The Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) is gaining momentum across the country as a cost-effective and compassionate way to support the desires of frail elders to live in their homes and communities and avoid premature nursing home placement. With 118 PACE centers in 32 states, the program is considered the gold standard of care for seniors.
A One Stop Shop
The PACE center is the heart of the program and serves as a "one stop shop" for enrollees, otherwise known as Participants, to receive care and services tailored to meet individual needs. Participants visit the PACE center as needed, up to five days per week, where they receive a majority of care and services. Additionally, transportation is provided to and from the PACE center daily or services can be provided at home to support participant independence. Care is coordinated, provided and paid for by the PACE Interdisciplinary Team (IDT) that knows each Participant’s needs and desires and tailors care and services accordingly. A typical PACE center is comprised of a fully functioning and equipped primary care clinic, adult day center and rehabilitation therapy gym. In addition, it includes find dining areas, large group activity spaces, a PT and rehab space, meditation spaces and a medical clinic capable of primary care. Participants can watch TV, play organized games, relax in one of the many quiet spaces or simply talk to one another. The IDT of nurses, social workers, dieticians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, transportation and primary care physicians is available to attend to a Participant’s needs.
Design and Planning Considerations
Averaging 18,000SF – 22,000SF, the ideal PACE facility is a single story building with a large outdoor covered portico allowing for safe all-weather loading and unloading of Participants. Corridors are approximately 8 foot wide to accommodate the above average number of wheelchairs, as well as other mobility devices, and have a minimal number of corridor bends. Participant socialization spaces are adjacent to one another to reduce walking distances and are connected via large openings rather than doors. While dependent on the population demographics, specific areas are also designed for Participants with dementia related behaviors. Each center has a kitchen for meal preparation and/or serving. Many existing centers buy ready-made meals from vendors and simply reheat in the kitchen thus saving time in preparation and potentially saving significant costs in not having to design and construct a full commercial kitchen.

The fully functioning clinic provides basic primary care to Participants only. Family members are not able to use the clinic as an Urgent Care center or equivalent. The clinic space has an average of 4-6 exam rooms that are enlarged to accommodate wheel chairs. Modular casework is preferred over custom millwork to help budget constraints as modular can offer 40% savings. Medical equipment requirements are not as intensive as an acute care hospital, again supporting the smaller modular casework concept.
For Participant activity areas, a large oven and microwave are included to allow for baking demonstrations or competitions. Several computer terminals with internet access are also available. A patio or landscaped area provides Participants the opportunity to be outdoors to relax or participate in a variety of outdoor activities.
As expected in all healthcare facilities, the safetyand security of Participants is critical. A PACE center’s safety features include an electronic access control system to prohibit wandering and elopement. Additionally, all participant spaces are equipped with a nurse call system that can alert staff in the case of an emergency. Nurse call stations are located in bathrooms, bathing and personal care areas, exam rooms and activity spaces.
In addition to Participant program spaces, each center includes meeting spaces for the IDT. In order for the 11 member IDT to plan, provide and coordinate direct care for Participants, the center must include an adequate large space for daily group meetings as well as multiple smaller work spaces. Staff and administrative work areas are typically located away from Participant program spaces. As opposed to constructing private offices, many staff work spaces are shared work stations that save space and reduce cost.
Business Fundamentals
Ideally, the PACE program will relieve hospital emergency departments of minor medical issues not warranting an ED visit and will reduce hospitalization rates by improving access to care. National research also shows Participants having reduced morbidity and mortality rates and a higher quality of life compared to those living in nursing homes. PACE also provides flexibility to families by relieving the burden of care without taking a family member away from their home. In addition to the high family satisfaction ratings, the program has very low disenrollment. Despite the recognition of the model’s success, PACE programs have grown incrementally and care for only a fraction of their potential population mainly due to CMS regulations.
Conclusion
The benefits of PACE are very apparent and the program is gaining momentum across the country. There is hope that new regulation will provide even more operational flexibility to support expansion and allow PACE programs to operate more competitively in the post-health care reform marketplace. Identifying opportunities to relieve ED volume, reduce cost, improve access and most importantly increase quality of life for our aging population is critical to solving our healthcare dilemma. PACE has proven to be a successful component and vital part of this equation.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Oct 5, 2023
Top 115 Healthcare Construction Firms for 2023
Turner Construction, Brasfield & Gorrie, JE Dunn Construction, DPR Construction, and McCarthy Holdings top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest healthcare sector contractors and construction management (CM) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report. Note: This ranking includes revenue related to all healthcare buildings work, including hospitals, medical office buildings, and outpatient facilities.
Giants 400 | Oct 5, 2023
Top 90 Healthcare Engineering Firms for 2023
Jacobs, WSP, IMEG, BR+A, and Affiliated Engineers head BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest healthcare sector engineering and engineering/architecture (EA) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report. Note: This ranking includes revenue related to all healthcare buildings work, including hospitals, medical office buildings, and outpatient facilities.
Giants 400 | Oct 5, 2023
Top 175 Healthcare Architecture Firms for 2023
HDR, HKS, CannonDesign, Stantec, and SmithGroup top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest healthcare sector architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report. Note: This ranking includes revenue related to all healthcare buildings work, including hospitals, medical office buildings, and outpatient facilities.
Adaptive Reuse | Sep 19, 2023
Transforming shopping malls into 21st century neighborhoods
As we reimagine the antiquated shopping mall, Marc Asnis, AICP, Associate, Perkins&Will, details four first steps to consider.
Healthcare Facilities | Sep 13, 2023
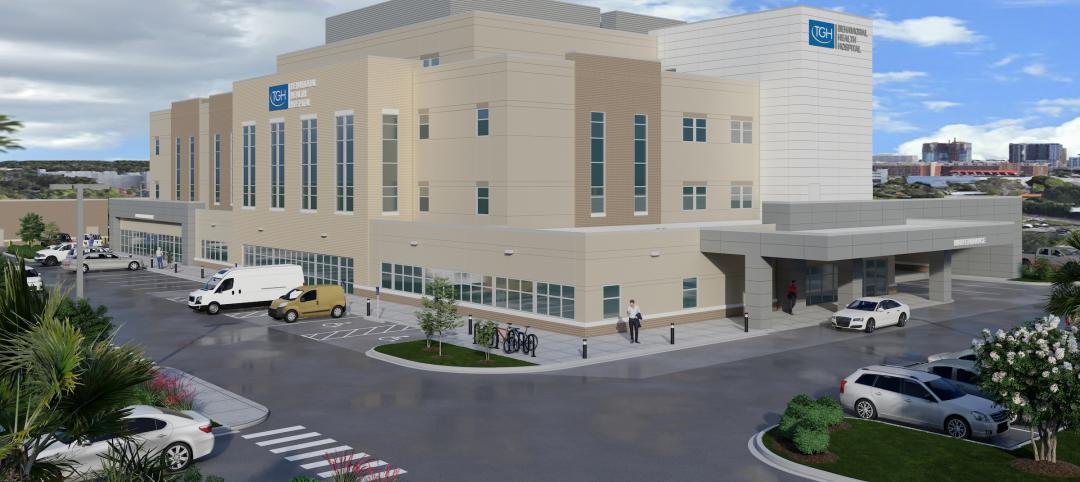
Florida’s first freestanding academic medical behavioral health hospital breaks ground in Tampa Bay
Construction kicked off recently on TGH Behavioral Health Hospital, Florida’s first freestanding academic medical behavioral health hospital. The joint venture partnership between Tampa General (a 1,040-bed facility) and Lifepoint Behavioral Health will provide a full range of inpatient and outpatient care in specialized units for pediatrics, adolescents, adults, and geriatrics, and fills a glaring medical need in the area.
Healthcare Facilities | Sep 8, 2023
Modern healthcare interiors: Healing and care from the outside in
CO Architects shares design tips for healthcare interiors, from front desk to patient rooms.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
Top 115 Architecture Engineering Firms for 2023
Stantec, HDR, Page, HOK, and Arcadis North America top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture engineering (AE) firms for nonresidential building and multifamily housing work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
2023 Giants 400 Report: Ranking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms
A record 552 AEC firms submitted data for BD+C's 2023 Giants 400 Report. The final report includes 137 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
Top 175 Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HKS, Perkins&Will, Corgan, and Perkins Eastman top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture firms for nonresidential building and multifamily housing work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Healthcare Facilities | Aug 21, 2023
Sutter Health’s new surgical care center finishes three months early, $3 million under budget
Sutter Health’s Samaritan Court Ambulatory Care and Surgery Center (Samaritan Court), a three-story, 69,000 sf medical office building, was recently completed three months early and $3 million under budget, according to general contractor Skanska.