Bringing people back downtown and to shopping streets will require confidence that the health crisis is abating, and a future outbreak will be minimized. States are now starting to re-open retail, and California Governor Gavin Newsom announced this week that California is moving to Phase Two of the State’s re-opening strategy, which includes some retail stores, with restrictions.
A vaccine is perhaps many months (or even years) away, and widespread testing infeasible in the near future. Cities and communities will need to adjust public space to allow customers back in with distancing in mind. Restaurants present an opportunity that already has many indicators of success: repurpose sidewalks, street-side parking, and parking lots into outdoor dining areas.
Alfresco dining offers the community a way to enjoy the outdoors while supporting restaurants. There is evidence Coronavirus does spread while airborne, but it may lose strength with sun and warm weather. Outdoor dining areas could be popular as the warmer summer months approach, and they would provide the area needed for establishments to enact social distancing while maintaining feasible occupancy levels.
Main Streets are critical parts of our cities’ economies and social culture, and they will need support during recovery to bring people back. More outdoor dining will send a signal to consumers that it's safe to go back out, with people being the biggest attractor of people.
As reported by Jon Henley, in the Guardian, Lithuania’s capital, Vilnius, has announced plans to turn the city into a vast open-air cafe by giving over much of its public space to the hard-hit bar and restaurant owners so they can put their tables outdoors and still observe physical distancing rules.
Kerry Cavanaugh, Los Angeles Times editorial writer who is focused on housing, transportation, and the environment, advocates that when Los Angeles starts allowing businesses to reopen in the coming weeks and months, the city could take a cue from Lithuania. She writes, “Of course, Lithuania is very different from Los Angeles. But L.A. could take some inspiration from Vilnius’ willingness to experiment with public spaces to help the city return to some safer version of normalcy. How about closing off parking spots or lanes to cars on some neighborhood commercial strips, so restaurants and cafes could place more tables outside? Or perhaps closing some less-traveled streets so people have more space to exercise outdoors while still socially distancing?”
Parklets
This approach has already been proven effective in Parklet programs in Southern California, where some curbside parking spaces have been converted to dining or congregating areas. The current situation with reduced traffic and parking demand may reduce the inevitable resistance to taking away parking spaces for other uses – a situation cities should take advantage of.
The Long Beach Parklet Program began in 2011 as a tactical urbanism pilot project deployed by Studio One Eleven in partnership with the City of Long Beach and privately-owned, local businesses.
Parklets are now part of the fabric of the City of Long Beach and have been hailed by the city as increasing community and encouraging walking and biking within the city, and as effective in uplifting economically disadvantaged areas.
By constructing street decks or concrete bulb-outs to expand the sidewalk, Parklets convert existing curbside parking stalls into outdoor seating, community gathering spots, and even areas for fitness activities. Each Parklet is tailored to the unique characteristics of its retail business partner, creating a vibrant public realm. The Parklets provide dining space for existing restaurants to expand while remaining in place. Parklets act to calm traffic and encourage pedestrian activity. Each Parklet design addresses environmental sustainability with recyclable materials and bio-swales that repurpose stormwater.
Creating Flex Zones
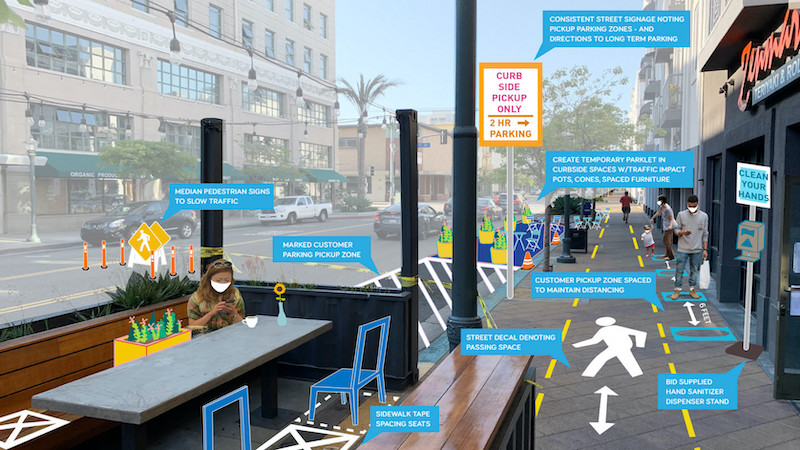
Cities can quickly establish retail and restaurant zones or ‘Flex Zones.’ Flex Zones are opportunities to provide temporary infrastructure similar to a Parklet, in a lighter, quicker, and cost-effective manner. Flex Zones serve to calm traffic while facilitating socially distanced dining and curbside pick-ups with cheerful surface graphics using materials such as spray chalk and stencils or even decals, along with modular structures and protective barriers like potted plants and water-filled k-rail. These are nimble ways to create temporary or longer-term outdoor zones that add atmosphere while establishing and communicating the new ways of interacting. Starting with the street, demarcation of crosswalks and added median structures and landscapes set the tone. Passenger loading zones (or restaurant take-out zones) can be clearly marked with consistent, easily recognizable, easily read signs that indicate passenger loading zone and its restraints, as well as direct drivers to the nearest long-term parking. In order to manage foot traffic for social distancing, a distancing lane on the sidewalk is marked for six feet while stations supply hand sanitizer to help stop the spread of infection.
Pop-up dining areas within these Flex Zones expand the capacity of a restaurant, enticing diners to the open-air seating that is pre-set for social distancing. The pop-up dining areas can be indicated with graphics that include where to sit and where not to sit. Cleaning standards and schedules are also posted. Flex Zones with dining areas can be created by repurposing existing streetside parking spots on traffic-calmed streets, the boundaries of the zone are set by using impact-resistant planters.
After an initial period of transition and pilot program, it is possible, or even likely, that perception will shift so communities will come to believe curbside space is actually too valuable for parking cars. These temporary zones can then be further developed as permanent parts of the urban fabric.
Relaxing Requirements
Cities can accelerate this movement by allowing for the conditional permitting of temporary zones and implementing pilot programs. These tactical interventions quickly and affordably make space for new uses that may include curbside pick-up and drop-off zones, pop-up dining, repurposing a vehicular travel lane or parking lane to create an extended sidewalk addressing the current demand on the public realm with the number of people walking right now for their mental health and exercise.
Temporary relaxing of permitting and licensing requirements will help facilitate the changes, and bring signs of much-needed vitality to shopping and dining districts, and most importantly, create conditions that serve to re-build restaurant patronage.
Examples of relaxed permitting and licensing abound, such as in California where wine, beer, and cocktails are now commonly offered on take-out menus, or as Henry Grabar writes in Slate: “In Brookhaven, a suburb of Atlanta, Mayor John Ernst has given restaurants permission to turn their parking into restaurant space. ‘For the next 90 days, Brookhaven will embrace alfresco dining,’ he said.”
A proven example, The Long Beach Parklet Program, which started as a pilot program, has inspired other cities in California and in Europe to inquire as to how to replicate the program in their respective cities. Now is the time to embrace this program and roll it out as a way to build community, encourage people out of their homes, and support the restaurant business and culture that is a distinctive part of what makes our cities cultural centers.


An existing Parklet, At Last Café in Long Beach, offers sidewalk dining, pictured here pre-Covid-19. The At Last Cafe Parklet site plan illustrates how this project, built as a bulb-out, added a four-way stop that calms traffic and encourages pedestrian activity.
Patrick West, Long Beach City Manager from 2007-2109, said, “One of the most unique and successful initiatives has been the Parklet Program, a great project for the City that demonstrated collaboration and a successful public-private partnership in place making. The impact and outcomes of the Program have been much more than just the retention of revenue and jobs. As a pioneering initiative, the Parklet Program garnered significant publicity and contributed to making the City of Long Beach a desirable place in Southern California.”
As a good idea generally for creating community, as Shelter-at-Home orders lift, this becomes an even better idea for reopening our cities.
About the Authors
Alan Pullman, AIA, is Founding Principal, and Shannon Heffernan, AICP, is Urban Design Director and Senior Associate with Studio One Eleven.
Related Stories
Augmented Reality | Jan 27, 2023
Enhancing our M.O.O.D. through augmented reality therapy rooms
Perkins Eastman’s M.O.O.D. Space aims to make mental healthcare more accessible—and mental health more achievable.
K-12 Schools | Nov 30, 2022
School districts are prioritizing federal funds for air filtration, HVAC upgrades
U.S. school districts are widely planning to use funds from last year’s American Rescue Plan (ARP) to upgrade or improve air filtration and heating/cooling systems, according to a report from the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council. The report, “School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic,” says air filtration and HVAC upgrades are the top facility improvement choice for the 5,004 school districts included in the analysis.
Giants 400 | Nov 14, 2022
4 emerging trends from BD+C's 2022 Giants 400 Report
Regenerative design, cognitive health, and jobsite robotics highlight the top trends from the 519 design and construction firms that participated in BD+C's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 20, 2022
Is telehealth finally mainstream?
After more than a century of development, telehealth has become a standard alternative for many types of care.
Coronavirus | May 20, 2022
Center for Green Schools says U.S. schools need more support to fight COVID-19
The Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council released a new report detailing how school districts around the country have managed air quality within their buildings during the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Industry Research | Mar 9, 2022
Survey reveals five ways COVID-19 changed Americans’ impressions of public restrooms and facilities
Upon entering the third year of the pandemic, Americans are not only more sensitive to germs in public restrooms, they now hold higher standards for the cleanliness, condition and technology used in these shared spaces, according to the annual Healthy Handwashing Survey™ from Bradley Corporation conducted in January.
Codes and Standards | Feb 21, 2022
New standard for ultraviolet germicidal irradiation
The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) recently introduced the standard, ANSI/IES RP-44-21 Recommended Practice: Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation.
Coronavirus | Jan 20, 2022
Advances and challenges in improving indoor air quality in commercial buildings
Michael Dreidger, CEO of IAQ tech startup Airsset speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield about how building owners and property managers can improve their buildings' air quality.
Coronavirus | Jul 20, 2021
5 leadership lessons for a post-pandemic world from Shawmut CEO Les Hiscoe
Les Hiscoe, PE, CEO of Shawmut, a $1.5 billion construction management company headquartered in Boston, offers a 5-point plan for dealing with the Covid pandemic.
Resiliency | Jul 15, 2021
A new report urges federal investment in healthier buildings
The National Institute of Building Sciences also calls for code changes and greater cooperation between building owners and the AEC community.