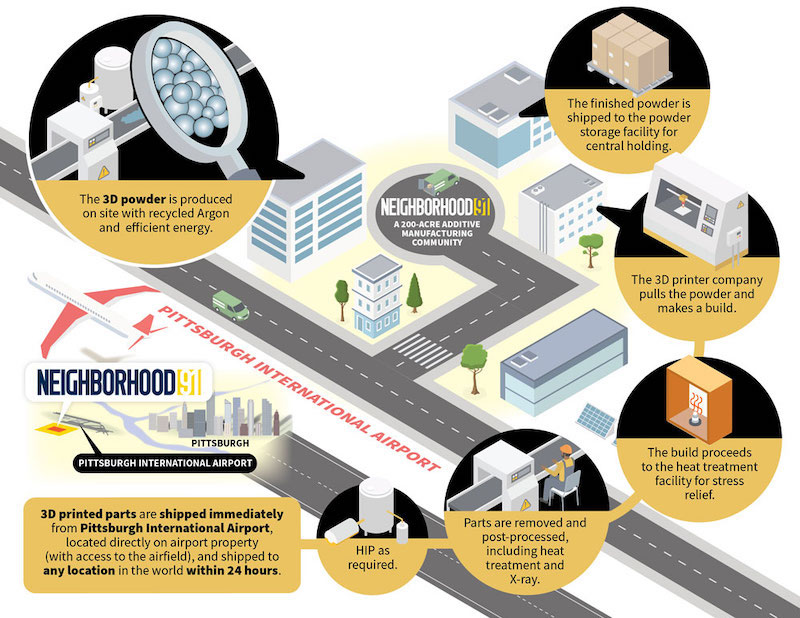
Late last month, the Allegheny County Airport Authority revealed that its 195-acre Pittsburgh Airport Innovation Center, known locally as Neighborhood 91, would focus on additive manufacturing (AM).
The Authority and the state of Pennsylvania have invested $22 million in the initial development of Neighborhood 91, which is being positioned as the first innovation campus in the nation to condense and connect all of the supply-chain components of 3D printing and additive manufacturing.
Neighborhood 91—so named because it will be Pittburgh’s 91st distinct neighborhood—is located near two major highways, 18 railways, and the largest inland port in the U.S. It also sits atop the Marcellus Shale, potentially the second-largest natural gas field.
The first 24 acres of Neighborhood 91 have been cleared, and infrastructure and utilities installed. (MS Consultants was involved in the land preparation design.) David Storer, the Authority’s director of business development, tells BD+C that the first phase would include multiple buildings that total between 150,000 and 200,000 sf. He says that there could be six or seven buildings ranging from 15,000 to 35,000 sf each, or fewer, larger buildings. “It’s up to the tenants,” he explains, which will be signing ground leases spanning from 30 to 50 years.
The tenants will also choose their own teams to design, engineer, and construct the buildings within the campus, as well as their equipment suppliers. Storer adds that it’s possible, in later phases, that the Authority would work with a master developer. The buildout of Neighborhood 91 is expected to be three to five years. The completed Airport Innovation Center is expected to create 1,000 permanent jobs.
Barnes Group Advisors, a specialist in AM, serves as the project’s strategic development consultant.
The Pittsburgh Airport Innovation Center will be a complete end-to-end ecosystem that provides material storage, areas for testing and analysis, a supply and recycling system all tenant companies can tap into, and access to the microgrid that will help reduce their operating costs. Its proximity to the airport and other transportation modes should also reduce shipping and receiving costs, and shorten lead times by as much as 80%. (The availability of on-site noble gases could be attractive to prospective additive manufacturers for which up to 60% of their manufacturing costs are related to gas expense.)
“This is something that isn’t happening elsewhere, and we are excited to be the foundation upon which the Neighborhood is built,” says Storer.
See Also: Steely resolve: Carnegie Mellon University fuels Pittsburgh's post-industrial reinvention
Neighborhood 91’s first tenant is Arencibia, an Allentown, Pa.-based supplier and recycler of noble gas, which is used to provide an inert environment for metal manufacturing and 3D printing. Arencibia, which operates 14 facilities, is also a partner in this campus project, as it will be supplying argon gas to the Innovation Center’s other tenants.
Its president and CEO, Joseph Arencibia, says his company’s recycling contract agreements typically are for 15-year terms. As for site construction on the campus, he says his company hasn’t chosen its Building Team yet. He explains that most of the space his company needs at Neighborhood 91 will be for a gas-recycling process plant whose footprint will be between 3,000 and 5,000 sf on a concrete pad. Beyond that, Arencibia will have building space of around 2,000 sf to house its offices, control room, spare parts, etc.
Storer, the Authority’s business development director, says that Neighborhood 91 can be seen as a modern continuation of Pittsburgh’s “historic strength” in manufacturing. It also takes advantage of Pittsburgh’s academic resources, as the University of Pittsburgh has agreed to help guide this project and to provide research power in engineering and AM. Pitt Chancellor Patrick Gallagher was instrumental in moving the Innovation Center forward.
Storer sees the campus as a “continuum” with Hazelwood Green, the 178-acre redevelopment of abandoned steel mills into a 264,000-sf R&D mecca for robotics, AI, and other cutting-edge technologies.
Neighborhood 91 is the latest innovation from the Allegheny County Airport Authority. Its collaboration with researchers at Carnegie Mellon University resulted in the creation of the NavCog app to help vision-impaired travelers navigate airports. The Authority’s partnership with the tech firm Zensors helped create an AI-powered system that estimates TSA wait times to an accuracy unmatched in the airport industry.
Related Stories
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.
Student Housing | Mar 13, 2023
University of Oklahoma, Missouri S&T add storm-safe spaces in student housing buildings for tornado protection
More universities are incorporating reinforced rooms in student housing designs to provide an extra layer of protection for students. Storm shelters have been included in recent KWK Architects-designed university projects in the Great Plains where there is a high incidence of tornadoes. Projects include Headington and Dunham Residential Colleges at the University of Oklahoma and the University Commons residential complex at Missouri S&T.
AEC Innovators | Mar 3, 2023
Meet BD+C's 2023 AEC Innovators
More than ever, AEC firms and their suppliers are wedding innovation with corporate responsibility. How they are addressing climate change usually gets the headlines. But as the following articles in our AEC Innovators package chronicle, companies are attempting to make an impact as well on the integrity of their supply chains, the reduction of construction waste, and answering calls for more affordable housing and homeless shelters. As often as not, these companies are partnering with municipalities and nonprofit interest groups to help guide their production.
Modular Building | Mar 3, 2023
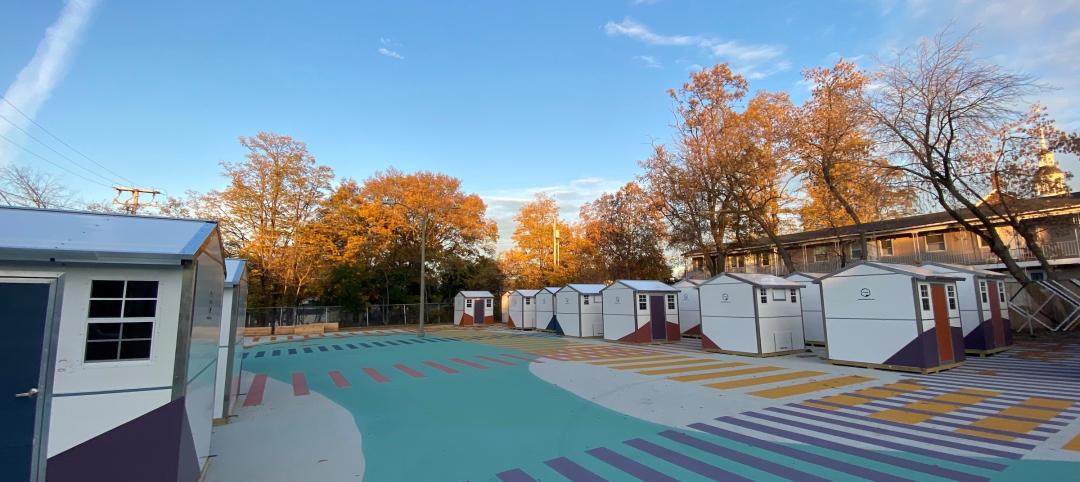
Pallet Shelter is fighting homelessness, one person and modular pod at a time
Everett, Wash.-based Pallet Inc. helped the City of Burlington, Vt., turn a municipal parking lot into an emergency shelter community, complete with 30 modular “sleeping cabins” for the homeless.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 1, 2023
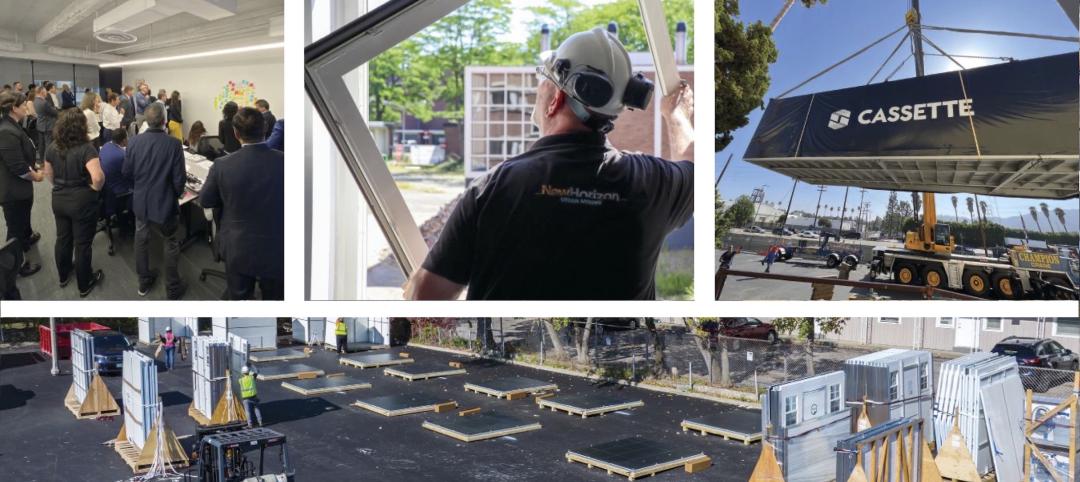
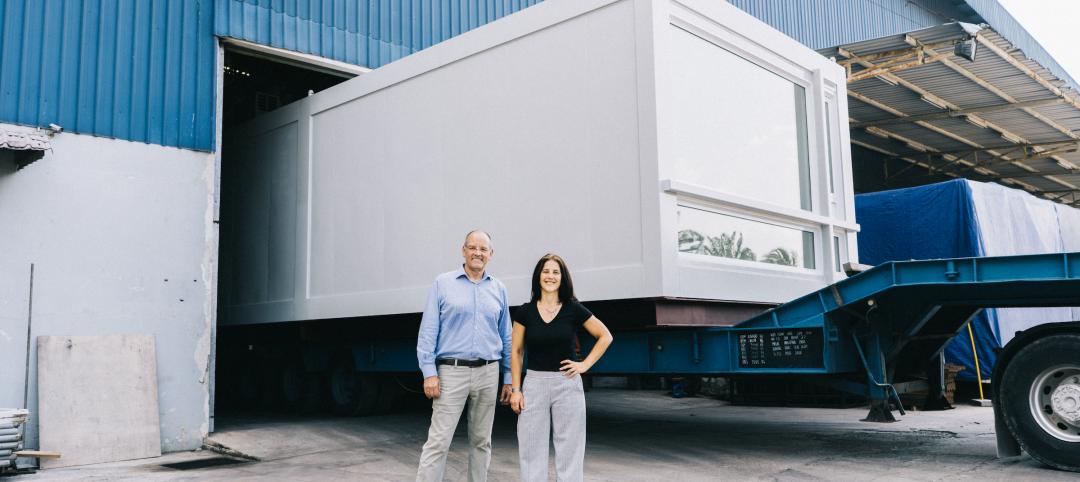
Multifamily construction startup Cassette takes a different approach to modular building
Prefabricated modular design and construction have made notable inroads into such sectors as industrial, residential, hospitality and, more recently, office and healthcare. But Dafna Kaplan thinks that what’s held back the modular building industry from even greater market penetration has been suppliers’ insistence that they do everything: design, manufacture, logistics, land prep, assembly, even onsite construction. Kaplan is CEO and Founder of Cassette, a Los Angeles-based modular building startup.
Sustainability | Feb 8, 2023
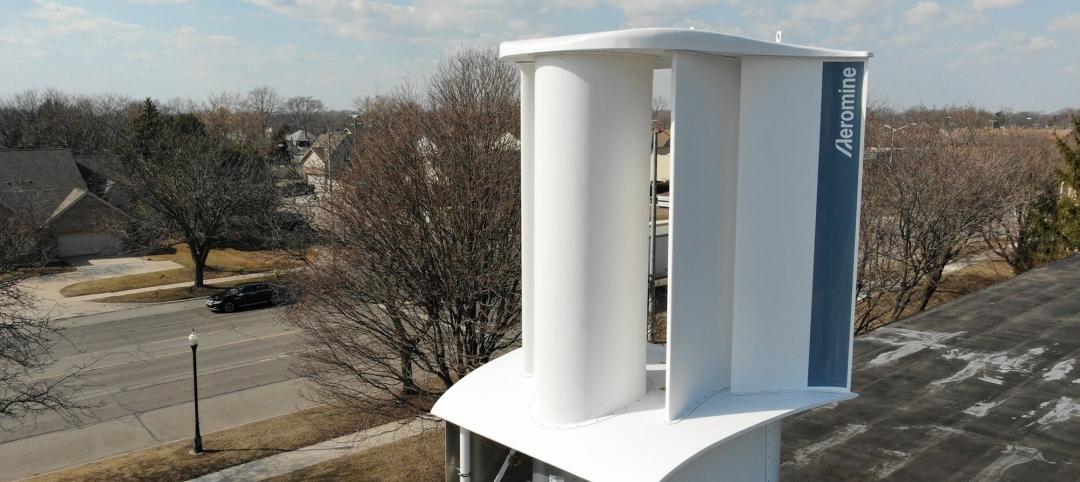
A wind energy system—without the blades—can be placed on commercial building rooftops
Aeromine Technologies’ bladeless system captures and amplifies a building’s airflow like airfoils on a race car.