The ubiquitous open office layout is “about to get a major makeover” that will emphasize coworking, personal development, and a reimaging of the workplace—including the role of the built environment and technology—with an eye toward putting workers first.
In its 90-page “2017 Global Workplace Trends” report, Sodexo—an international food services and facilities management provider whose 420,000 workers serve 10,000 companies in 80 countries—makes this prediction as part of a larger thesis that the ideal workplace is one that places a premium on its employees’ value, work-life balance, safety and comfort, health, and opportunities for growth.
Drawing on the knowledge and observations of 50 experts in business, academia, NGOs, research and trade groups, foundations and think tanks, Sodexo identifies three dynamics that are compelling changes in the workplace:
•The embrace of coworking, which structures work teams to be cross disciplinary;
•The “squashing” of generational stereotyping and the support of a culture of personal development, and
•A reimaging of the entire workplace, including the built environment, technology, and amenities, with the goal of improving conditions for workers.
“Technology and interactivity are increasingly shaping how people work as well as where,” the report states. “As work becomes more about adding value than cranking handles and pushing food carts, organizations are learning that communicating their values is imperative as their work to motivate and engage employees.”
Sodexo divides its 2017 report into 10 subject areas that touch on such topics as understanding the impact of migration on the workplace (the United Nations estimates that 3.3% of the world’s population are migrants, and 73% of them are working age), to how robotics is transforming the way people work (quoting a McKinsey Global Institute report that 45% of human work can be automated, and that two million jobs will be created by robots in the next eight years).
Designing people-focused workspaces
Readers from the AEC universe will take special note of the report’s chapters on how companies are putting design principles to work, and how they are unlocking Millennial talent.
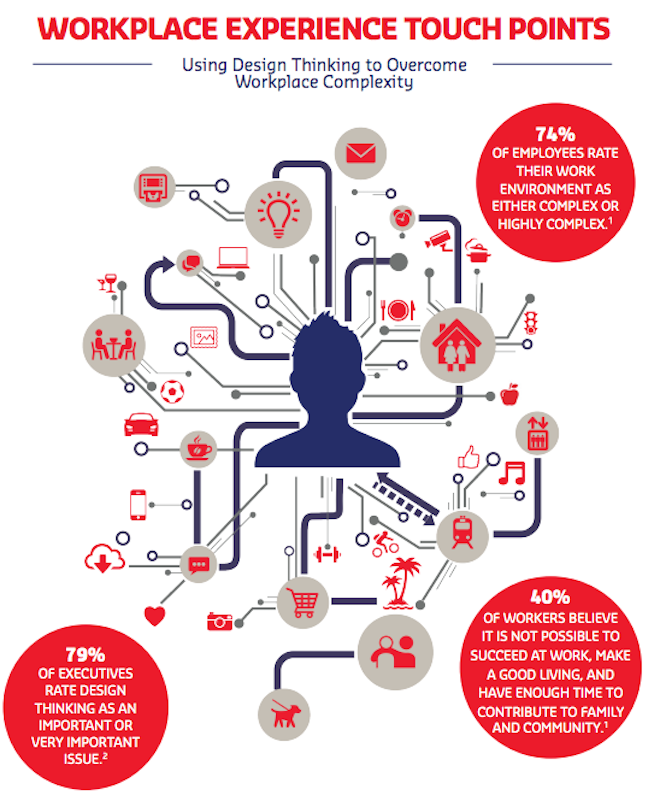 Many employees feel that their workplaces are too complex for them to succeed, or make it virtually impossible to balance their work and family lives. Image: Sodexo 2017 Global Workplace Trends.
Many employees feel that their workplaces are too complex for them to succeed, or make it virtually impossible to balance their work and family lives. Image: Sodexo 2017 Global Workplace Trends.
Sodexo cites Deloitte’s 2016 Global Human Capital Trends report, in which nearly 80% of executives surveyed rated “design thinking” an important or very important issue. And the current approach to experience design should be “the practice of designing a service, journey, or other component of the workplace with the focus on the employee throughout,” explains Dr. Rachel Permuth, Sodexo’s Global Vice President of Research-Corporate Services.
It’s imperative for companies to acknowledge that design thinking shouldn’t be confined within the four walls of an office. “The workplace experience begins at home, when workers are preparing to travel into the office, and ends when they are leaving for the day,” says Mark Newlands, Johnson & Johnson’s Global Workplace Experience Lead.
Good workplace design blurs the lines between work, play, and life. Health and well-being move to the foreground. And by improving a worker’s quality of life, the workplace experience can play a significant role in a company’s competing for and retaining their market’s best talent.
Design thinking also removes roadblocks that keep employees from being optimally efficient, and can overcome the perception among nearly three-quarters of employees polled that their work environments are overly complex. (In fact, two-thirds of companies also believe complexity is an obstacle to business success and productivity.)
Consequently, “getting buy-in from workers on design—i.e., reaching decisions collaboratively—yields the best design solutions and greatest acceptance from employees,” observes Randy Fiser, CEO of the American Society of Interior Designers.
The Sodexo report notes that as a people-centered, rather than process-centered, discipline, design thinking can be a catalyst for reorienting existing organizational roles. “HR, facilities management, corporate real estate, and IT should champion the discipline and tap into its signature skills of observation, empathy, and insight.”
How to make Millennials leaders: more mentorship
Millennials already make up a sizable portion of the global workforce, and could account for 75% of all employees by 2025. So companies ignore at their own peril a 2016 survey of 7,700 Millennials in 29 countries, which found that one in four would quit his or her job or do something different within the next year. (In fact, 20% of American Millennials did changes jobs within the past year.)
Part of the problem is the perception among Millennials that their jobs are dead ends. Another part of the problem is that what Millennials want is often hard to read: a 2014 survey of Millennials and Gen Z employees across 10 global markets found both generations saying healthcare was their most important benefit; two years later, in a follow-up study, their priorities had shifted to work flexibility—even though only 34% of companies now offer it.
Employers need to understand that what ultimately drives Millennials is the idea of YOLO: you only live once. “So the question for a Millennial becomes, if I only live once, why would I want to work for you?” says Crystal Kadakia, the author of “The Millennial Myth: Transforming Misunderstanding into Workplace Breakthroughs.”
While the consensus among employers is that Millennials make great managers, companies aren’t doing enough to prepare them for leadership roles. The 2016 Deloitte survey found that 63% of Millennials don’t believe their leadership skills are being fully developed. “Employers should be creating new experiences where Millennials can learn so they don’t feel like they’re stagnating,” says Elisabetg Kelan, Ph.D, Professor of Leadership at Cranfield University’s School of Management in the United Kingdom.
Kelan goes on to say that stagnation leads to disengagement, whose antidote is continuous feedback. “They have understood that only by receiving feedback can the be at the top of their game.”
Related Stories
Market Data | Jun 21, 2017
Design billings maintain solid footing, strong momentum reflected in project inquiries/design contracts
Balanced growth results in billings gains in all sectors.
Industry Research | Jun 15, 2017
Commercial Construction Index indicates high revenue and employment expectations for 2017
USG Corporation (USG) and U.S. Chamber of Commerce release survey results gauging confidence among industry leaders.
Industry Research | Jun 13, 2017
Gender, racial, and ethnic diversity increases among emerging professionals
For the first time since NCARB began collecting demographics data, gender equity improved along every career stage.
Industry Research | May 25, 2017
Project labor agreement mandates inflate cost of construction 13%
Ohio schools built under government-mandated project labor agreements (PLAs) cost 13.12 percent more than schools that were bid and constructed through fair and open competition.
Market Data | May 24, 2017
Design billings increasing entering height of construction season
All regions report positive business conditions.
Market Data | May 24, 2017
The top franchise companies in the construction pipeline
3 franchise companies comprise 65% of all rooms in the Total Pipeline.
Industry Research | May 24, 2017
These buildings paid the highest property taxes in 2016
Office buildings dominate the list, but a residential community climbed as high as number two on the list.
Market Data | May 16, 2017
Construction firms add 5,000 jobs in April
Unemployment down to 4.4%; Specialty trade jobs dip slightly.
Industry Research | May 4, 2017
How your AEC firm can go from the shortlist to winning new business
Here are four key lessons to help you close more business.
Engineers | May 3, 2017
At first buoyed by Trump election, U.S. engineers now less optimistic about markets, new survey shows
The first quarter 2017 (Q1/17) of ACEC’s Engineering Business Index (EBI) dipped slightly (0.5 points) to 66.0.