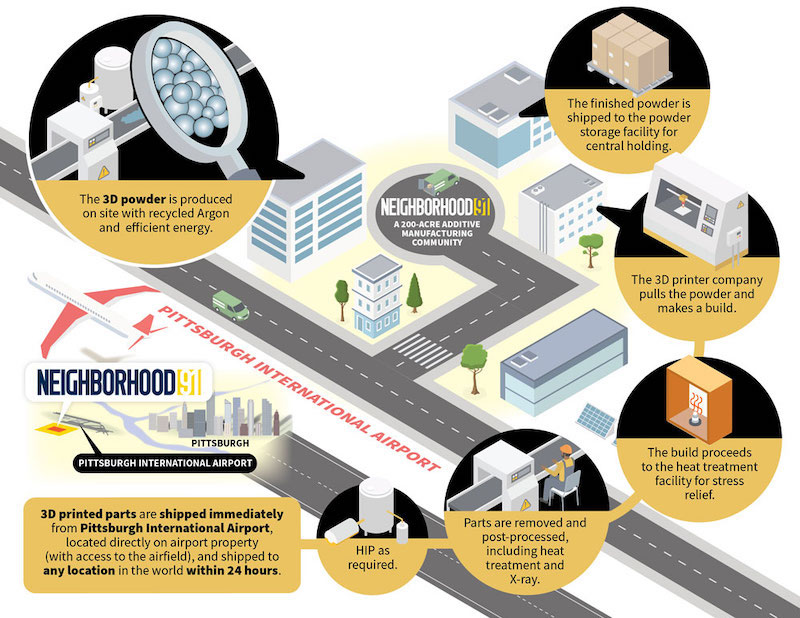
Late last month, the Allegheny County Airport Authority revealed that its 195-acre Pittsburgh Airport Innovation Center, known locally as Neighborhood 91, would focus on additive manufacturing (AM).
The Authority and the state of Pennsylvania have invested $22 million in the initial development of Neighborhood 91, which is being positioned as the first innovation campus in the nation to condense and connect all of the supply-chain components of 3D printing and additive manufacturing.
Neighborhood 91—so named because it will be Pittburgh’s 91st distinct neighborhood—is located near two major highways, 18 railways, and the largest inland port in the U.S. It also sits atop the Marcellus Shale, potentially the second-largest natural gas field.
The first 24 acres of Neighborhood 91 have been cleared, and infrastructure and utilities installed. (MS Consultants was involved in the land preparation design.) David Storer, the Authority’s director of business development, tells BD+C that the first phase would include multiple buildings that total between 150,000 and 200,000 sf. He says that there could be six or seven buildings ranging from 15,000 to 35,000 sf each, or fewer, larger buildings. “It’s up to the tenants,” he explains, which will be signing ground leases spanning from 30 to 50 years.
The tenants will also choose their own teams to design, engineer, and construct the buildings within the campus, as well as their equipment suppliers. Storer adds that it’s possible, in later phases, that the Authority would work with a master developer. The buildout of Neighborhood 91 is expected to be three to five years. The completed Airport Innovation Center is expected to create 1,000 permanent jobs.
Barnes Group Advisors, a specialist in AM, serves as the project’s strategic development consultant.
The Pittsburgh Airport Innovation Center will be a complete end-to-end ecosystem that provides material storage, areas for testing and analysis, a supply and recycling system all tenant companies can tap into, and access to the microgrid that will help reduce their operating costs. Its proximity to the airport and other transportation modes should also reduce shipping and receiving costs, and shorten lead times by as much as 80%. (The availability of on-site noble gases could be attractive to prospective additive manufacturers for which up to 60% of their manufacturing costs are related to gas expense.)
“This is something that isn’t happening elsewhere, and we are excited to be the foundation upon which the Neighborhood is built,” says Storer.
See Also: Steely resolve: Carnegie Mellon University fuels Pittsburgh's post-industrial reinvention
Neighborhood 91’s first tenant is Arencibia, an Allentown, Pa.-based supplier and recycler of noble gas, which is used to provide an inert environment for metal manufacturing and 3D printing. Arencibia, which operates 14 facilities, is also a partner in this campus project, as it will be supplying argon gas to the Innovation Center’s other tenants.
Its president and CEO, Joseph Arencibia, says his company’s recycling contract agreements typically are for 15-year terms. As for site construction on the campus, he says his company hasn’t chosen its Building Team yet. He explains that most of the space his company needs at Neighborhood 91 will be for a gas-recycling process plant whose footprint will be between 3,000 and 5,000 sf on a concrete pad. Beyond that, Arencibia will have building space of around 2,000 sf to house its offices, control room, spare parts, etc.
Storer, the Authority’s business development director, says that Neighborhood 91 can be seen as a modern continuation of Pittsburgh’s “historic strength” in manufacturing. It also takes advantage of Pittsburgh’s academic resources, as the University of Pittsburgh has agreed to help guide this project and to provide research power in engineering and AM. Pitt Chancellor Patrick Gallagher was instrumental in moving the Innovation Center forward.
Storer sees the campus as a “continuum” with Hazelwood Green, the 178-acre redevelopment of abandoned steel mills into a 264,000-sf R&D mecca for robotics, AI, and other cutting-edge technologies.
Neighborhood 91 is the latest innovation from the Allegheny County Airport Authority. Its collaboration with researchers at Carnegie Mellon University resulted in the creation of the NavCog app to help vision-impaired travelers navigate airports. The Authority’s partnership with the tech firm Zensors helped create an AI-powered system that estimates TSA wait times to an accuracy unmatched in the airport industry.
Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Mar 11, 2024
BIM at LOD400: Why Level of Development 400 matters for design and virtual construction
As construction projects grow more complex, producing a building information model at Level of Development 400 (LOD400) can accelerate schedules, increase savings, and reduce risk, writes Stephen E. Blumenbaum, PE, SE, Walter P Moore's Director of Construction Engineering.
AEC Innovators | Feb 28, 2024
How Suffolk Construction identifies ConTech and PropTech startups for investment, adoption
Contractor giant Suffolk Construction has invested in 27 ConTech and PropTech companies since 2019 through its Suffolk Technologies venture capital firm. Parker Mundt, Suffolk Technologies’ Vice President–Platforms, recently spoke with Building Design+Construction about his company’s investment strategy.
MFPRO+ Special Reports | Feb 22, 2024
Crystal Lagoons: A deep dive into real estate's most extreme guest amenity
These year-round, manmade, crystal clear blue lagoons offer a groundbreaking technology with immense potential to redefine the concept of water amenities. However, navigating regulatory challenges and ensuring long-term sustainability are crucial to success with Crystal Lagoons.
AEC Tech | Feb 20, 2024
AI for construction: What kind of tool can artificial intelligence become for AEC teams?
Avoiding the hype and gathering good data are half the battle toward making artificial intelligence tools useful for performing design, operational, and jobsite tasks.
Building Tech | Feb 20, 2024
Construction method featuring LEGO-like bricks wins global innovation award
A new construction method featuring LEGO-like bricks made from a renewable composite material took first place for building innovations at the 2024 JEC Composites Innovation Awards in Paris, France.
Modular Building | Jan 19, 2024
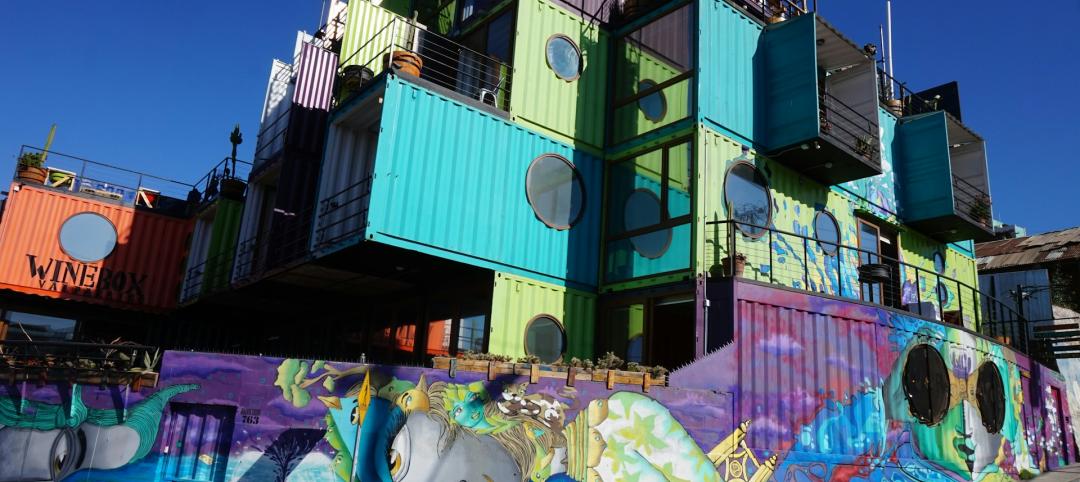
Building with shipping containers not as eco-friendly as it seems
With millions of shipping containers lying empty at ports around the world, it may seem like repurposing them to construct buildings would be a clear environmental winner. The reality of building with shipping containers is complicated, though, and in many cases isn’t a net-positive for the environment, critics charge, according to a report by NPR's Chloe Veltman.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Jan 17, 2024
Waterproofing deep foundations for new construction
This continuing education course, by Walter P Moore's Amos Chan, P.E., BECxP, CxA+BE, covers design considerations for below-grade waterproofing for new construction, the types of below-grade systems available, and specific concerns associated with waterproofing deep foundations.
Sustainability | Nov 1, 2023
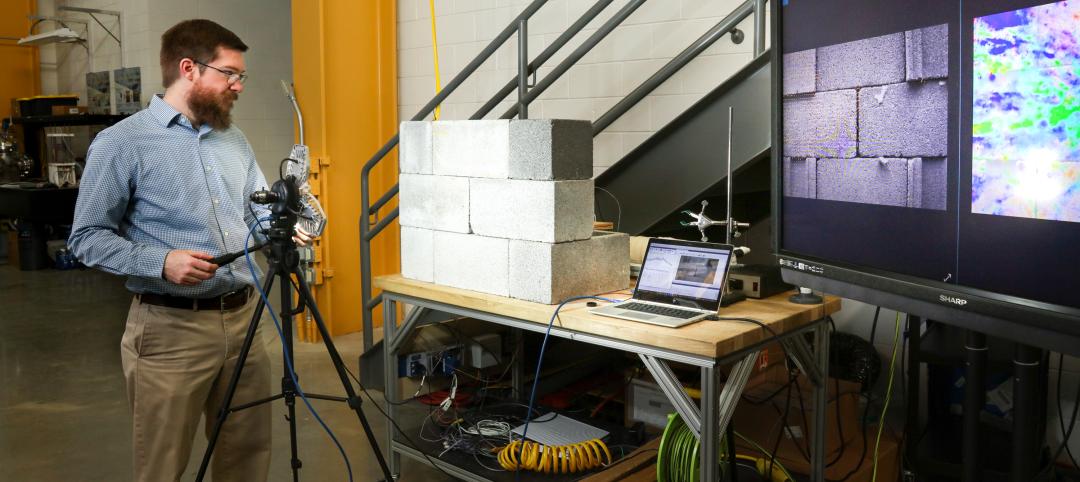
Researchers create building air leakage detection system using a camera in real time
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a system that uses a camera to detect air leakage from buildings in real time.
Engineers | Oct 12, 2023
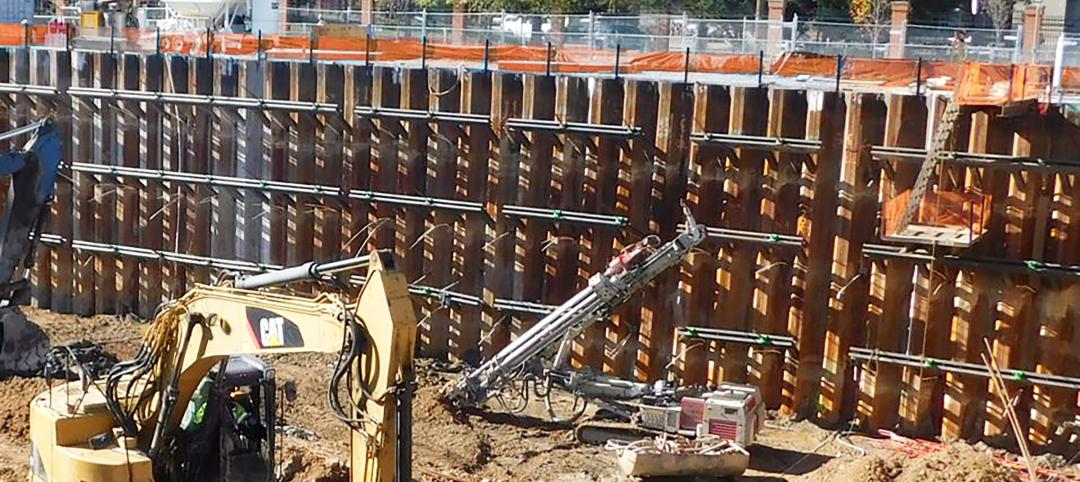
Building science: Considering steel sheet piles for semi-permanent or permanent subsurface water control for below-grade building spaces
For projects that do not include moisture-sensitive below-grade spaces, project teams sometimes rely on sheet piles alone for reduction of subsurface water. Experts from Simpson Gumpertz & Heger explore this sheet pile “water management wall” approach.
Metals | Sep 11, 2023
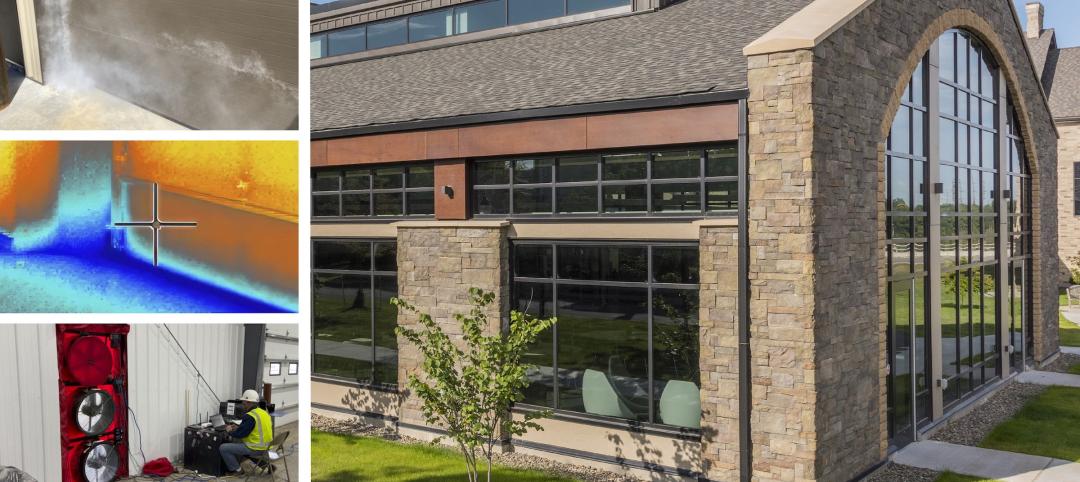
Best practices guide for air leakage testing for metal building systems released
The Metal Building Manufacturers Association (MBMA) released a new guidebook, Metal Building Systems - Best Practices to Comply with Whole-Building Air Leakage Testing Requirements.