The Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) is gaining momentum across the country as a cost-effective and compassionate way to support the desires of frail elders to live in their homes and communities and avoid premature nursing home placement. With 118 PACE centers in 32 states, the program is considered the gold standard of care for seniors.
A One Stop Shop
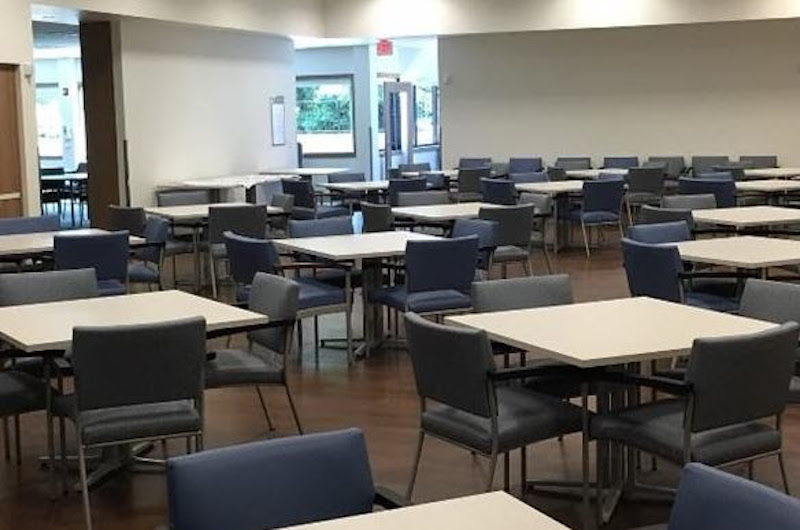
The PACE center is the heart of the program and serves as a "one stop shop" for enrollees, otherwise known as Participants, to receive care and services tailored to meet individual needs. Participants visit the PACE center as needed, up to five days per week, where they receive a majority of care and services. Additionally, transportation is provided to and from the PACE center daily or services can be provided at home to support participant independence. Care is coordinated, provided and paid for by the PACE Interdisciplinary Team (IDT) that knows each Participant’s needs and desires and tailors care and services accordingly. A typical PACE center is comprised of a fully functioning and equipped primary care clinic, adult day center and rehabilitation therapy gym. In addition, it includes find dining areas, large group activity spaces, a PT and rehab space, meditation spaces and a medical clinic capable of primary care. Participants can watch TV, play organized games, relax in one of the many quiet spaces or simply talk to one another. The IDT of nurses, social workers, dieticians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, transportation and primary care physicians is available to attend to a Participant’s needs.
Design and Planning Considerations
Averaging 18,000SF – 22,000SF, the ideal PACE facility is a single story building with a large outdoor covered portico allowing for safe all-weather loading and unloading of Participants. Corridors are approximately 8 foot wide to accommodate the above average number of wheelchairs, as well as other mobility devices, and have a minimal number of corridor bends. Participant socialization spaces are adjacent to one another to reduce walking distances and are connected via large openings rather than doors. While dependent on the population demographics, specific areas are also designed for Participants with dementia related behaviors. Each center has a kitchen for meal preparation and/or serving. Many existing centers buy ready-made meals from vendors and simply reheat in the kitchen thus saving time in preparation and potentially saving significant costs in not having to design and construct a full commercial kitchen.

The fully functioning clinic provides basic primary care to Participants only. Family members are not able to use the clinic as an Urgent Care center or equivalent. The clinic space has an average of 4-6 exam rooms that are enlarged to accommodate wheel chairs. Modular casework is preferred over custom millwork to help budget constraints as modular can offer 40% savings. Medical equipment requirements are not as intensive as an acute care hospital, again supporting the smaller modular casework concept.
For Participant activity areas, a large oven and microwave are included to allow for baking demonstrations or competitions. Several computer terminals with internet access are also available. A patio or landscaped area provides Participants the opportunity to be outdoors to relax or participate in a variety of outdoor activities.
As expected in all healthcare facilities, the safetyand security of Participants is critical. A PACE center’s safety features include an electronic access control system to prohibit wandering and elopement. Additionally, all participant spaces are equipped with a nurse call system that can alert staff in the case of an emergency. Nurse call stations are located in bathrooms, bathing and personal care areas, exam rooms and activity spaces.
In addition to Participant program spaces, each center includes meeting spaces for the IDT. In order for the 11 member IDT to plan, provide and coordinate direct care for Participants, the center must include an adequate large space for daily group meetings as well as multiple smaller work spaces. Staff and administrative work areas are typically located away from Participant program spaces. As opposed to constructing private offices, many staff work spaces are shared work stations that save space and reduce cost.
Business Fundamentals
Ideally, the PACE program will relieve hospital emergency departments of minor medical issues not warranting an ED visit and will reduce hospitalization rates by improving access to care. National research also shows Participants having reduced morbidity and mortality rates and a higher quality of life compared to those living in nursing homes. PACE also provides flexibility to families by relieving the burden of care without taking a family member away from their home. In addition to the high family satisfaction ratings, the program has very low disenrollment. Despite the recognition of the model’s success, PACE programs have grown incrementally and care for only a fraction of their potential population mainly due to CMS regulations.
Conclusion
The benefits of PACE are very apparent and the program is gaining momentum across the country. There is hope that new regulation will provide even more operational flexibility to support expansion and allow PACE programs to operate more competitively in the post-health care reform marketplace. Identifying opportunities to relieve ED volume, reduce cost, improve access and most importantly increase quality of life for our aging population is critical to solving our healthcare dilemma. PACE has proven to be a successful component and vital part of this equation.
Related Stories
Sustainability | Apr 4, 2023
NIBS report: Decarbonizing the U.S. building sector will require massive, coordinated effort
Decarbonizing the building sector will require a massive, strategic, and coordinated effort by the public and private sectors, according to a report by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS).
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 26, 2023
UC Davis Health opens new eye institute building for eye care, research, and training
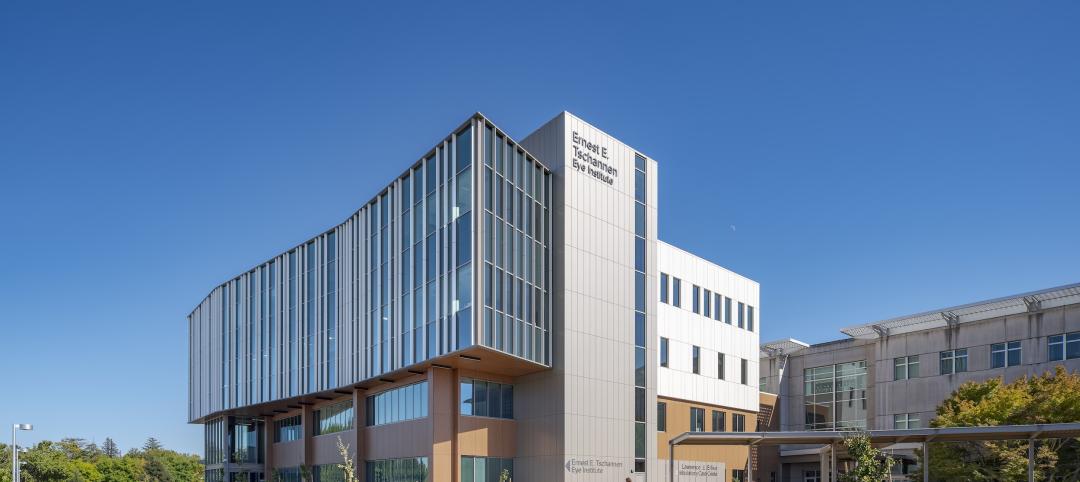
UC Davis Health recently marked the opening of the new Ernest E. Tschannen Eye Institute Building and the expansion of the Ambulatory Care Center (ACC). Located in Sacramento, Calif., the Eye Center provides eye care, vision research, and training for specialists and investigators. With the new building, the Eye Center’s vision scientists can increase capacity for clinical trials by 50%.
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 25, 2023
California medical center breaks ground on behavioral health facility for both adults and children
In San Jose, Calif., Santa Clara Valley Medical Center (SCVMC) has broken ground on a new behavioral health facility: the Child, Adolescent, and Adult Behavioral Health Services Center. Designed by HGA, the center will bring together under one roof Santa Clara County’s behavioral health offerings, including Emergency Psychiatric Services and Urgent Care.
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 22, 2023
New Jersey’s new surgical tower features state’s first intraoperative MRI system
Hackensack (N.J.) University Medical Center recently opened its 530,000-sf Helena Theurer Pavilion, a nine-story surgical and intensive care tower designed by RSC Architects and Page. The county’s first hospital, Hackensack University Medical Center, a 781-bed nonprofit teaching and research hospital, was founded in 1888.
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
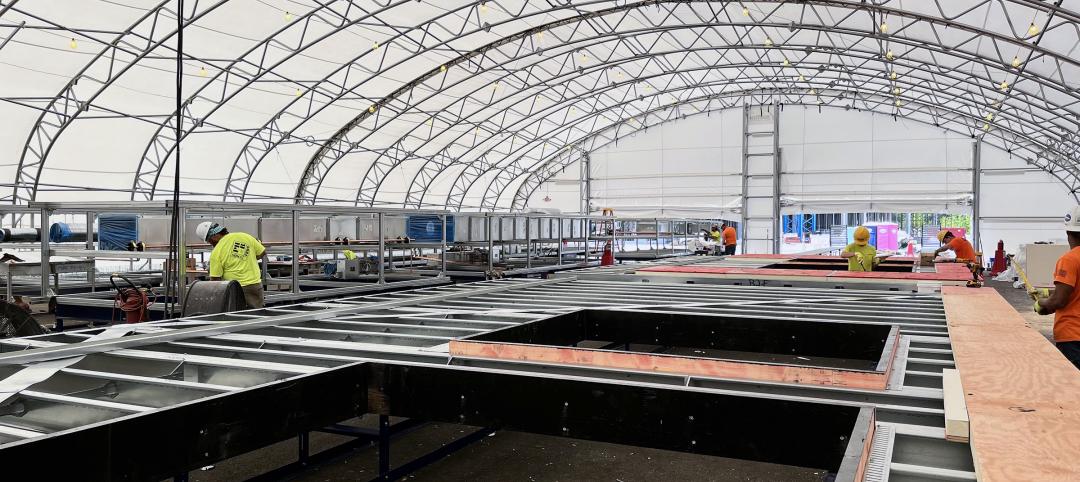
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Modular Building | Mar 20, 2023
3 ways prefabrication doubles as a sustainability strategy
Corie Baker, AIA, shares three modular Gresham Smith projects that found sustainability benefits from the use of prefabrication.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 13, 2023
Next-gen behavioral health facilities use design innovation as part of the treatment
An exponential increase in mental illness incidences triggers new behavioral health facilities whose design is part of the treatment.
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 6, 2023
NBBJ kicks off new design podcast with discussion on behavioral health facilities
During the second week of November, the architecture firm NBBJ launched a podcast series called Uplift, that focuses on the transformative power of design. Its first 30-minute episode homed in on designing for behavioral healthcare facilities, a hot topic given the increasing number of new construction and renovation projects in this subsector.
Sustainability | Mar 2, 2023
The next steps for a sustainable, decarbonized future
For building owners and developers, the push to net zero energy and carbon neutrality is no longer an academic discussion.