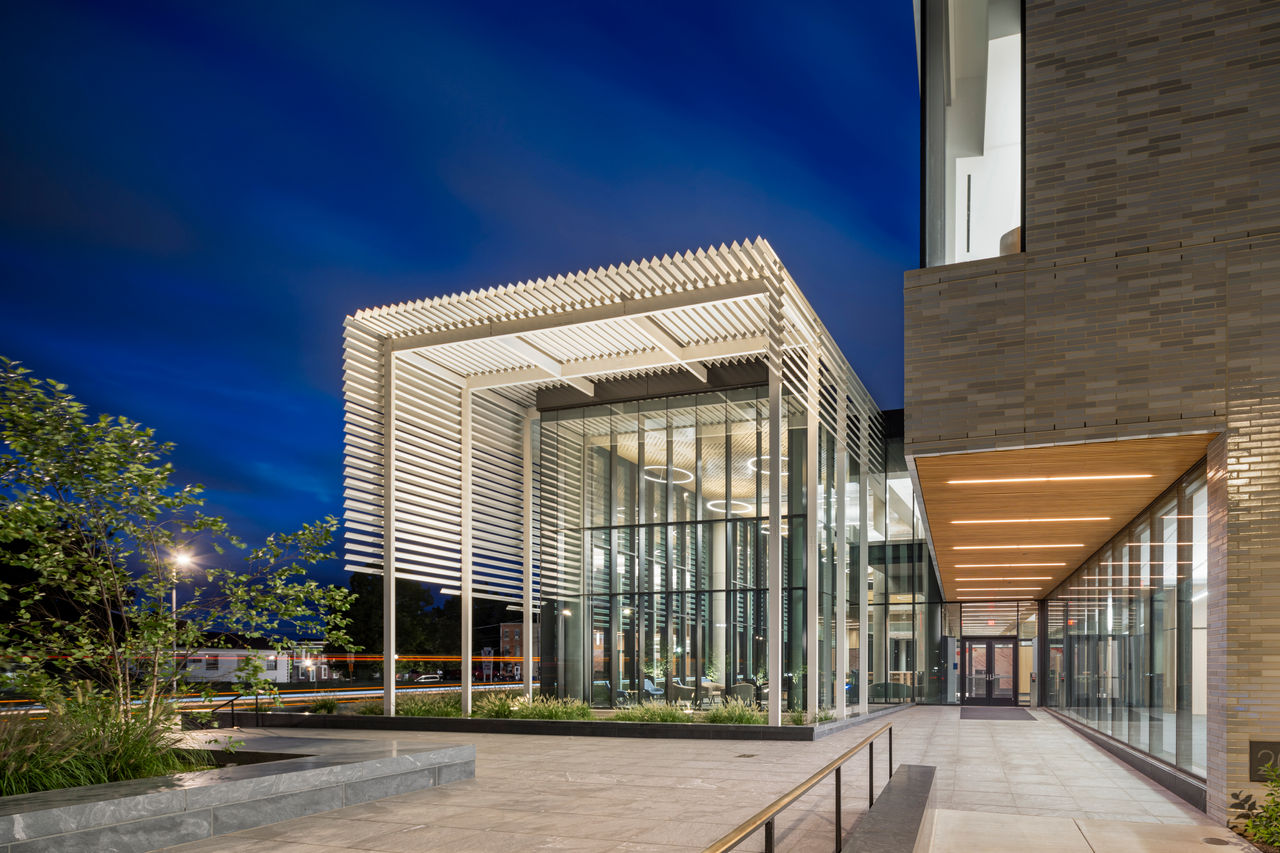
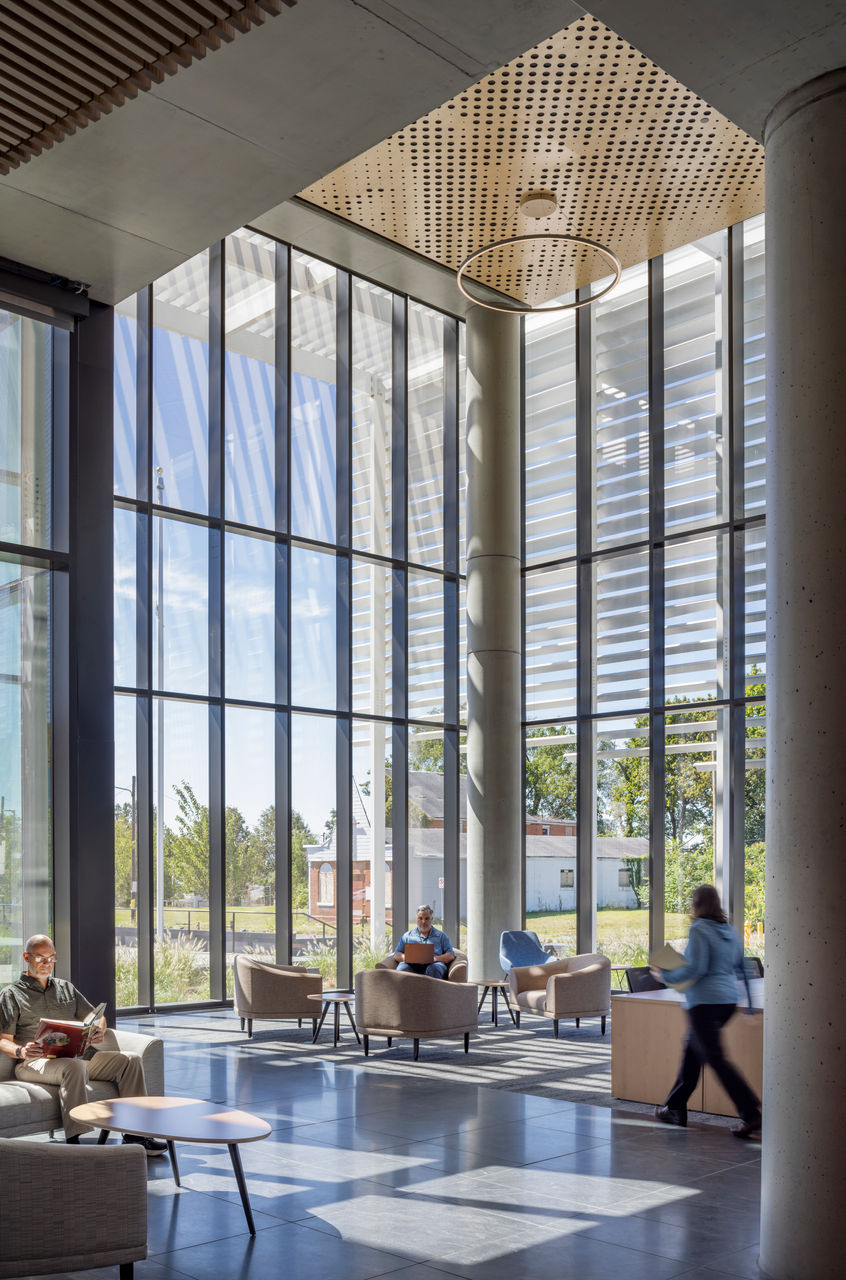
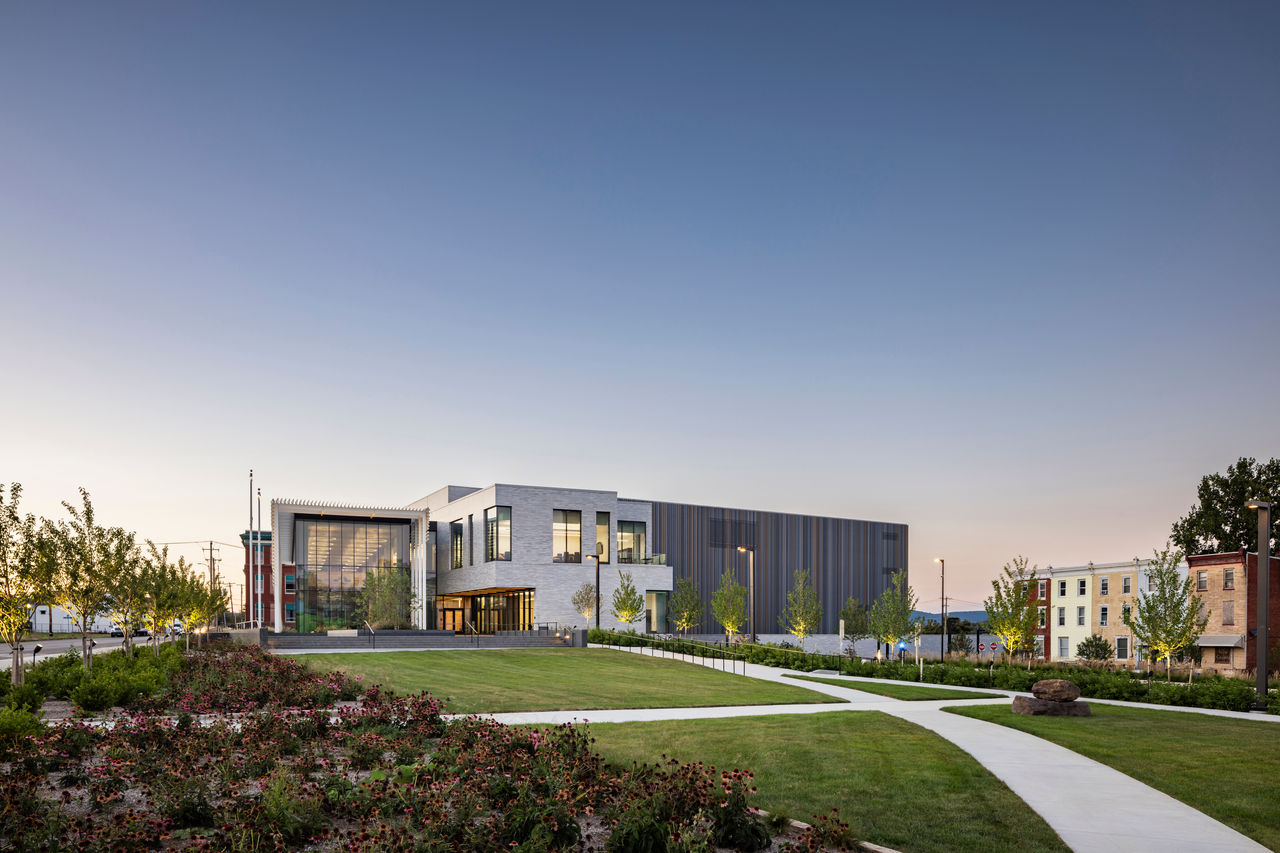
Work was recently completed on a new Pennsylvania State Archives building in Harrisburg, Penn. The HGA-designed, 146,000-sf facility offers numerous amenities, including computers, scanners, printers, a kitchenette with seating, lockers, a meeting room, a classroom, an interactive video wall, gallery, and all-gender restrooms. The features are all intended to provide a welcoming and comfortable environment for visitors.
The state’s Division of Public Records was created in 1903. It became recognized as its own bureau upon joining the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission (PHMC) in 1945. By 2000, its first permanent home in the Capitol Complex was reaching capacity and its low floor-to-floor height, together with a small floor plate, affected operational efficiency and would not allow for necessary environmental upgrades.
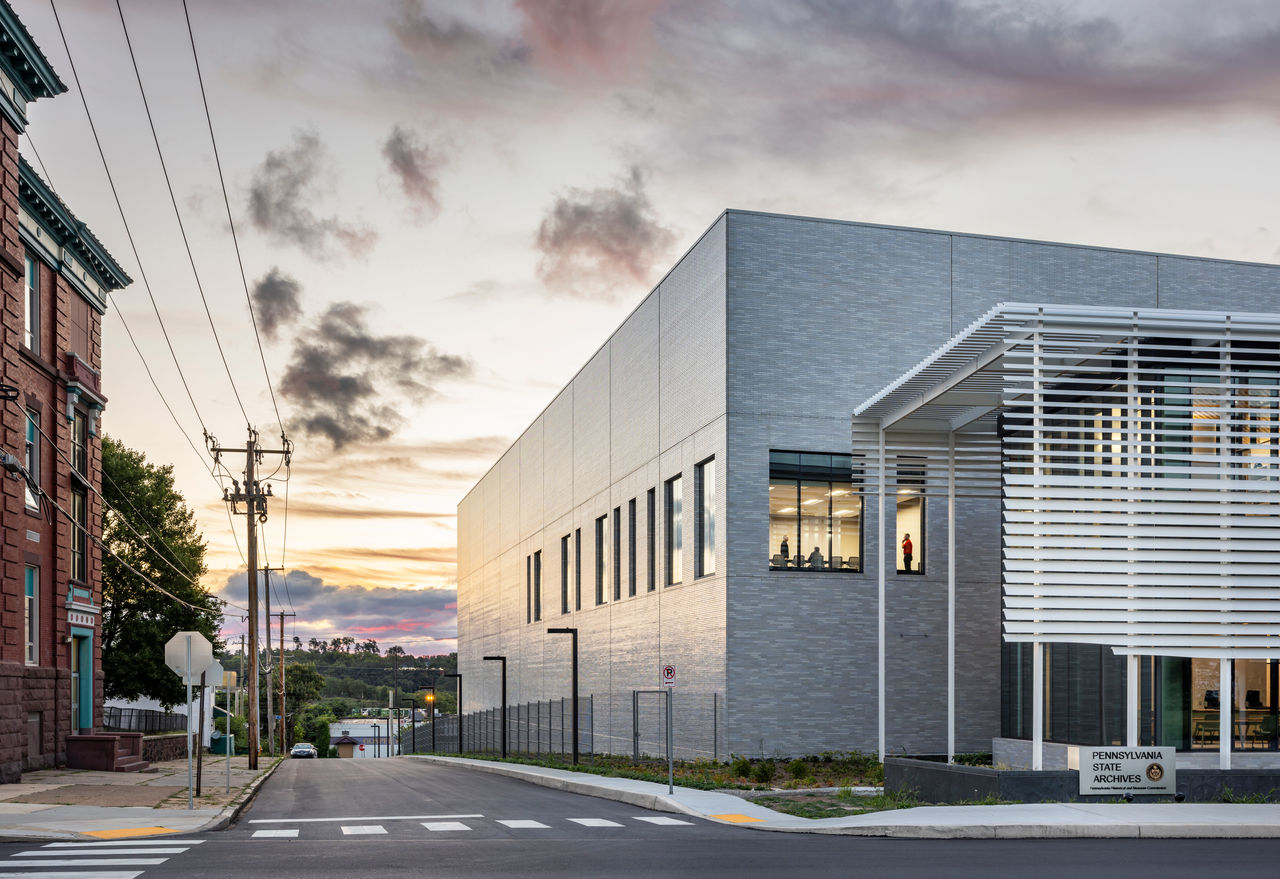
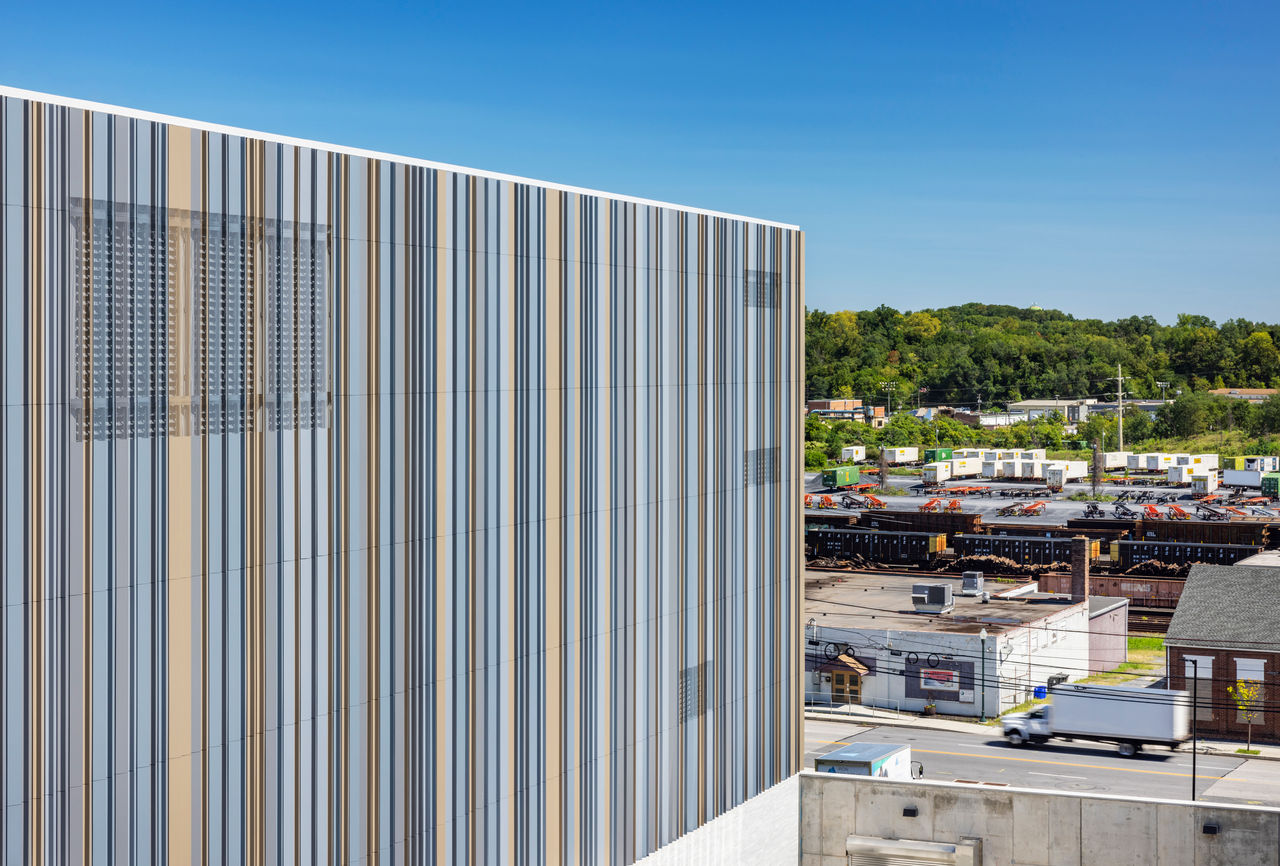
The goal was to find a site close to the Capitol Complex, and an urban parcel in a neglected neighborhood was selected. Built amid the few remaining rental row houses, light commercial structures, and the city’s rail yards, the facility is intended to have a positive impact on the neighborhood and city.
The building’s features include:
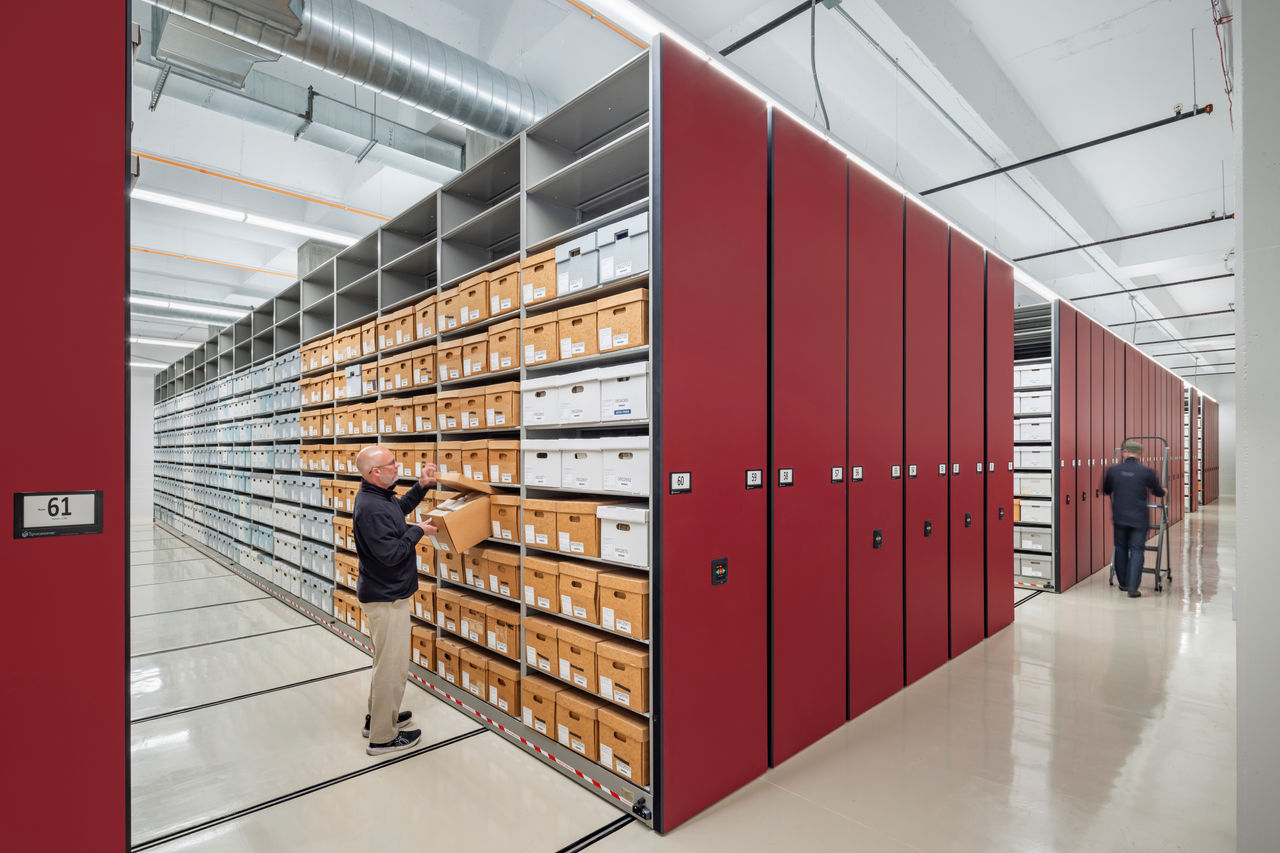
Collections space: A glazed-brick volume and high-thermal-mass concrete structure forms the body of the building, housing acid-free boxes and flat-file maps on high density shelving. The rectangular volume is windowless, well insulated, and projective. Total storage on three floors is 47,000 sf with space for growth, and 12-foot-tall high-density shelving makes the collections rooms highly efficient. Archives’ storage rooms are tightly controlled to keep out all daylight
Mechanical systems: A metal-clad mechanical bay links efficient HVAC systems to archive rooms on each floor, providing tightly modulated temperature and humidity to each kind of environment and material—paper, print photography, or film.
Public space: A double-height glass and aluminum pavilion set in a public garden with native plants allows for individual and group research with a sense of openness and accessibility.
The facility was designed to provide a climate resilient, durable, 50-to 100-year space to protect the archives while enduring extreme conditions. Areas of concern included railroad accidents, extreme or intense precipitation, theft, pests, moisture/mold growth, extreme wind, excessive snow load, and power failure.
To address the railroad yard disaster concern, a sensor was specified for the mechanical louvers that would shut down air intake if any harmful chemicals at elevated concentrations are detected. To mitigate extreme precipitation, no roof drains or roof penetrations are located over the archive rooms. Rain landing on the low slope roof runs down to roof drains over the mechanical rooms.
To prevent theft, security from the facility includes cameras and restricted access to the original documents room where staff members monitor visitors’ movements. Staff entry and exit paths with security systems are choreographed as well, for additional security.
HGA negotiated with electric utility Pennsylvania Power and Light to get two points of electricity service, one primary and one backup, each arriving from a different buried feeder line path to the site. In addition, the facility includes a standby generator with 48 hours of fuel capacity.
Ash wood was used for all interior building woodwork. Now disappearing across the country due to the Emerald Ash Borer, the wood wall panels will one day illustrate the beauty of the once-common native tree. Additionally, the site’s original granite street curbs were used as planter curbs and boulders found buried there were used as landscaping features in the public garden. The stone for the exterior pavers, interior floors, and the front desk was quarried in the Appalachian Mountains, and the glazed brick was manufactured in Pennsylvania.
On the project team:
Owner and/or developer: Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
Design architect: HGA and Vitetta
MEP engineer: HGA
Structural engineer: HGA
General contractor/construction manager: Mascaro Construction










Related Stories
| Dec 28, 2014
Robots, drones, and printed buildings: The promise of automated construction
Building Teams across the globe are employing advanced robotics to simplify what is inherently a complex, messy process—construction.
| Dec 28, 2014
AIA course: Enhancing interior comfort while improving overall building efficacy
Providing more comfortable conditions to building occupants has become a top priority in today’s interior designs. This course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.
| Dec 28, 2014
10 key design interventions for a healthier, happier, and more productive workplace
Numerous studies and mountains of evidence confirm what common sense has long suggested: healthy, happier workers are more productive, more likely to collaborate with colleagues, and more likely to innovate in ways that benefit the bottom line, writes Gensler's Kirsten Ritchie.
| Dec 28, 2014
Workplace design trends: Make way for the Millennials
Driven by changing work styles, mobile technology, and the growing presence of Millennials, today’s workplaces are changing, mostly for the better. We examine the top office design trends.
| Dec 6, 2014
Future workplace designs shouldn’t need to favor one generation over another, says CBRE report
A new CBRE survey finds that what Millennials expect and need from offices doesn’t vary drastically from tenured employees.
| Nov 18, 2014
New tool helps developers, contractors identify geographic risk for construction
The new interactive tool from Aon Risk Solutions provides real-time updates pertaining to the risk climate of municipalities across the U.S.
| Nov 10, 2014
5 guiding principles for solving airflow issues in open-plenum office spaces
Although architecturally appealing, exposed ceilings can create unwanted drafts and airflow problems if not engineered correctly. McGuire Engineers' Bill Stangeland offers tips for avoiding airflow issues on these projects.
| Nov 5, 2014
Survey: More than 75% of workload takes place without face-to-face interactions
With the rise of technology, much of the workday—even the most productive morning hours—is spent corresponding via email or conference call, according to a recent survey of corporate workers by Mancini•Duffy.
| Nov 3, 2014
An ancient former post office in Portland, Ore., provides an even older art college with a new home
About seven years ago, The Pacific Northwest College of Art, the oldest art college in Portland, was evaluating its master plan with an eye towards expanding and upgrading its campus facilities. A board member brought to the attention of the college a nearby 134,000-sf building that had once served as the city’s original post office.
Sponsored | | Oct 23, 2014
From slots to public safety: Abandoned Detroit casino transformed into LEED-certified public safety headquarters
First constructed as an office for the Internal Revenue Service, the city's new public safety headquarters had more recently served as a temporary home for the MGM Casino. SPONSORED CONTENT