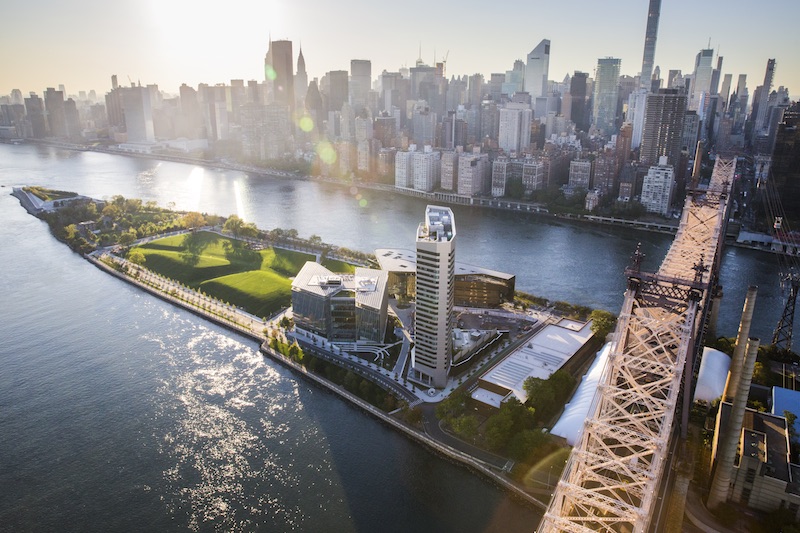
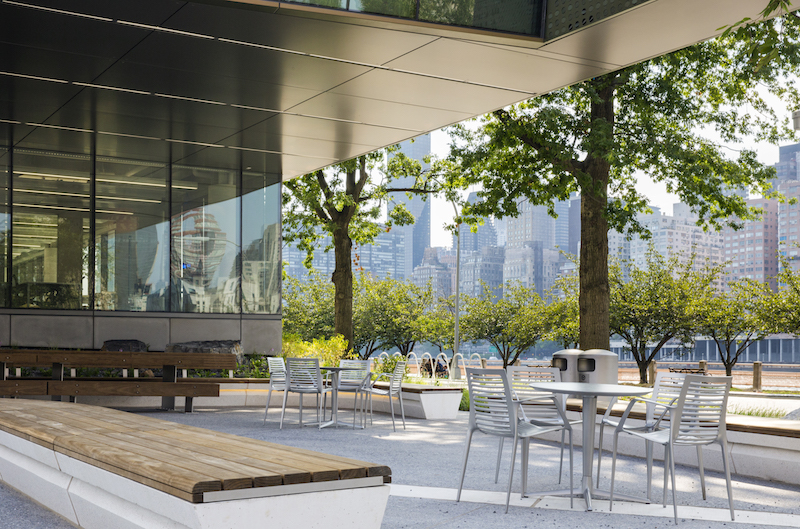
Since opening in September 2017, Cornell Tech’s New York campus has gained attention for its inventive, ambitious design. The bold architectural forms, dramatically sculpted topography of its Roosevelt Island site, and leading-edge sustainability credentials of the completed first phase signal an intention to rethink education for the 21st century.
But some of the project’s most important innovations lay in the more prosaic realm of process, collaborative development, and partnership structures. Reflecting a growing trend in American higher education, Cornell Tech used several alternative models of project implementation to make its holistic vision for the first phase of the campus a reality.
This trend is also reshaping the designer’s role. As Cornell Tech’s campus master planner, we took on the responsibility to guide the implementation process in close collaboration with multiple partners. This was a necessity given the complex stakeholder network: the city of New York and its agencies, Cornell University and its constituents, the Roosevelt Island community, and third-party partners.
During the project, our team at SOM played the role of an orchestra conductor, guiding the ensemble toward the creation of a harmonious whole.
 Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
The evolution of project delivery
Universities in the United States have traditionally relied on a project delivery approach known as design-bid-build. Clients first hire an architecture firm to create a design; then, when the design is complete, they hire a contractor to build it. But as schools look for ways to prioritize capital planning budgets, create more impact through partnerships, and synergize regional and global interest with institutional core strengths, they’re exploring different options.
Today, many of our university clients use an approach known as construction manager at risk. This injects construction expertise into projects from the earliest stages. Partners work collaboratively to optimize a project’s constructability, to find intelligent ways to accelerate the overall construction timeline, and to identify strategies to assist the project’s budget.
Public-private partnerships are also becoming more popular in higher education. Once used primarily for revenue-generating student housing, this financing structure is increasingly being applied to other project types.
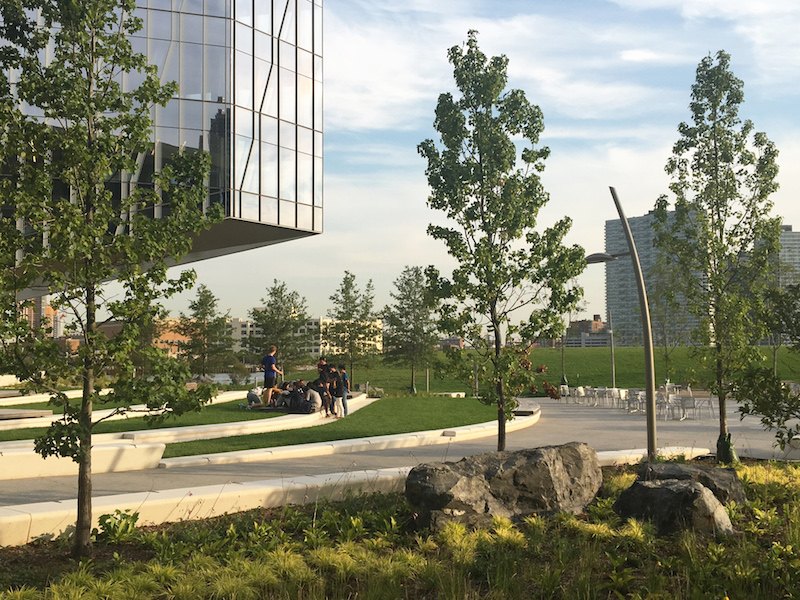

The unprecedented campus
Cornell Tech is unique in many ways, and its innovative approach to achieve a holistic campus is no exception. The school itself is a kind of public-private partnership between Cornell, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, and the City of New York. The city granted Cornell a 99-year lease for the land, but no single entity owns all campus buildings. (For example, a developer owns the corporate co-location facility known as the Tata Innovation Center, leasing space to industry partners and the university.) Within a tight timeline driven by Cornell’s partnership with the City of New York, SOM led the planning process for the first phase of a cohesive campus that integrates several buildings designed and built by separate teams.
The nuances of each building’s development within the whole ultimately made the campus financially feasible. This approach also supported the city’s and the university’s goal of broad-ranging collaboration and experimentation. With an ever-expansive team, SOM helped Cornell to synthesize all campus elements within one cohesive plan.
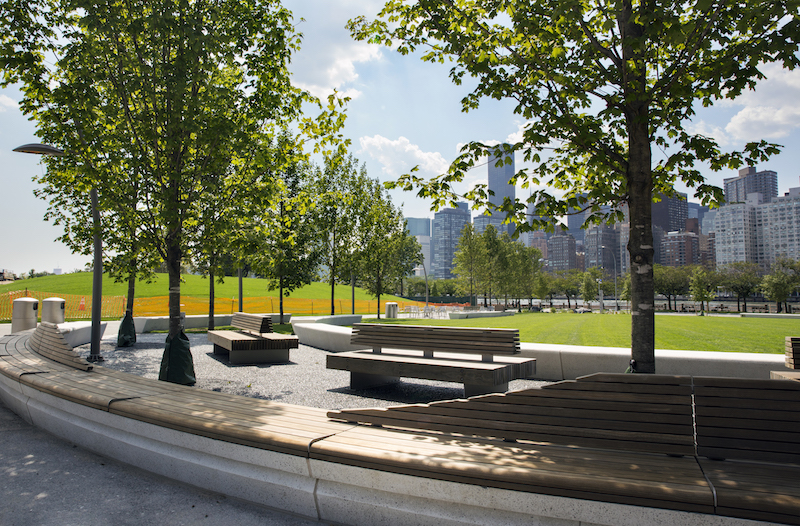 Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
This was no small consideration for a project whose ultimate aim is to futureproof New York City’s economy. Cornell Tech grew out of the city’s desire to create a new applied sciences hub that would attract leading scientists, engineers, and businesspeople from around the globe for decades to come. It was therefore critical to make the campus itself a beacon that reinforces the strengths of Cornell’s academic curriculum, while fusing this intelligence with real-world partnership. We worked closely with Cornell to shape a framework plan that would make the campus lively, accessible, and resilient.
Keeping score
To ensure that the teams working on each building understood the framework plan’s goals and tailored their plans accordingly, we worked with Cornell to develop a tool that we called the Scorecard. This list of nine criteria clearly spelled out the core targets for campus-wide sustainable site development parameters as they pertained to individual buildings. It took into account factors ranging from the practical (for instance, where to create tax lots, situate buildings, and coordinate utility points of entry) to the experiential (how a cohesive campus landscape meets the building edges). Ultimately, this simple list of clear parameters helped Cornell balance the diverse needs of individual building projects, while building consensus around a holistic campus plan.
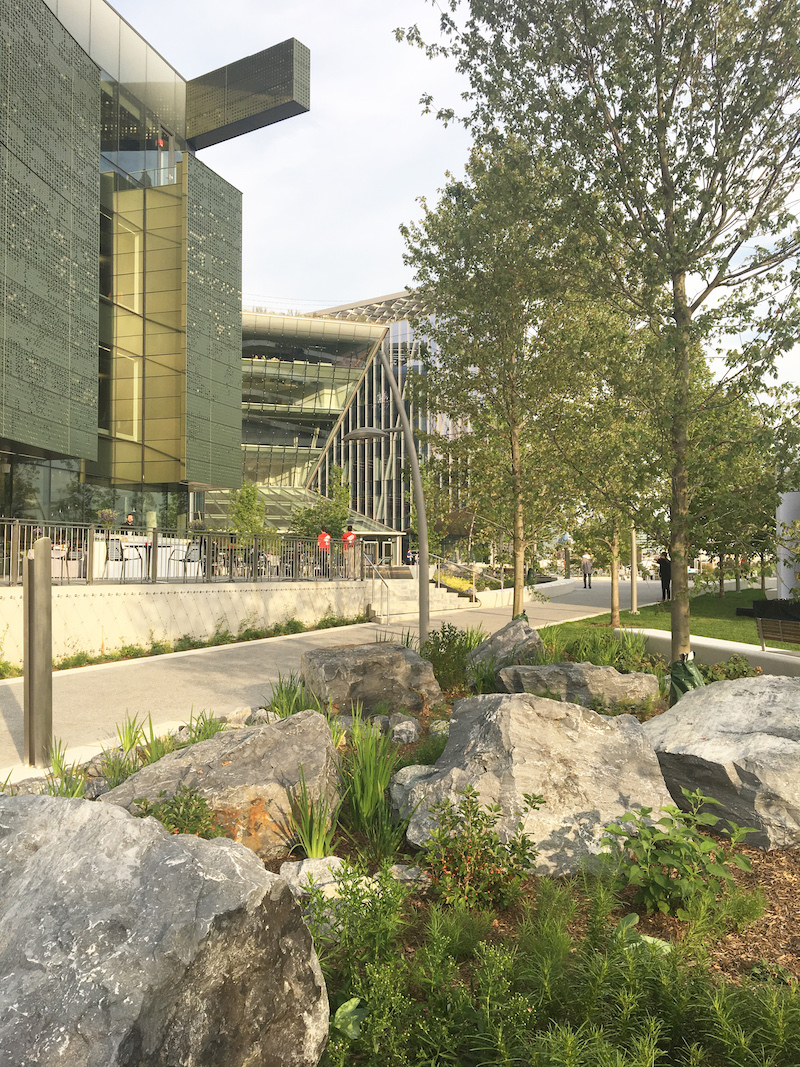

As each building team was brought on board, SOM held a kickoff geared to introduce each team to the Scorecard. We asked the architects, developers, and subconsultants involved to prioritize the specific building needs and design advancement, while utilizing the Scorecard items to talk through potential challenges (such as constructability, interfaces, timing, utilities distribution, signage and wayfinding, and open space interventions). We then worked collectively to find the best solutions.
Once each project team completed a major milestone, we repeated this process, which we referred to as a “reconciliation” period. Reviewing the Scorecard with key players, we determined the fixed parameters that the campus plan should govern, and which aspects could be revisited collaboratively.
With so many separate building teams involved, the Scorecard helped to keep everyone accountable to the overall campus plan. It kept teams on track as individual projects progressed—for instance, it helped us to reconcile the initial, theoretical energy loads we established for the campus with the actual loads for each building.
This process also resulted in a number of important breakthroughs. We helped contribute to the net-zero-energy target of the Bloomberg Center, the main academic building, by coordinating strategic elements of the site development: housing 80 geothermal wells and situating a 40,000-gallon underground tank to capture rainwater for use in the building’s plumbing, cooling, and irrigation systems.
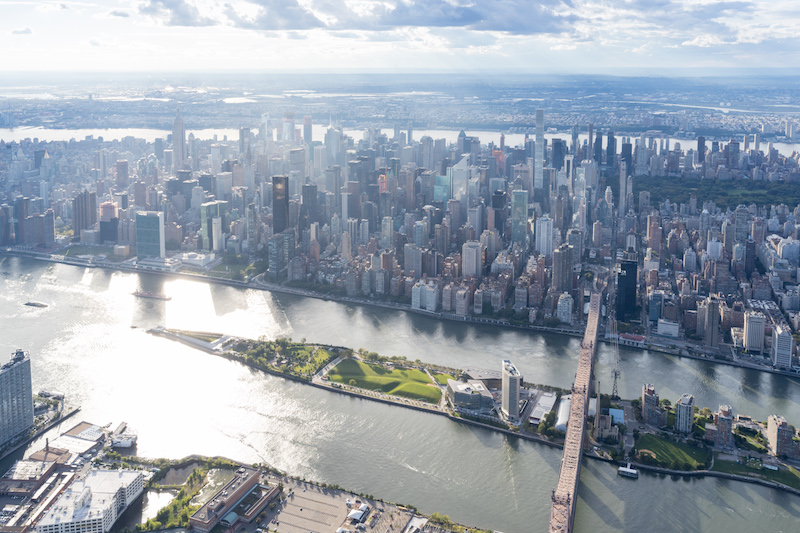 Courtesy SOM, Iwan Baan.
Courtesy SOM, Iwan Baan.
Another success story: the resilient campus infrastructure. To protect Cornell Tech from rising sea levels and future storms, the master plan established the island’s natural central ridge as the main pedestrian circulation route. As a result, all primary building entrances are located along this elevated pathway. The ridge is also used as the main artery to distribute the electrical supply across the campus. As a result, this often vulnerable infrastructure is kept several feet above the base floodplain elevations, and on higher ground than most of Lower Manhattan, in fact.
Looking to the future
Although our Scorecard method worked well for Cornell Tech, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution for helping clients in higher education—or any other field—navigate alternative project delivery or implementation models. In a fast-changing market, designers need to return to first principles for every project, working to understand the specific challenges and opportunities involved and to craft solutions accordingly.
These skills will become even more important as climate change reshapes cities and college campuses alike. To address broad-ranging infrastructure vulnerabilities, universities are increasingly partnering with local governments and other entities. Designers have a unique role to play in this process: helping all parties understand the potential of a given site or system, and working together to realize it.
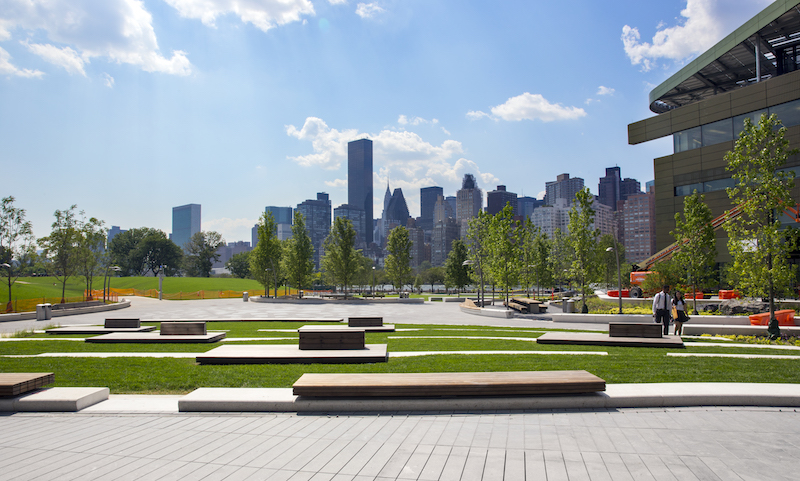 Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
Courtesy SOM, Lucas Blair Simpson.
Related Stories
| Jan 2, 2014
Measuring whole building energy use among big changes in LEED v4
A new prerequisite in LEED v4 calls for each project to measure whole building energy use, and then share that data with USGBC.
| Dec 26, 2013
WDMA launches project to create ISO-compliant architectural doors
WDMA's National Architectural Door Council has initiated a project to create ISO-compliant Product Category Rules for architectural wood flush and stile and rail doors
| Dec 20, 2013
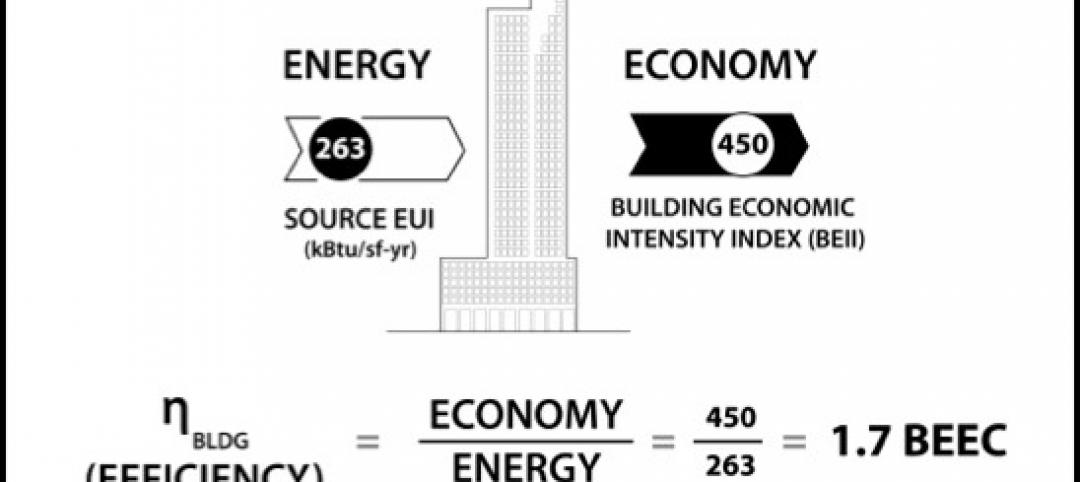
Can energy hogs still be considered efficient buildings? Yes, say engineers at Buro Happold
A new tool from the engineering firm Buro Happold takes into account both energy and economic performance of buildings for a true measure of efficiency.
| Dec 19, 2013
NRDC report relates green infrastructure investments to commercial property value [Infographic]
The Natural Resources Defense Council has released The Green Edge: How Commercial Property Investment in Green Infrastructure Creates Value -- a first-ever illustrative and well-documented report that helps demonstrate the value of green infrastructure. It draws from available published material to capture the multitude of tangible, monetizable non-water quality and water quality benefits that green infrastructure investments (trees, rain gardens, and porous pavement, rainwater harvesting cisterns, bioswales, etc.) can unlock for the commercial real estate sector, including commercial property owners and their tenants.
| Dec 19, 2013
Urban populations, climate change demand resilient design: Report
With over fifty percent of the population already living in urban areas, cities must grapple with the potentially catastrophic effects of climate change (think: Superstorm Sandy in New York). In a new report, Jones Lang LaSalle has identified steps cities can take to make their infrastructure more resilient to changing climate conditions.
| Dec 17, 2013
Nation's largest net-zero K-12 school among winners of 2013 Best of Green Schools award
The Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, was named a winner of USGBC's annual award, along with nine other schools, individuals and communities working toward the common goal of healthy, high-performing learning places.
| Dec 10, 2013
16 great solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
From a crowd-funded smart shovel to a why-didn’t-someone-do-this-sooner scheme for managing traffic in public restrooms, these ideas are noteworthy for creative problem-solving. Here are some of the most intriguing innovations the BD+C community has brought to our attention this year.
| Dec 9, 2013
What is life cycle cost optioneering?
Life cycle cost optioneering is a way of assessing alternative design options, analyzing their long-term capital and operational costs to identify those with the lowest price tag, over the entire life cycle.
| Nov 27, 2013
LEED for Healthcare offers new paths to green
LEED for Healthcare debuted in spring 2011, and certifications are now beginning to roll in. They include the new Puyallup (Wash.) Medical Center and the W.H. and Elaine McCarty South Tower at Dell Children’s Medical Center of Central Texas in Austin.
| Nov 25, 2013
Manufacturers race to offer EPDs, HPDs in response to LEED v4
Under LEED v4, projects are awarded points for using at least 20 building products that have issued Environmental Product Declarations or Health Product Declarations. In response, manufacturers are racing to offer EPDs and HPDs for their product lines.