The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year.
Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate,” which advocates for the measuring and reducing of EC in core and shell industrial buildings, one of the more vibrant commercial construction sectors.
The report was produced by BranchPattern, a Kansas City-based building consultancy dedicated to creating a better built environment. BranchPattern’s study partners for this report include Prologis, Brookfield Properties, IDI Logistics, Bridge Industrial, and Affinius Capital.

“We are at a pivotal moment for owners and developers of real estate to look beyond the greenhouse gasses emitted during building operations,” says Chris Brown, IDI Logistics’ Solar Development and ESG Director. “Working with industry peers, key partners, and suppliers to create pathways to lower carbon materials, design and construction techniques is an integral part of reducing the impact of buildings have in climate change.”
Building operations and building construction account for 28% and 11%, respectively, of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the International Energy Agency. As buildings have become more energy efficient, operational carbon has been reduced. Therefore, addressing EC emissions “will become increasingly critical to meet climate goals,” states BranchPattern’s report, especially given that the global building area for industrial typologies is projected to double by 2050.
Right now, most of the available EC data are derived from lifecycle assessments of multifamily and office buildings. But based on conservative assumptions, EC is projected to account for 17.4% of a typical industrial building’s total emissions over 60 years. The report calls for greater access to EC measurement tools and comparative data that can help the industrial sector making informed design and construction decisions.
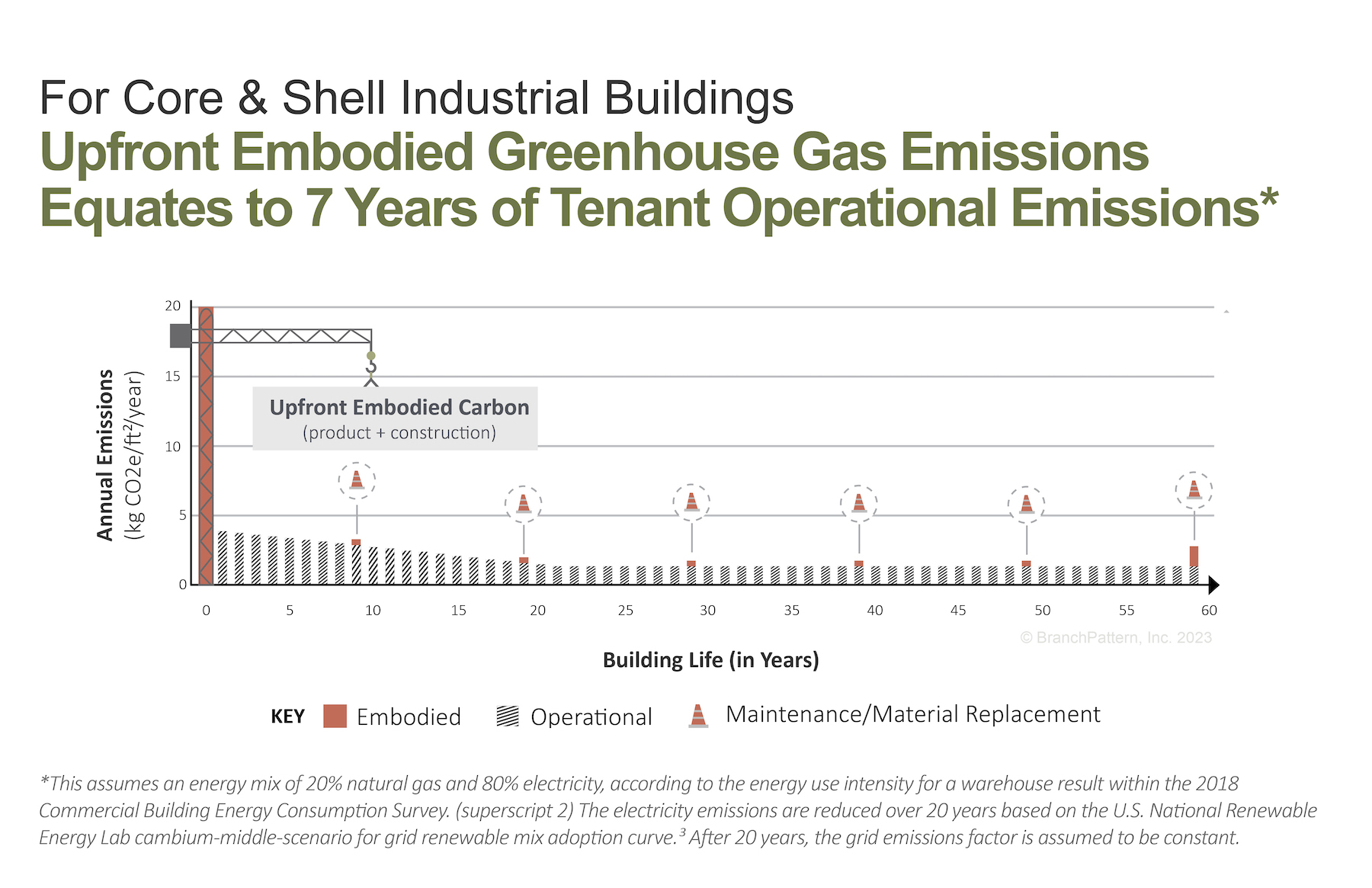
Stakeholders within an industrial building project have varying responsibilities and financial interests in reducing EC in their buildings. The developer, for example, makes decisions about building materials and design. The tenant, on the other hand, might participate in improvements that include MEP systems and interior finishes.
A small but telling sample
In 2022, BranchPattern conducted 46 lifecycle assessments, of which 26 for nine separate real estate developers or owners in six geographic regions of the U.S. are included in its report. The analyses were confined to Class A core and shell industrial warehouses of similar scope. The reference period for the lifetimes of the buildings was 60 years.
BranchPattern compared its EC intensity finding with a 2017 Carbon Benchmark Study of two buildings whose average EC intensity was 20.2 kg per sf.
The report concedes that its own sample isn’t large enough from which to draw definitive conclusions. “A larger, more robust dataset is required to determine regional variation with statistical significance,” the report states. That being said, BranchPattern’s study shows “a strong, positive, linear correlation” between a building’s size and its EC emissions.
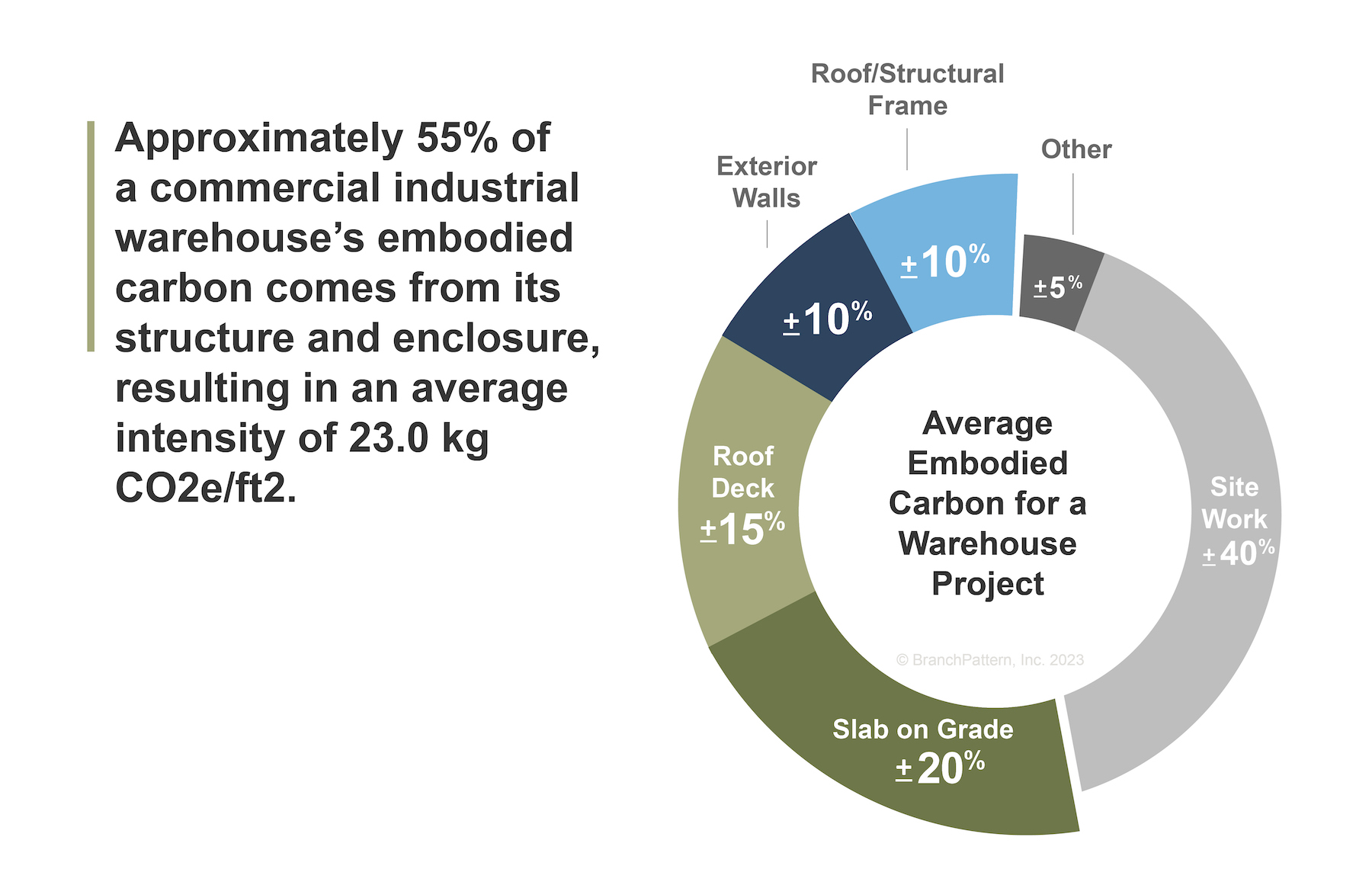
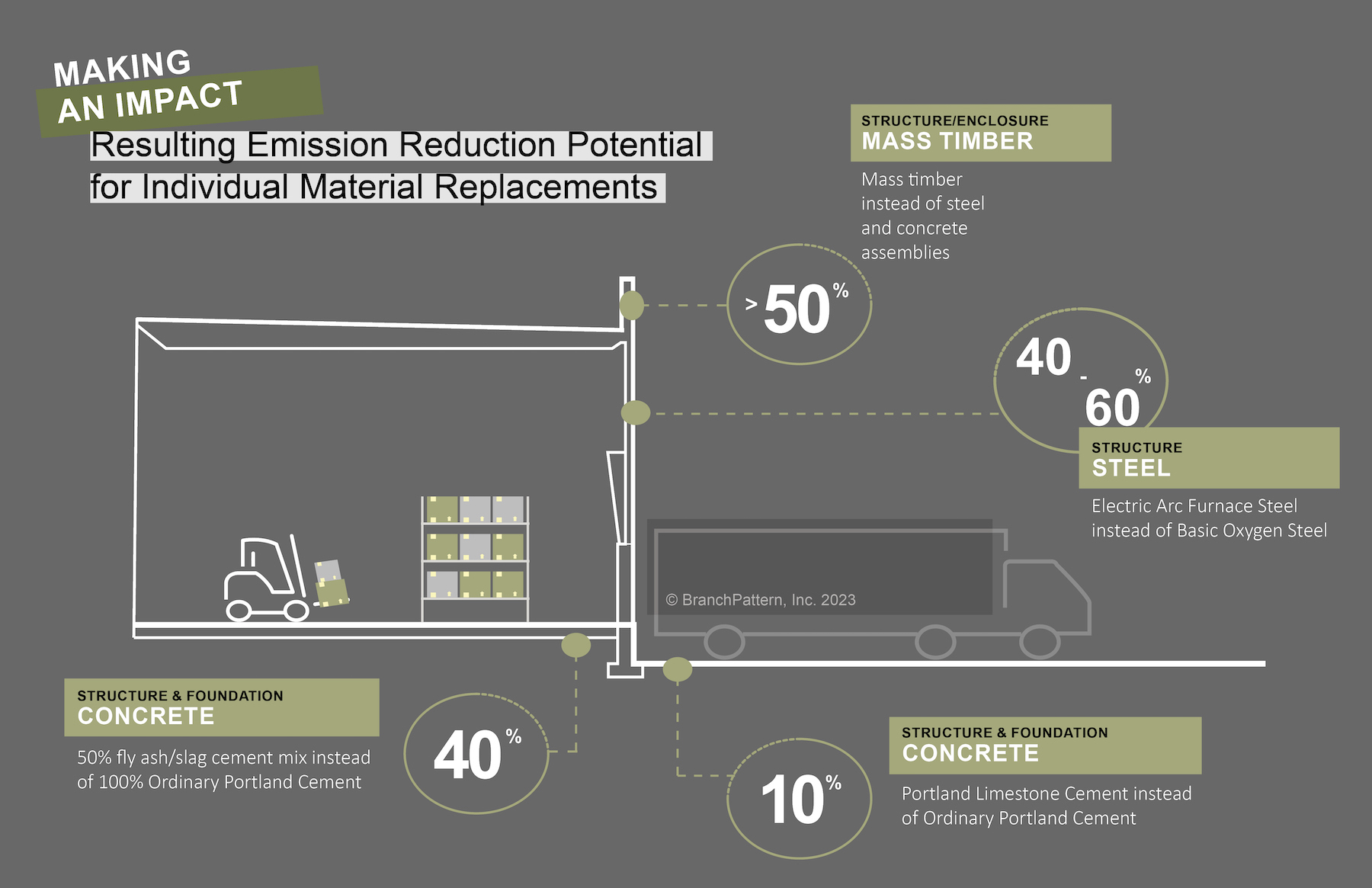
The report finds that, on average, 55% of an industrial warehouse’s EC comes from its structure and enclosure, such as slab-on-grade, exterior walls, framing, and roofdeck. Consequently, an optimal EC reduction strategy addresses emissions from building materials like concrete and steel, which alone account for 11% and 10%, respectively, of global greenhouse gas emissions. For example, cement accounts for about 80% of the carbon emissions from a traditional concrete mix. Switching that mix from 100% ordinary Portland Cement to 50% fly ash/slag cement could reduce the mix’s carbon footprint by approximately 40%.
Buildings might also be designed to reduce their overall concrete volume via alternate wall assemblies or insulated metal panels. BranchPattern’s report estimates that substituting mass timber for steel or concrete assemblies would reduce the carbon footprint from the building’s structure/enclosure by 50%. (Affinius Capital recently completed a 161,200-sf Class A warehouse with mass timber, resulting in a 60% reduction in EC compared to a concrete build.) Even using Electric Arc Furnace-produced steel instead of basic oxygen furnace-produced steel cuts EC emissions by 40% to 60%.
Electric Arc Furnace steel is more likely to have a higher recycled content. Recycled materials in general typically have lower EC than virgin materials. However, the report observes that conventional demolition is still cheaper than recovering materials, especially wood. “A building designed for disassembly may have greater residual value, as the integrity of more materials is preserved.”
A call to action
The Paris Climate Accords have set a goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions 40% by 2030, compared to 1990 emissions. To achieve that goal, “we must now focus on embodied carbon,” the BranchPattern report states. That will require transparent and clear carbon accounting methods that support stakeholder engagement. “To reduce, we must measure,” asserts the report.
Government funding and policy changes are increasing the development and implementation of low-carbon construction solutions. Green building certification programs “will continue to play a significant role mainstreaming embodied carbon knowledge within various building sectors,” the report predicts. The availability of lower-carbon materials will increase and be cost competitive. Engineering solutions in areas like carbon capture, utilization and storage will advance.
“Embodied carbon related emission reductions are possible, necessary, and promising,” the report concludes.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Construction under way on LEED Platinum DOE energy lab
Centennial, Colo.-based Haselden Construction has topped out the $64 million Research Support Facilities, located on the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) campus in Golden, Colo. Designed by RNL and Stantec to achieve LEED Platinum certification and net zero energy performance, the 218,000-sf facility will feature natural ventilation through operable ...
| Aug 11, 2010
NASA plans federal government's greenest building
NASA is set to break ground on what the agency expects to be the highest-performing building in the federal government's portfolio. Named Sustainability Base, the building at Ames Research Center in Sunnyvale, Calif., will be a showplace for sustainable technologies, featuring some of the agency's most advanced recycling and intelligent controls technologies originally developed to support NASA...
| Aug 11, 2010
Stimulus funding helps get NOAA project off the ground
The award-winning design for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s new Southwest Fisheries Science Center replacement laboratory saw its first sign of movement last month with a groundbreaking ceremony held in La Jolla, Calif. The $102 million project is funded primarily by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act.
| Aug 11, 2010
Robotic storage facility protects exotic automobiles, fine wines, artwork
Miller Construction Company, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., has completed construction on a high-tech robotic storage facility designed to store and protect valued possessions such as exotic automobiles, fine wines, artwork, and jewelry. Designed and built to resist Category 5 hurricanes, the RoboVault facility features automated storage retrieval, biometric recognition, private access with 24/7 securi...
| Aug 11, 2010
Research Facility Breaks the Mold
In the market for state-of-the-art biomedical research space in Boston's Longwood Medical Area? Good news: there are still two floors available in the Center for Life Science | Boston, a multi-tenant, speculative high-rise research building designed by Tsoi/Kobus & Associates, Boston, and developed by Lyme Properties, Hanover, N.
| Aug 11, 2010
Special Recognition: Triple Bridge Gateway, Port Authority Bus Terminal New York, N.Y.
Judges saw the Triple Bridge Gateway in Midtown Manhattan as more art installation than building project, but they were impressed at how the illuminated ramps and bridges—14 years in the making—turned an ugly intersection into something beautiful. The three bridges span 9th Avenue at the juncture where vehicles emerge from the Lincoln Tunnel heading to the Port Authority of New Yor...
| Aug 11, 2010
American Tobacco Project: Turning over a new leaf
As part of a major revitalization of downtown Durham, N.C., locally based Capitol Broadcasting Company decided to transform the American Tobacco Company's derelict 16-acre industrial plant, which symbolized the city for more than a century, into a lively and attractive mixed-use development. Although tearing down and rebuilding the property would have made more economic sense, the greater goal ...







