Since 1985, there have been well over 400 studies conducted that have dissected how key design elements impact commercial buildings and their occupants. That body of research has quantified how high-performance buildings reduce energy and maintenance costs and increase asset values. (Buildings consume 40% of the energy in the U.S. and European Union, and nearly 14% of potable water use.) Newer research has tracked on how high-performance buildings can improve their occupants’ work habits and health.
But there’s been scant analysis of whether upfront investments in high-performance buildings translate into stronger long-term profits for the companies in them.
stok, a global real-estate service provider, released a report that outlines the financial benefits to owner-occupants and tenants that invest in high-performance buildings. The report assumes that these buildings benefit their occupants, and concludes from its analysis that these benefits can produce significant positive impacts on a company’s bottom line.
stok concedes some limitations in its methodology: that productivity is difficult to measure; that there’s little data available to assess employee retention patterns in association with high-performance buildings; and that cost baselines vary markedly by location. stok also laments that, regardless of methodology, there has yet to be a real-world case study that baselines all the metrics listed in its report and compares them to an occupant moving into a high-performance building. “For a comprehensive study to occur, an organization's human resources, finance and accounting, IT, management, and others would all need to work together and transparently share resources and data.”
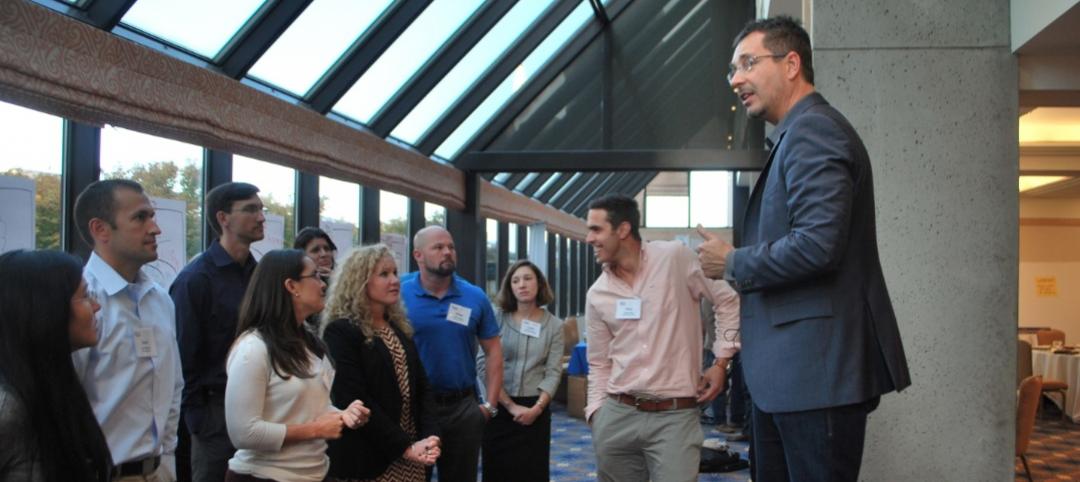
Businesses can reap significant cost savings and stronger earnings from working out of a high-performance building. Image: Stōk
Nevertheless, the report infers that the proposition about how much a company can benefit from working in a high-performance building now supersedes questions about how much that building costs either to construct or retrofit.
“Rather than focusing on the lowest costs possible, owner-occupants and tenants should shift their perspective to the long-term opportunities of high-performance buildings,” the report states. If more than 80% of a company’s value is based on its people, “shouldn't buildings be designed to optimize their performance and wellness?”
Most people work in buildings that were not designed to support their well-being. And multiple reports show that only between 1% and 4% of a building’s total cost goes toward its initial design and construction.
High-performance buildings, on the other hand, share certain traits, says stōk. They enhance the occupant experience and improve human health and wellness, optimize resource efficiency, minimize environmental impacts from design to demolition, increase resiliency, and deliver a higher financial return than traditional buildings of the same use type.
stok’s report applies financial impact calculations to the findings from 60-plus research studies on the effects of high-performance buildings in three key areas: productivity, retention, and wellness.
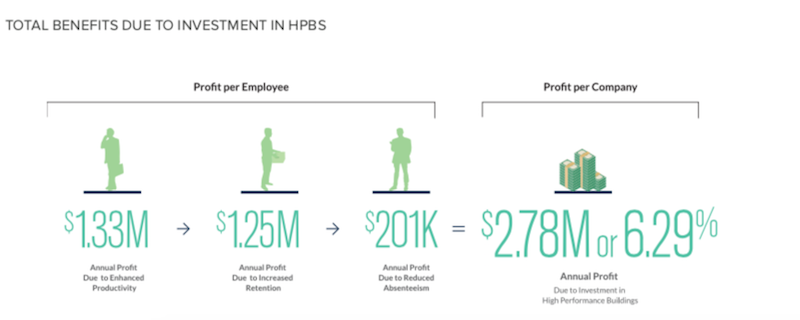
The report’s calculations assume a hypothetical company with 820 employees that occupies 150,000 sf in the building, or 183 sf per worker. This hypothetical company’s baseline annual revenue is $540,000 per employee who works 265 days per year and whose salary averages $100,000. The hypothetical company’s baseline profit margin is 10%.
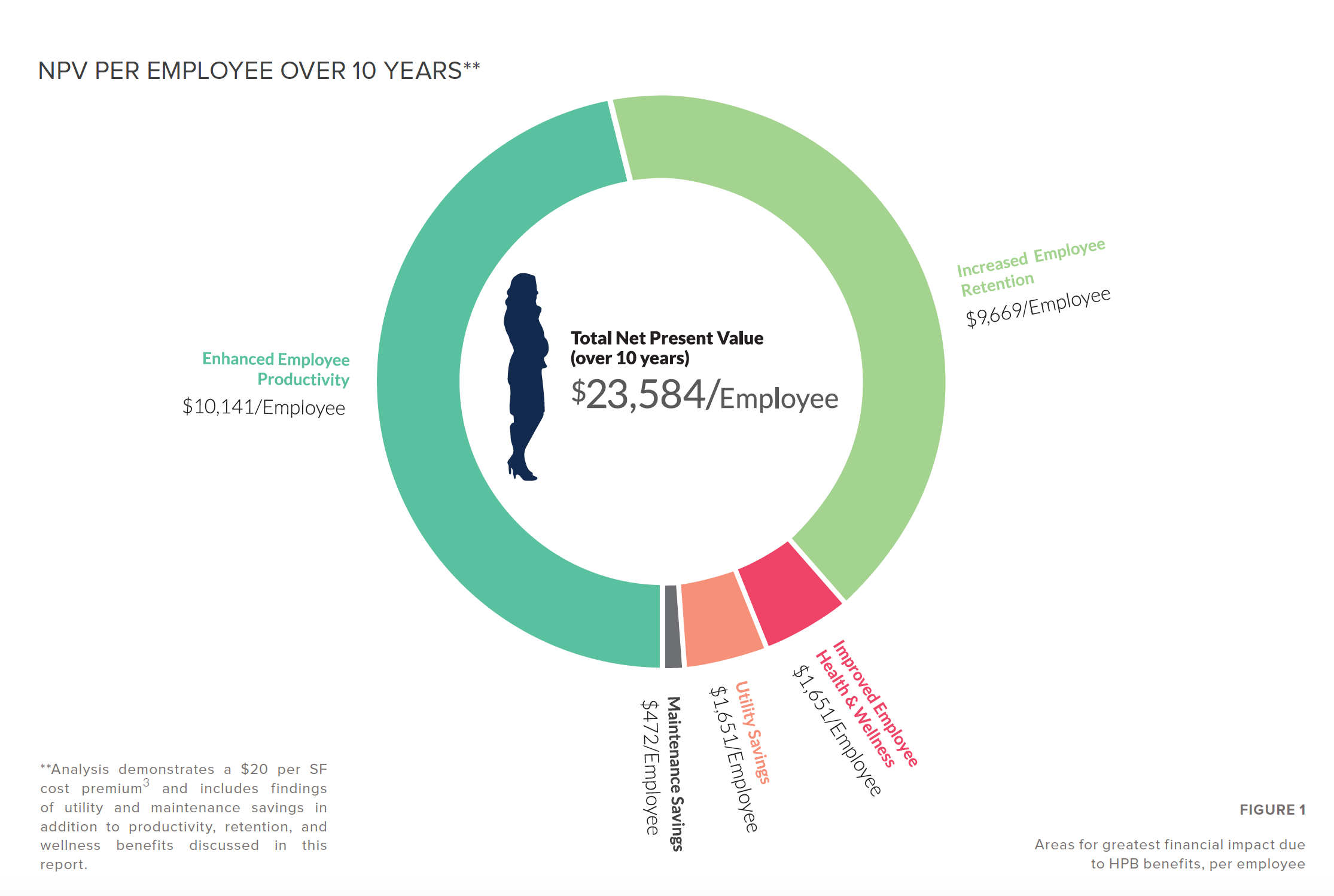
The results of stok’s math—which also assumes a $20 per sf premium for construction costs—show that companies occupying high-performance buildings gain a median $3,395 in annual profit per employee, or $18.56 per sf. Over a 10-year period, this works out to a “Net Present Value” of $21,172 in profit gain per employee, or $115 per sf. The combined total benefit equals $2.78 million in annual profit gain, or 6.29% of a company’s annual earnings.
And these calculations only measure the gains related to productivity, employee retention, and wellness; when cost savings for utilities and maintenance are factored in, companies would realize a $23,584 profit gain per employee, or $129 per sf, over a decade.
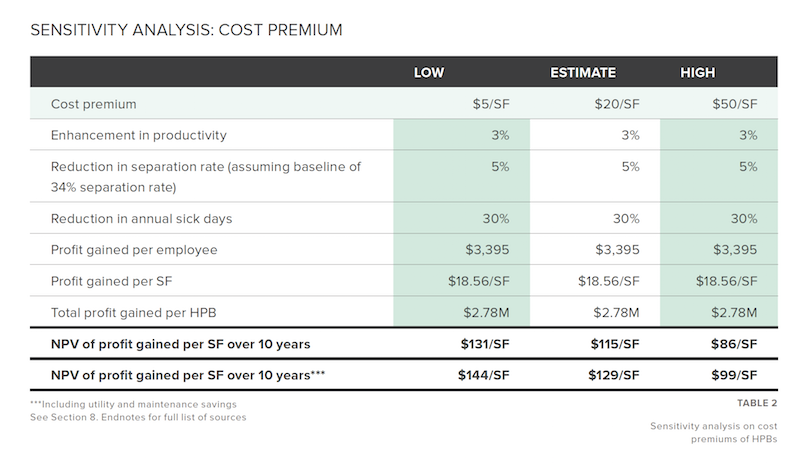
Assuming different construction premium levels, Stōk breaks down the profit gains by productivity, employee retention, and wellness. Image: Stōk
The report's calculations assume that its hypothetical company undergoes a 34% annual “separation rate” where employees leave voluntarily. Empty desks cost companies anywhere from 90% to 200% of an employee’s annual salary. And at a time when businesses are competing fiercely for talent, high-performance buildings can be powerful recruiting and retention tools, says stōk.
A building that promotes wellness, too, can help companies attract and keep employees. Based on research it has analyzed, stōk finds that 69% of employers offer wellness promotions, 67% of U.S. building owners are interested in creating healthier buildings for people, 91% of employers offer health and wellness programs for reasons beyond medical cost savings, and 73% of employers believe their responsibility to ensure the health and wellness of their employees will increase over the next few years.
The report sees the value of investing in high-performance buildings from minimizing employee absenteeism.
The report projects that 41% to 48% of new construction going forward will be high-performance buildings, which should provide the flexibility these properties need to adapt to changing tenant requirements by offering modular systems, personal environment controls, and multi-use spaces.
And for those companies and developers that still insist on gauging a building’s investment value by its projected energy and operational savings, the ROI in high-performance buildings remains provable. stok cites the General Services Administration, which estimates that energy costs for traditional sustainable buildings are 28% lower than the national average. When retrofitting a building with the types of improvements associated with high performance, energy costs would be cut by 50%, with maintenance savings being reduced by approximately 12% of the national average.
Related Stories
| Oct 21, 2013
ASHRAE/IES publish 2013 Energy Standard
Major changes to requirements regarding building envelope, lighting, mechanical and the energy cost budget are contained in the newly published energy standard from ASHRAE and IES. ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2013, Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings, incorporates 110 addenda, reflecting changes made through the public review process.
| Oct 18, 2013
Meet the winners of BD+C's $5,000 Vision U40 Competition
Fifteen teams competed last week in the first annual Vision U40 Competition at BD+C's Under 40 Leadership Summit in San Francisco. Here are the five winning teams, including the $3,000 grand prize honorees.
| Oct 18, 2013
Cities may be more capable of driving sustainability than nations, experts say
With countries not tackling climate change aggressively, cities are in the best position to drive increased sustainability.
| Oct 15, 2013
15 great ideas from the Under 40 Leadership Summit – Vote for your favorite!
Sixty-five up-and-coming AEC stars presented their big ideas for solving pressing social, economic, technical, and cultural problems related to the built environment. Which one is your favorite?
| Oct 4, 2013
Sydney to get world's tallest 'living' façade
The One Central Park Tower development consists of two, 380-foot-tall towers covered in a series of living walls and vertical gardens that will extend the full height of the buildings.
| Sep 27, 2013
NYC releases first year-to-year energy performance data on commercial properties
A new report provides information on energy performance of New York City's largest buildings (mostly commercial, multi-family residential). It provides an analysis of 2011 data from city-required energy “benchmarking”—or the tracking and comparison of energy performance—in more than 24,000 buildings that are over 50,000 square feet.
| Sep 27, 2013
ASHRAE/IES publish first standard focused on commissioning process
ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 202, Commissioning Process for Buildings and Systems, identifies the minimum acceptable commissioning process for buildings and systems as described in ASHRAE’s Guideline 0-2005, The Commissioning Process. Standard 202 is ASHRAE’s first standard focused on the commissioning process.
| Sep 26, 2013
Sheep's wool insulation, bio-brick among Cradle to Cradle product innovation finalists
Ten finalists are competing for $250,000 in prizes from the Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute and Make It Right.
| Sep 26, 2013
Literature review affirms benefits of daylighting, architectural glazing
The use of glass as a building material positively impacts learning, healing, productivity and well-being, according to a white paper published by Guardian Industries and the University of Michigan Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning. The findings highlight the significant influence daylighting and outside views have on employees, workers, students, consumers and patients.
| Sep 19, 2013
What we can learn from the world’s greenest buildings
Renowned green building author, Jerry Yudelson, offers five valuable lessons for designers, contractors, and building owners, based on a study of 55 high-performance projects from around the world.