The negative impact of the coronavirus is expected to result in nonresidential construction declining by 10% to 15% this year. That decline is also expected to lower construction costs by 2% to 5%.
Those are some of the predictions in JLL’s Construction Outlook for the second half of 2020. This report includes a section that specifically evaluates the impact of the pandemic on construction. JLL found that 93% of ongoing construction work had been in jurisdictions with stay-at-home orders that covered most of the U.S. population and jobsites.

JLL's recovery timeline for the construction industry.
More than one-quarter—26%—of construction work was in the seven states that had issued shutdown orders whose average length was 41 days. Construction in locations with shutdowns had temporarily dropped by an average of 70%. There was also decreased demand for new projects in sectors closed by COVID-19, like retail, entertainment, and offices.
The most expensive impact for most projects was schedule changes required to comply with physical distancing rules, which are expected to remain a concern through the remainder of 2020. While careful scheduling and additional shifts can alleviate some of the bottlenecks, extended schedules are still commonplace.
Not surprisingly, construction ranked third among the industries that received loans through the federal government’s Paycheck Protection Program, with Small Business Administration data showing that over $63 billion was provided to construction firms through June 12.
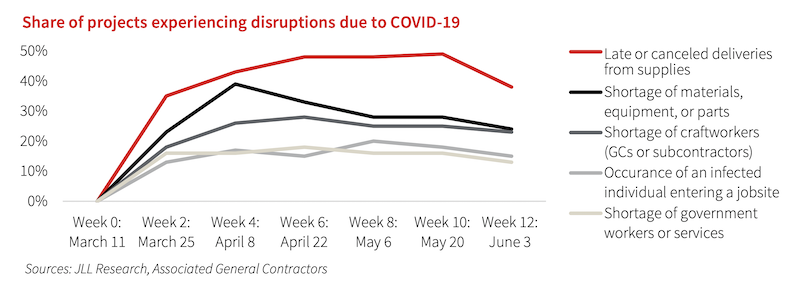
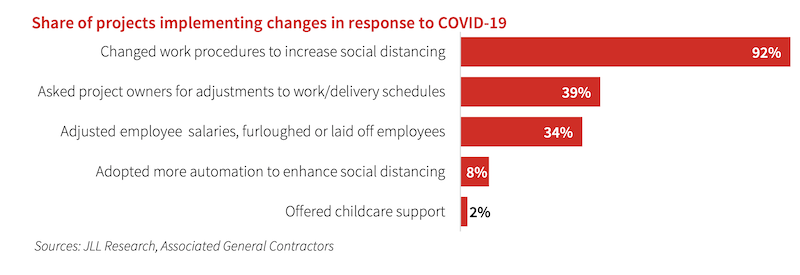
Jobsites struggled with social distancing and procurement during the pandemic.
EMPLOYMENT SANK TO ITS NADIR
That money was needed desperately, as the construction sector in April incurred its largest one-month increase in unemployment ever recorded, jumping above 16% and spread across all sectors and job types. A quick bounce-back in employment was a positive development in May and June, with almost half of the jobs lost in the prior two months recovered. Still, while the labor situation was steadier by early July than during the initial impacts of the pandemic, it remained in much worse condition than at any point in the last seven years.
Construction employment levels are expected to be down 5% to 10% for the year, which JLL thinks will drive down average construction costs for the first time since 2010.
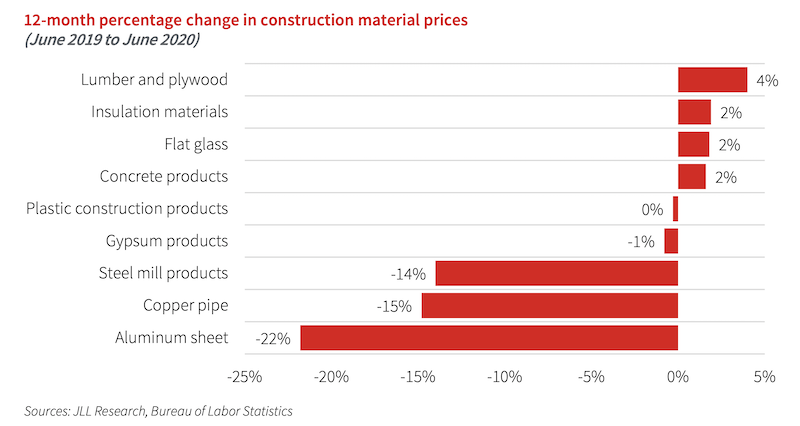
Average construction material prices are expected to begin to rebound in the second half of the year, and materials prices at the end of 2020 are expected to be higher than they are today. However, overall construction material prices will remain lower in 2020 than they were in 2019, before the pandemic led to the initial crash.
One silver lining to the weaker labor market has been an easing of the labor shortage that gripped construction over the last five years. The share of contractors reporting difficulty finding skilled workers has fallen to 46% in the second quarter, compared to 61% a year ago.
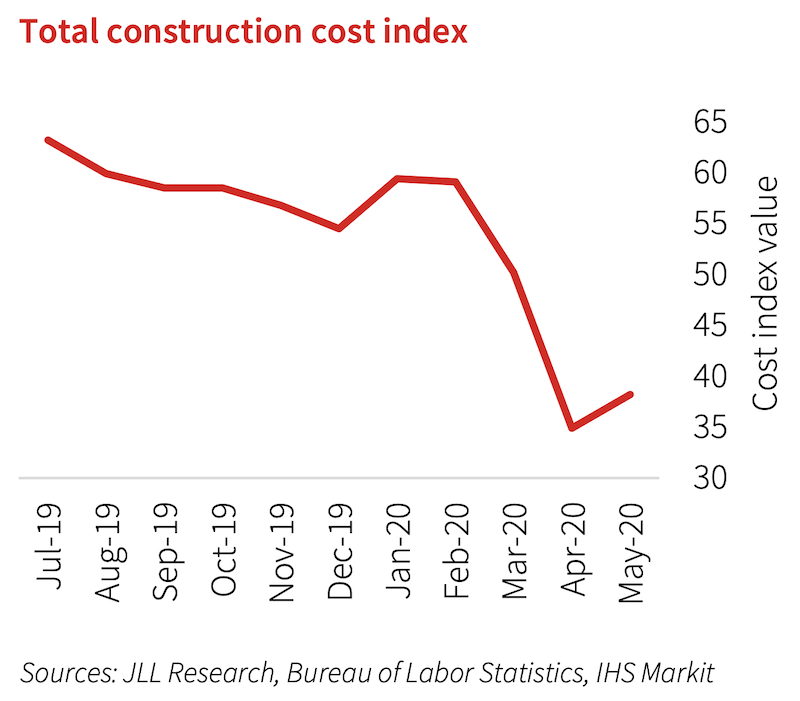
Construction costs are expected to fall for the first time in a decade.
Construction stats are expected to stabilize and remain relatively flat (within plus or minus 5% growth) from Q3 2020 to Q3 2021. The decline in costs will partially be a factor of flat labor costs and temporarily lower materials prices. However, the primary driver for lower costs will be more aggressive bidding. Longer term (Q3 2021 – Q2 2022), the overall industry is expected to shift back to between 2% and 4% growth, with spending, employment, backlog, and costs all rising.
SIX FACTORS THAT COULD IMPACT 2021
JLL’s report offers six forecasts that it believes will reshape the industry into next year:
•These start with the prediction that COVID-19 will continue to challenge construction operations for the rest of this year, and the risk of renewed shutdowns remains possible.
•JLL cites a recent survey by the National League of Cities which found that 65% of cities have already canceled or delayed capital expenditures for infrastructure investments, due to budget shortfalls. Therefore, cutbacks in state and local budgets will create a major risk for construction, especially since public spending had been the primary growth driver over the past two years.
•Since July, U.S. Senate has had the Moving Forward Act, which the House of Representatives already passed. This large-scale infrastructure investment bill, if enacted, would funnel more than $1.5 trillion to roads, schools, hospitals and other public sector projects. JLL states that the upcoming 2020 election creates political risk and uncertainty, with the potential for both positive and negative outcomes for construction regardless of which party wins.
•Construction confidence will remain negative through the end of the year, even as the difference in sentiment between sectors will be even wider than it was pre-pandemic. One change to note is the large drop in sentiment for the hospitals and healthcare sector, which reflects the longer-term challenges in that industry due to the pandemic.
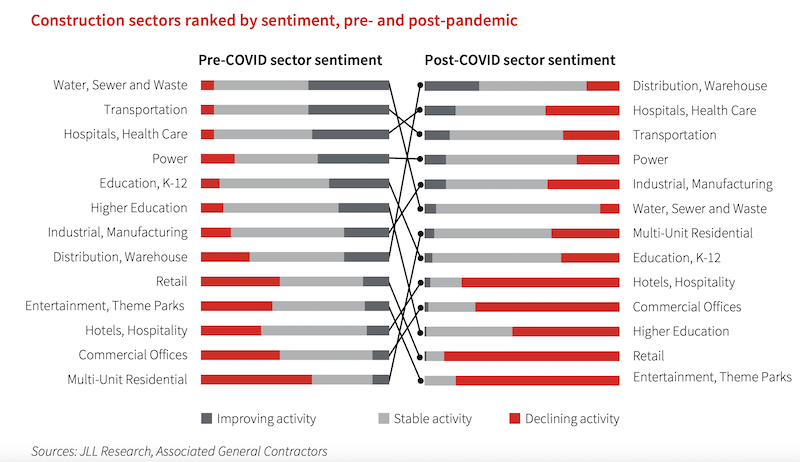
Construction sentiment about the future could take a while to recover.
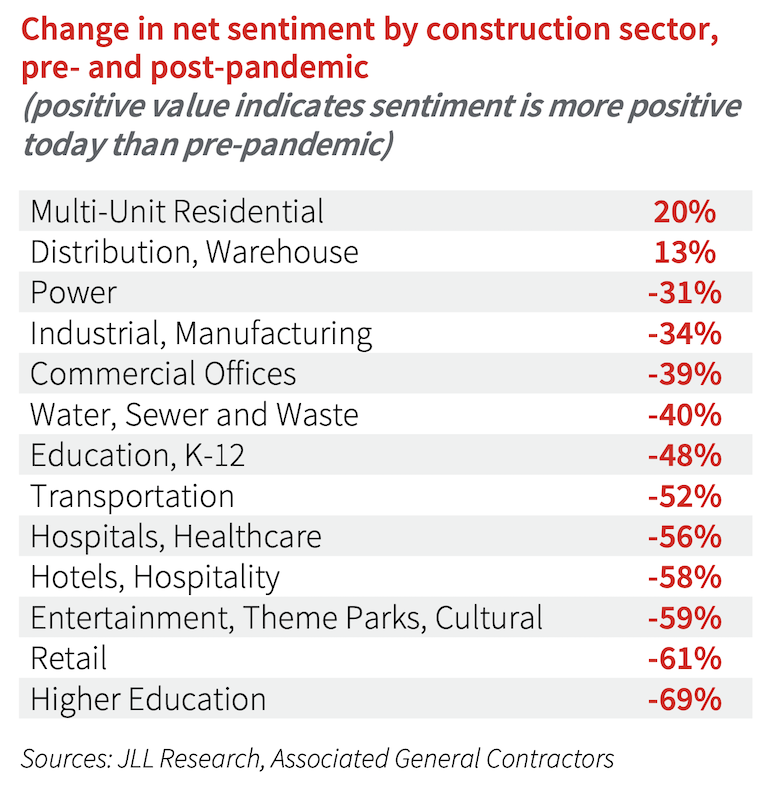
•In addition, long-term construction sentiment is positive for the first time since 2014, and optimism for growth in 2022– 2025 will remain much higher than it was before the coronavirus recession. The share of architecture firms that expect industry prospects to improve in three years jumped to 67% in a recent survey, up from 20% in the fourth quarter of 2019, before the pandemic. For general contractors, sentiment that the industry will improve now stands at 62%, up from 10% at the end of last year.
•The pandemic is leading to a permanent and industry-wide embrace of construction technology. “New health and safety requirements created a whole new class of problems for technology to solve, from health monitoring to contact tracing. An already burgeoning construction tech industry saw a jump in immediate demand,” writes Henry D’Esposito, the report’s author and JLL Americas Research’s Construction Research Lead.
Some of the sectors of construction tech expected to benefit the most will be digital collaboration tools, construction wearables, and offsite construction methods, which should provide both immediate benefits in the coronavirus environment and consistent payoffs once the pandemic is resolved.
Related Stories
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
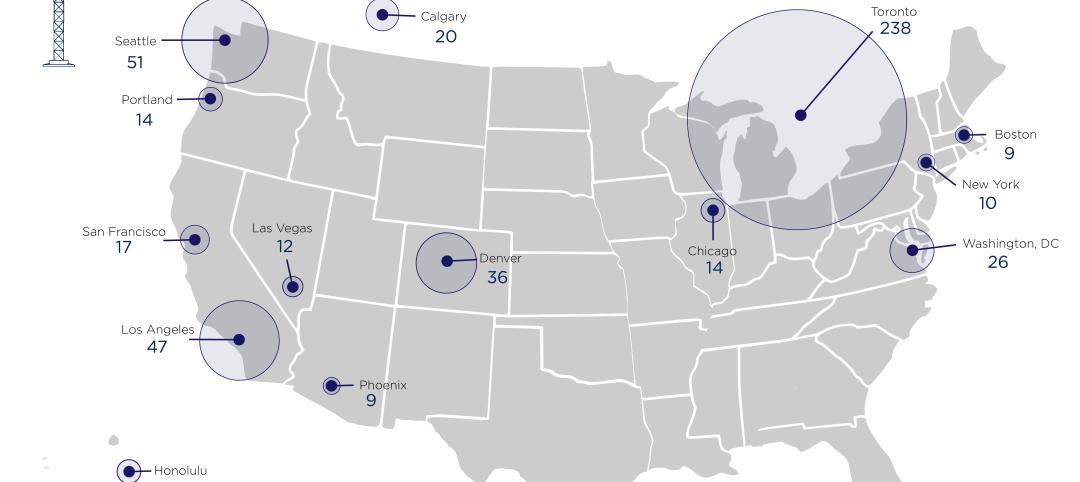
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
Contractors | Apr 11, 2023
The average U.S. contractor has 8.7 months worth of construction work in the pipeline, as of March 2023
Associated Builders and Contractors reported that its Construction Backlog Indicator declined to 8.7 months in March, according to an ABC member survey conducted March 20 to April 3. The reading is 0.4 months higher than in March 2022.
Market Data | Apr 6, 2023
JLL’s 2023 Construction Outlook foresees growth tempered by cost increases
The easing of supply chain snags for some product categories, and the dispensing with global COVID measures, have returned the North American construction sector to a sense of normal. However, that return is proving to be complicated, with the construction industry remaining exceptionally busy at a time when labor and materials cost inflation continues to put pricing pressure on projects, leading to caution in anticipation of a possible downturn. That’s the prognosis of JLL’s just-released 2023 U.S. and Canada Construction Outlook.
Market Data | Apr 4, 2023
Nonresidential construction spending up 0.4% in February 2023
National nonresidential construction spending increased 0.4% in February, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data published by the U.S. Census Bureau. On a seasonally adjusted annualized basis, nonresidential spending totaled $982.2 billion for the month, up 16.8% from the previous year.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 24, 2023
Average size of new apartments dropped sharply in 2022
The average size of new apartments in 2022 dropped sharply in 2022, as tracked by RentCafe. Across the U.S., the average new apartment size was 887 sf, down 30 sf from 2021, which was the largest year-over-year decrease.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 14, 2023
Multifamily housing rent rates remain flat in February 2023
Multifamily housing asking rents remained the same for a second straight month in February 2023, at a national average rate of $1,702, according to the new National Multifamily Report from Yardi Matrix. As the economy continues to adjust in the post-pandemic period, year-over-year growth continued its ongoing decline.
Contractors | Mar 14, 2023
The average U.S. contractor has 9.2 months worth of construction work in the pipeline, as of February 2023
Associated Builders and Contractors reported today that its Construction Backlog Indicator increased to 9.2 months in February, according to an ABC member survey conducted Feb. 20 to March 6. The reading is 1.2 months higher than in February 2022.
Industry Research | Mar 9, 2023
Construction labor gap worsens amid more funding for new infrastructure, commercial projects
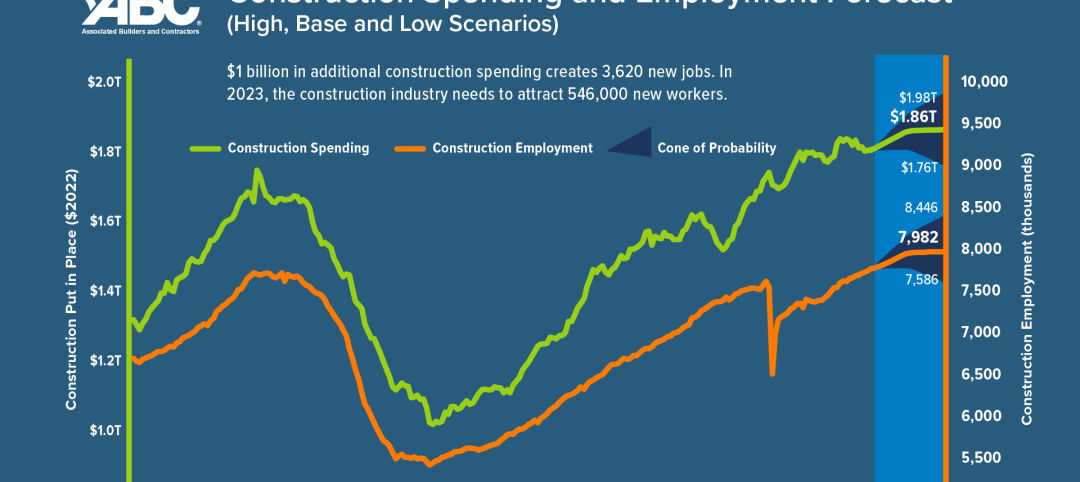
The U.S. construction industry needs to attract an estimated 546,000 additional workers on top of the normal pace of hiring in 2023 to meet demand for labor, according to a model developed by Associated Builders and Contractors. The construction industry averaged more than 390,000 job openings per month in 2022.
Market Data | Mar 7, 2023
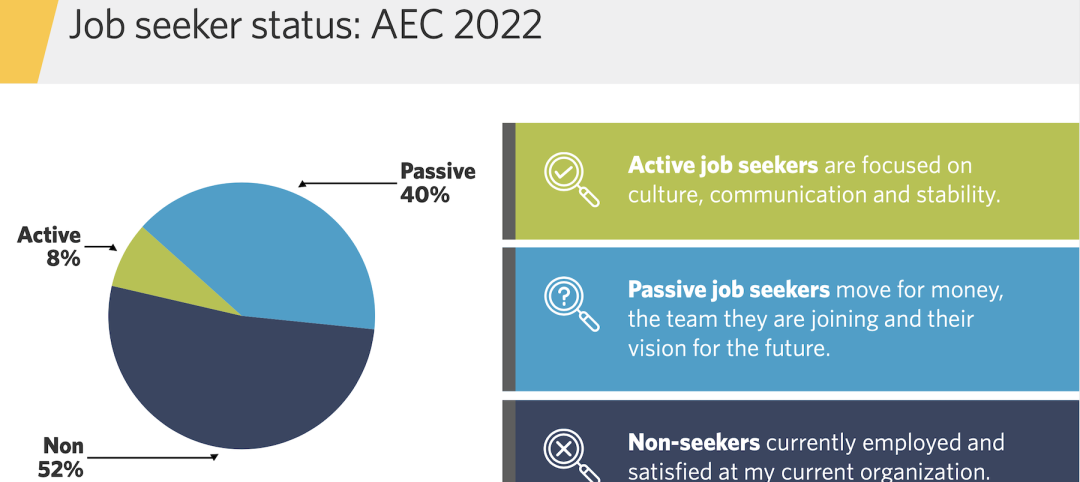
AEC employees are staying with firms that invest in their brand
Hinge Marketing’s latest survey explores workers’ reasons for leaving, and offers strategies to keep them in the fold.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 21, 2023
Multifamily housing investors favoring properties in the Sun Belt
Multifamily housing investors are gravitating toward Sun Belt markets with strong job and population growth, according to new research from Yardi Matrix. Despite a sharp second-half slowdown, last year’s nationwide $187 billion transaction volume was the second-highest annual total ever.