Nearly 40 million Americans live in apartments. And because of the COVID-19 pandemic, developers and residents have been forced to rethink apartment living in terms of health, space, and utility.
To capture these thoughts, and to understand the future of multifamily housing, a team at Grimm + Parker Architects, which specializes in affordable and sustainable architecture projects, last summer conducted a fact-based exploration of the challenges and pressures that developers and residents experienced during the health crisis, and how those factors are likely to affect apartment design.
Other design firms have speculated on the impact COVID-19 is likely to have on apartment living, but far fewer have provided solutions as specifically as Grimm + Parker.
The following article is based on the report that came out of that firm’s exploration, titled “The New Normal and the Future of Multifamily Housing,” and created from responses of a dozen developers and 91 residents in the Washington, D.C.–Maryland–Virginia markets. This article also draws from commentary from three Grimm + Parker design architects—Zak Schooley, AIA, LEED AP BD+C, Executive Vice President; Julio Cruz, Architectural Designer; and Lauren Gilmartin, Architectural Designer—whom BD+C interviewed last December.
The vast majority of the survey’s respondents—92%—saw the social and physical implications of COVID-19 as being at least moderate, and in some cases significant. “Quarantine is difficult enough, but the added noise from other residents makes it so much more difficult. I can hear doors slamming, cabinets slamming, constant thuds from neighbors above, dogs barking. It wears on mental sanity,” said one exasperated resident whom the report quoted. Download a PDF recap of the Grimm + Parker multifamily research report, The New Normal & The Future of Multifamily Housing.
Schooley pointed out that there was a lot of concern expressed about health and safety, and the increasing density of apartment projects, which complicated social distancing and the ability of residents to “separate” rooms within apartments for different uses. And 80% of residents indicated a shift in desired residential unit types, which was a disconnect in developer thinking.
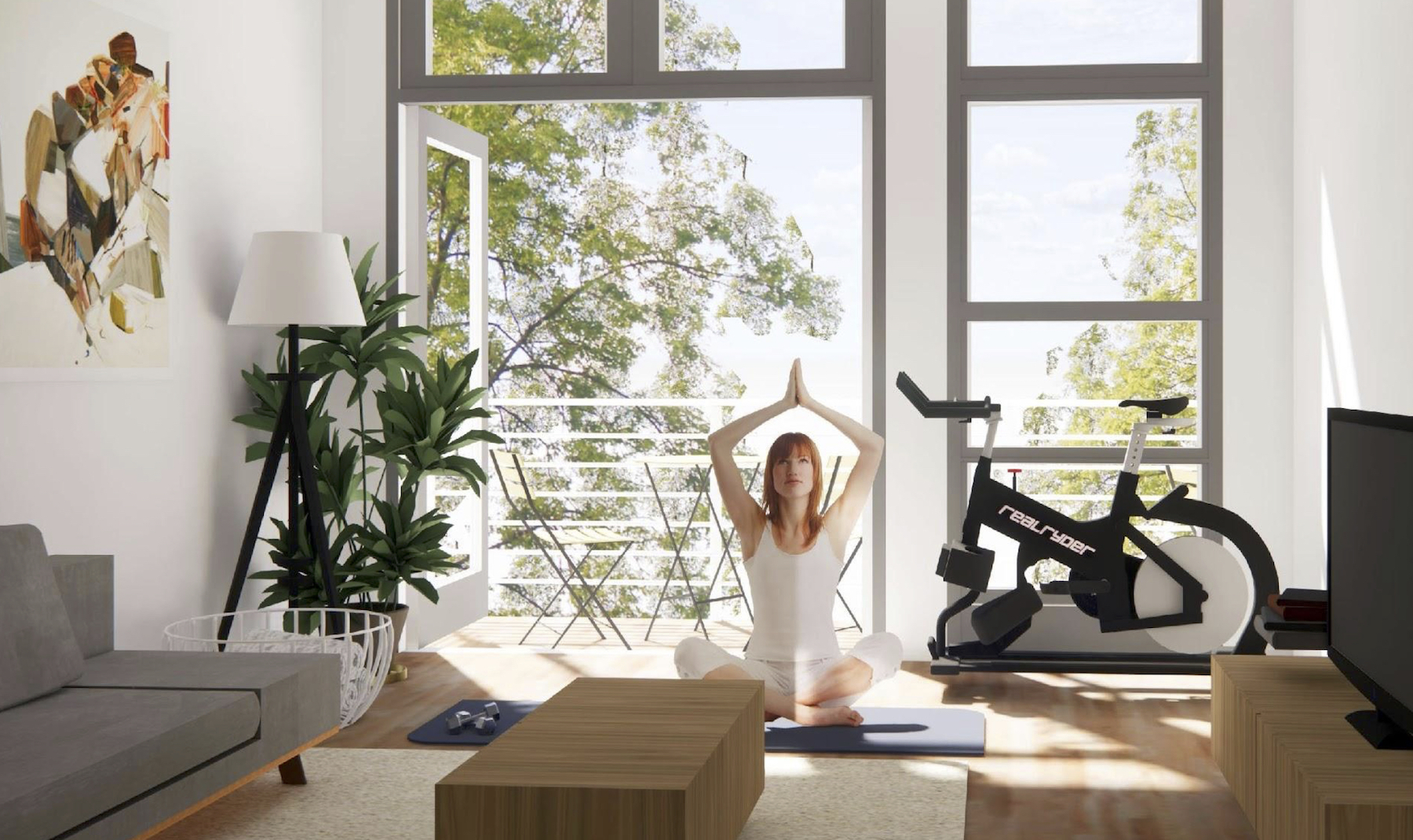
Common challenges cited by respondents included the lack of adequate space while sheltering-in-place, to live, work, and exercise. Only 11% of the resident-respondents lived in an apartment with a balcony, so quarantine made access to the outdoors problematic. Conversely, those respondents with balconies were able to adapt that space for, say, fitness or meditation.
The quarantine sometimes required residents to make purchases, like paper goods and cleaning products, in quantities that otherwise might seem extraneous. Many of the survey’s respondents had to come up with makeshift storage solutions by purchasing shelving or creating “contaminated” storage areas for wallets, keys, and bags.
SEEKING SPATIAL FLEXIBILITY IN MULTIFAMILY UNITS
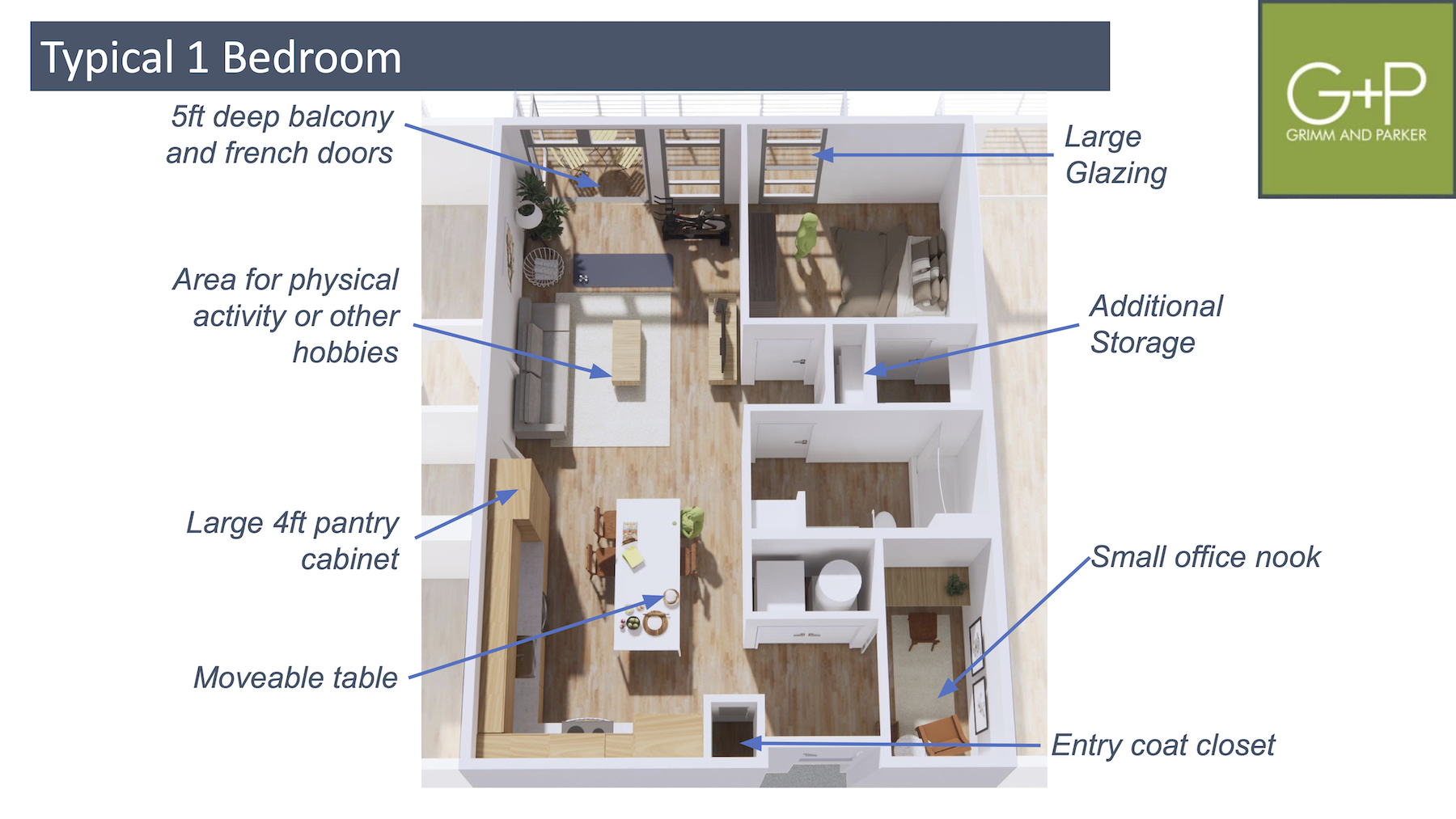
In its report, Grimm + Parker suggested myriad design changes for a typical 733-sf one-bedroom apartment. “With the projected success of the work-from-home business models, residents will need their units to become more versatile and adaptable, to provide users with enhanced technology, spatial flexibility, and separation, as well as provide adequate mental relief through connection to the outdoor environment and fresh air,” the report stated.
The firm highlighted changes that included five-foot-deep balconies and French doors; larger glazing for natural light; physical areas for activities and hobbies; four-foot-deep pantry cabinets; moveable tables; and additional storage.
Schooley noted that tenants also need places where they can “isolate,” even if for a short spell.
BIGGER AMENITIES SPACES FOR APARTMENT BUILDINGS
The report touched on how COVID-19 has altered tenants’ and developers’ perceptions about an apartment building’s amenities. For example, 80% of users said it was a challenge maintaining social distancing while exiting their buildings. More than 30% cited issues with the building’s cramped laundry rooms or package collection areas. And 91% said they’d be changing the way they use amenity spaces in the future.
Two-thirds of the developers who responded to the survey indicated they would like to see amenity spaces adjusted to fit social distancing standards and improved hygiene protocols. Elevators, lobbies, laundry rooms, and grocery pick-up zones were among the most mentioned spaces.
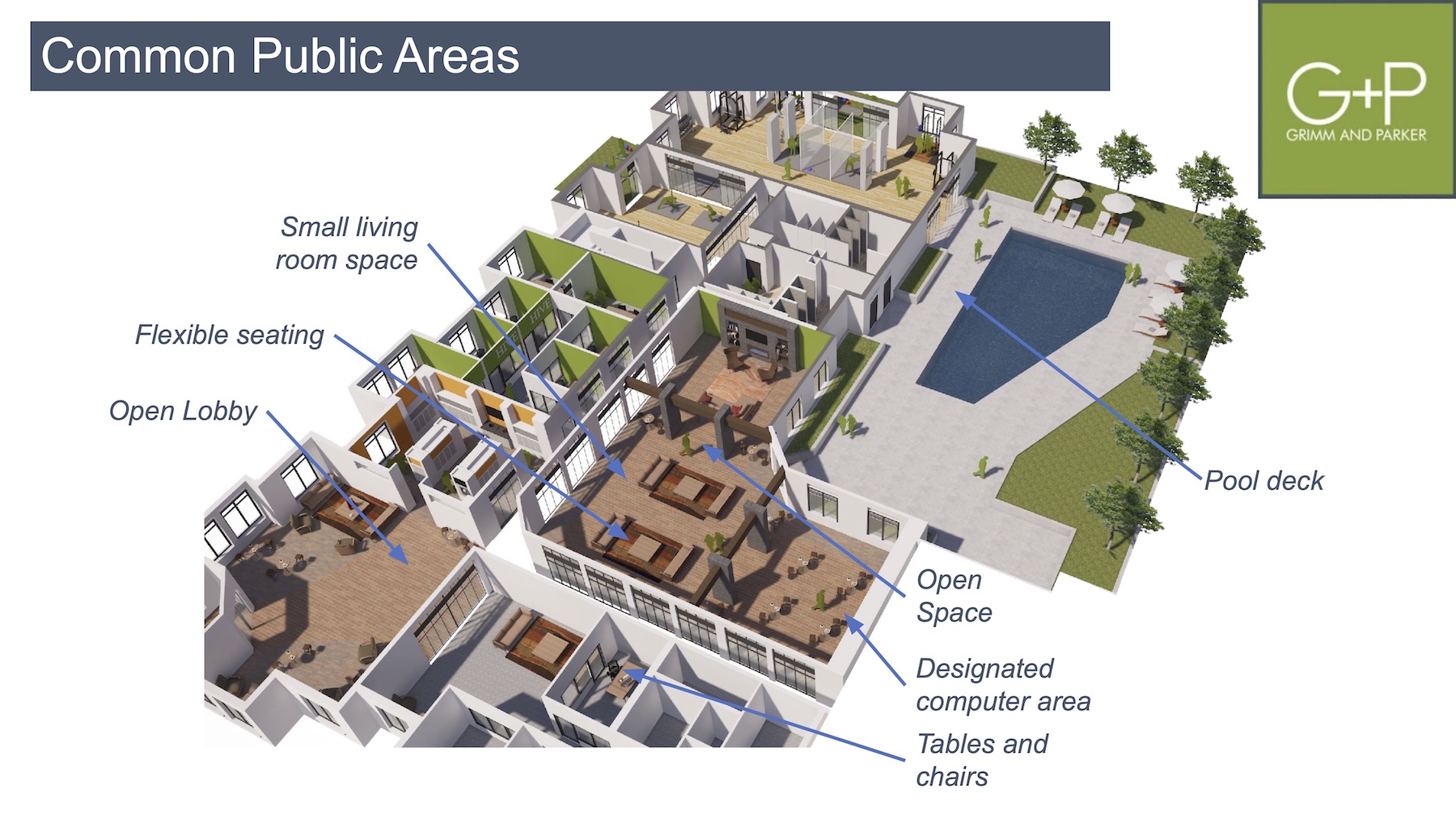
Cruz said that Grimm + Parker looked at how residents had been coping with COVID-19 to maintain some semblance of work-life balance, another key tenant concern. With that in mind, changes to common public spaces, said the report, should incorporate more offices and designated computer lounges, flexible seating, an open lobby, a pool deck, and a small living-room space. Common areas should also have operable doors that provide flexibility to size different rooms.
The report singled out how to make fitness rooms safer by enlarging them with an open floor plan. These areas should offer hand-sanitizing stations and designated spaces for individual and group exercise that include outdoor options. Operable doors would introduce more fresh air into the indoor space and allow for flexibility to scale rooms according to usage and need.
ONLINE PURCHASES OVERWHELMED MULTIFAMILY BUILDINGS
The pandemic exposed the inability of apartment buildings to handle the sheer number of packages they were receiving as a result of their tenants’ online purchases. (Digital Commerce 360 estimates that online spending in the U.S. rose 44% to $861 billion in 2020, and accounted for 21.3% of total retail sales last year.) Gilmartin noted that most buildings’ mail rooms, pre-pandemic, weren’t large enough or equipped to handle big packages or grocery deliveries.
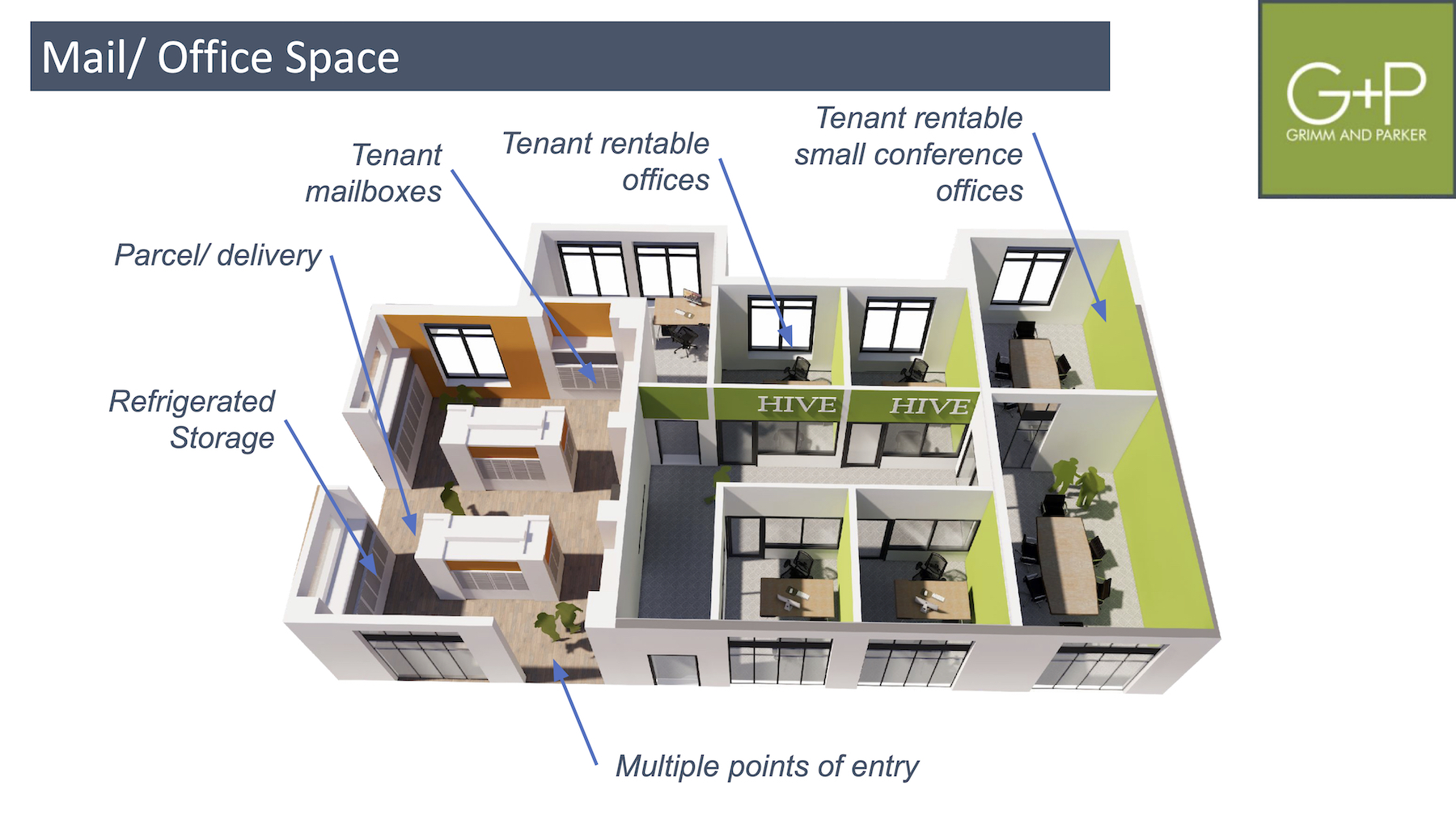
Grimm + Parker foresees the multifamily building of the future with electronic refrigerated storage and ample package pickup spaces. The firm also envisions mailrooms with tenant boxes that combine with rentable office and conference room space. The area, in this vision, would have multiple points of entry.
Such an environment might also benefit from individualized mechanicals and airflow zoning for each space.
Schooley says he could imagine tenants renting space just to get out of their apartments for a while to complete a project, or to give their kids cooped up in the apartment because of quarantine a temporary change of scenery.
Related Stories
| Mar 22, 2011
Mayor Bloomberg unveils plans for New York City’s largest new affordable housing complex since the ’70s
Plans for Hunter’s Point South, the largest new affordable housing complex to be built in New York City since the 1970s, include new residences for 5,000 families, with more than 900 in this first phase. A development team consisting of Phipps Houses, Related Companies, and Monadnock Construction has been selected to build the residential portion of the first phase of the Queens waterfront complex, which includes two mixed-use buildings comprising more than 900 housing units and roughly 20,000 square feet of new retail space.
| Mar 17, 2011
Perkins Eastman launches The Green House prototype design package
Design and architecture firm Perkins Eastman is pleased to join The Green House project and NCB Capital Impact in announcing the launch of The Green House Prototype Design Package. The Prototype will help providers develop small home senior living communities with greater efficiency and cost savings—all to the standards of care developed by The Green House project.
| Mar 11, 2011
Renovation energizes retirement community in Massachusetts
The 12-year-old Edgewood Retirement Community in Andover, Mass., underwent a major 40,000-sf expansion and renovation that added 60 patient care beds in the long-term care unit, a new 17,000-sf, 40-bed cognitive impairment unit, and an 80-seat informal dining bistro.
| Mar 11, 2011
Mixed-income retirement community in Maryland based on holistic care
The Green House Residences at Stadium Place in Waverly, Md., is a five-story, 40,600-sf, mixed-income retirement community based on a holistic continuum of care concept developed by Dr. Bill Thomas. Each of the four residential floors houses a self-contained home for 12 residents that includes 12 bedrooms/baths organized around a common living/social area called the “hearth,” which includes a kitchen, living room with fireplace, and dining area.
| Mar 11, 2011
Texas A&M mixed-use community will focus on green living
HOK, Realty Appreciation, and Texas A&M University are working on the Urban Living Laboratory, a 1.2-million-sf mixed-use project owned by the university. The five-phase, live-work-play project will include offices, retail, multifamily apartments, and two hotels.
| Mar 1, 2011
How to make rentals more attractive as the American dream evolves, adapts
Roger K. Lewis, architect and professor emeritus of architecture at the University of Maryland, writes in the Washington Post about the rising market demand for rental housing and how Building Teams can make these properties a desirable choice for consumer, not just an economically prudent and necessary one.
| Feb 15, 2011
New Orleans' rebuilt public housing architecture gets mixed reviews
The architecture of New Orleans’ new public housing is awash with optimism about how urban-design will improve residents' lives—but the changes are based on the idealism of an earlier era that’s being erased and revised.
| Feb 11, 2011
Chicago high-rise mixes condos with classrooms for Art Institute students
The Legacy at Millennium Park is a 72-story, mixed-use complex that rises high above Chicago’s Michigan Avenue. The glass tower, designed by Solomon Cordwell Buenz, is mostly residential, but also includes 41,000 sf of classroom space for the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and another 7,400 sf of retail space. The building’s 355 one-, two-, three-, and four-bedroom condominiums range from 875 sf to 9,300 sf, and there are seven levels of parking. Sky patios on the 15th, 42nd, and 60th floors give owners outdoor access and views of Lake Michigan.
| Feb 11, 2011
Sustainable community center to serve Angelinos in need
Harbor Interfaith Services, a nonprofit serving the homeless and working poor in the Harbor Area and South Bay communities of Los Angeles, engaged Withee Malcolm Architects to design a new 15,000-sf family resource center. The architects, who are working pro bono for the initial phase, created a family-centered design that consolidates all programs into a single building. The new three-story space will house a resource center, food pantry, nursery and pre-school, and administrative offices, plus indoor and outdoor play spaces and underground parking. The building’s scale and setbacks will help it blend with its residential neighbors, while its low-flow fixtures, low-VOC and recycled materials, and energy-efficient mechanical equipment and appliances will help it earn LEED certification.
| Feb 11, 2011
Apartment complex caters to University of Minnesota students
Twin Cities firm Elness Swenson Graham Architects designed the new Stadium Village Flats, in the University of Minnesota’s East Bank Campus, with students in mind. The $30 million, six-story residential/retail complex will include 120 furnished apartments with fitness rooms and lounges on each floor. More than 5,000 sf of first-floor retail space and two levels of below-ground parking will complete the complex. Opus AE Group Inc., based in Minneapolis, will provide structural engineering services.
















