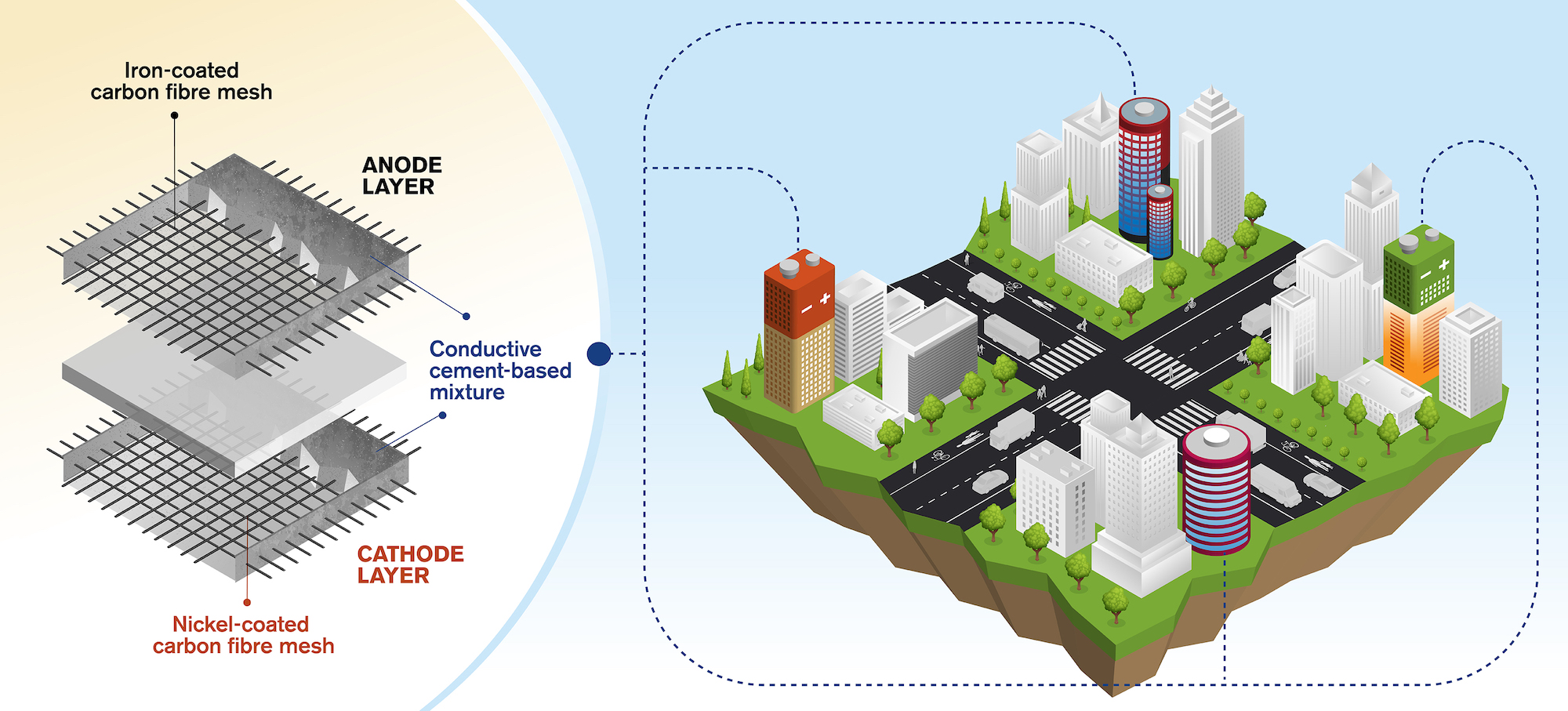
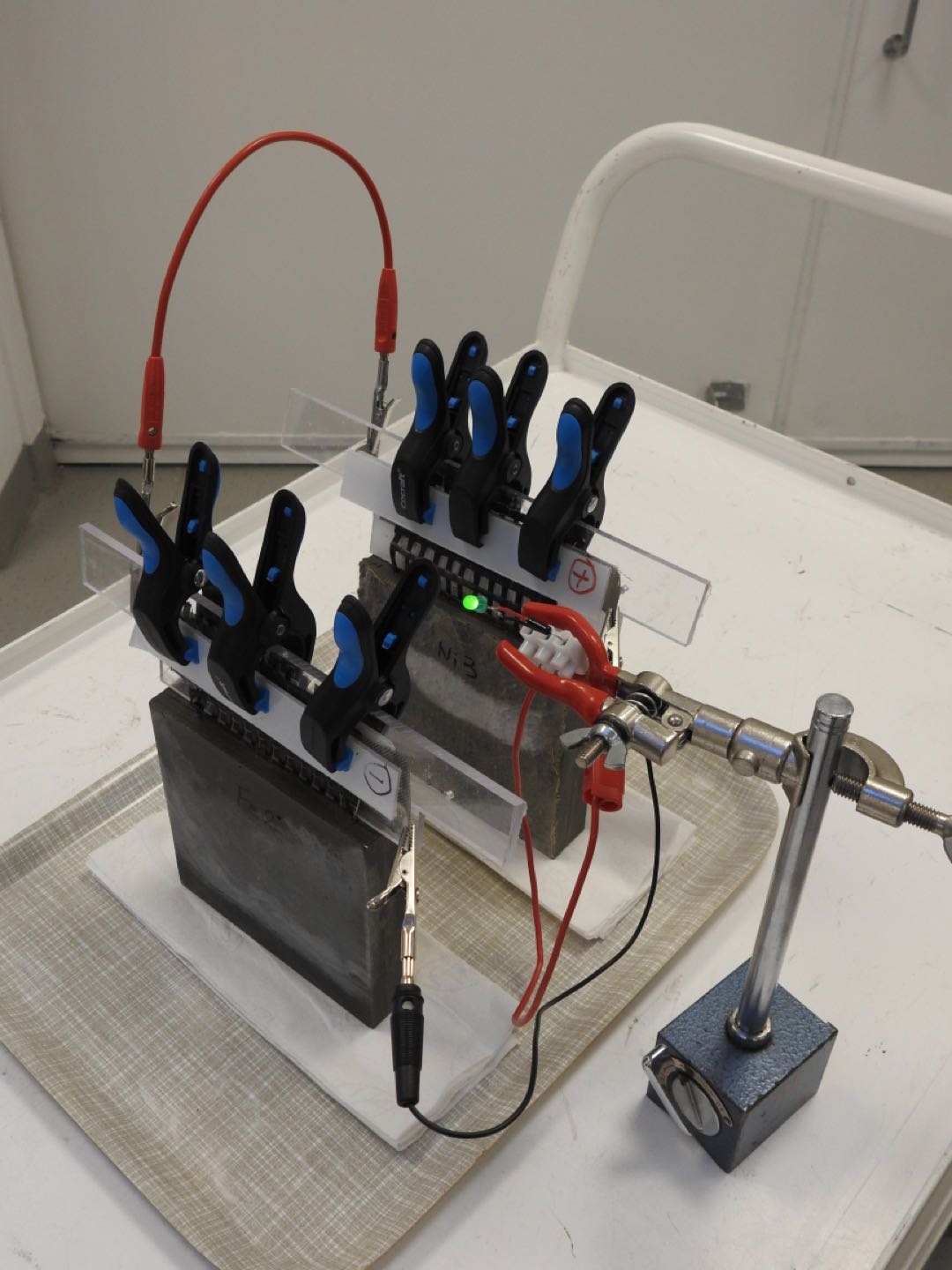
Researchers from the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering at Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden, have created a concept for rechargeable batteries made of cement.
The concept involves a cement-based mixture with small amounts of short carbon fibers added to increase conductivity and flexural toughness. Embedded within this mixture is a metal-coated carbon fiber mesh—iron for the anode and nickel for the cathode. Several combinations for the electrodes were tested before the iron anode and nickel-based oxide cathode were found to yield the best results. Additionally, researchers had to experiment with different ratios of carbon fiber before finding an optimal mixture of around 0.5% carbon fiber to improve the cement-based mixture’s conductivity for the electrolyte.
The resulting cement-based battery has an average density of 7 watt-hours per square meter during six charge and discharge cycles—low in comparison to commercial batteries, but still potentially very beneficial to the built environment considering the large volume at which the battery could be constructed when used in buildings, bridges, dams, and other concrete structures.
The research team—led by Chalmers Professor Luping Tang and Emma Zhang, PhD, formerly with the university, now Senior Development Scientist at Delta of Sweden—envisions possible applications for the concept that range from powering LEDs, providing 4G connections in remote areas, and cathodic protection against corrosion in concrete infrastructure.
“It could also be coupled with solar cell panels to provide electricity and become the energy source for monitoring systems in highways or bridges, where sensors operated by a concrete battery could detect cracking or corrosion,” said Zhang.
Technical questions that need to be answered before commercialization of the concrete technology include extending the service life of the battery and the development of recycling techniques. The batteries would need to either be able to match the 50-100 year life of a typical concrete building or be made easier to exchange and recycle when their service life is over.
Despite these obstacles, the researchers are optimistic the concept has plenty to offer as a future building material that contributes to additional functions such as renewable energy sources.
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Jan 19, 2016
Concrete innovation: voided biaxial slab slashes weight, saves concrete
System reduces slab dead load by 30% on medical clinic project
Great Solutions | Jan 19, 2016
Healing garden doubles as therapy trails
A Boston-area hospital takes the healing garden to the next level.
Great Solutions | Jan 14, 2016
WWII watchtower turned into ‘land yacht’
Architect Siemasko + Verbridge and contractor Windover Construction transformed a coastal wartime observation post into an amenity-filled guesthouse.
Great Solutions | Jan 12, 2016
Sprinkler system does double duty
Two innovations tap into the multi-use potential for fire/life safety infrastructure.
Great Solutions | Jan 7, 2016
Bacteria-killing paint and magnetic wallcovering highlight innovations in surface materials
Sherwin-Williams recently introduced Paint Shield, the first EPA-registered microbicidal paint that kills virtually all infection-causing bacteria after two hours of exposure on painted surfaces.
Great Solutions | Jan 6, 2016
Shepley Bulfinch develops elegant design solution to address behavioral issues in emergency departments
ED scheme allows staff to isolate unruly patients and visitors in a secure area.
Great Solutions | Jan 6, 2016
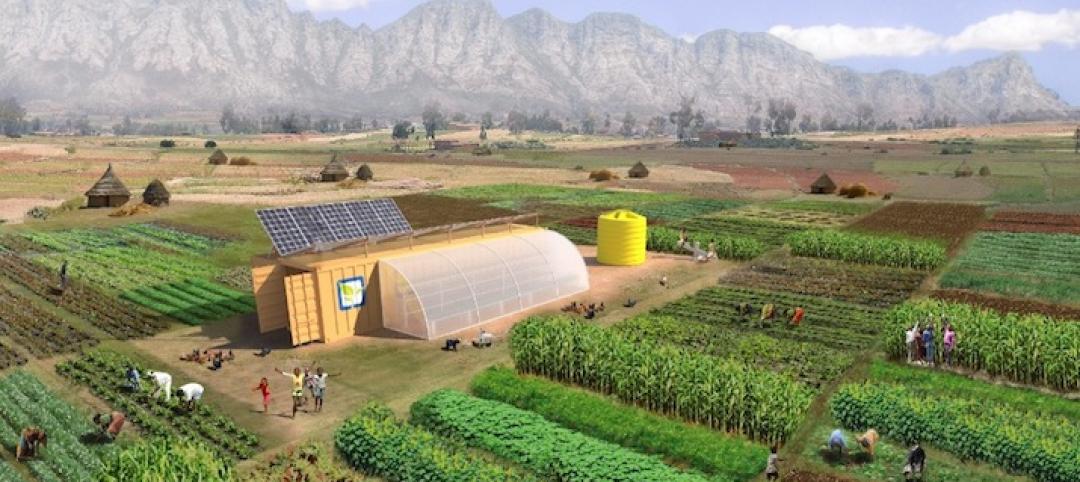
All-encompassing farming kit can provide communities with a sustainable food supply
Several manufacturers partnered with the group Farm from a Box to develop an off-the-grid farming solution for communities, all without the need for outside help.
Great Solutions | Jan 4, 2016
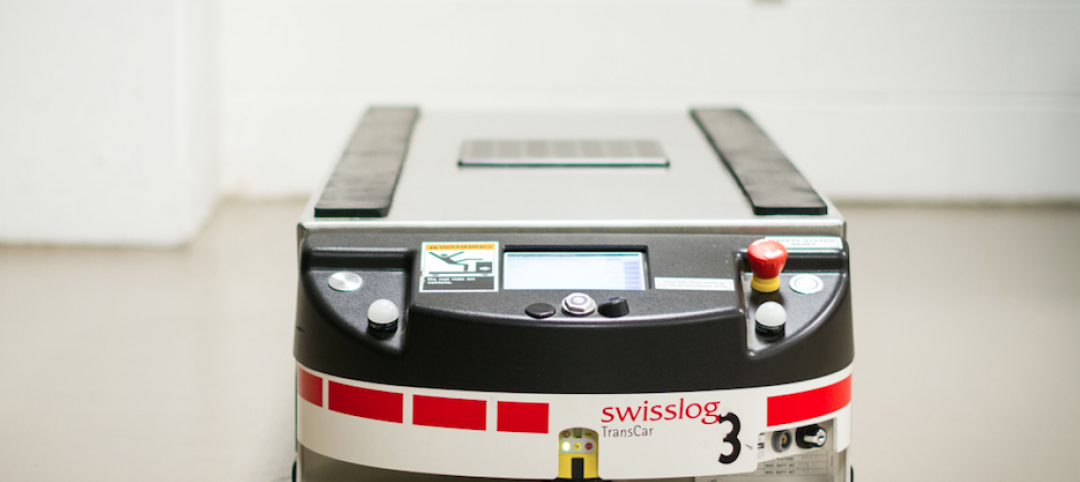
Toronto’s newest hospital employs 10 robots for moving food, supplies, and equipment
The 1.8 million-sf Humber River Hospital is loaded with high-tech gadgets. Its coolest innovation is the use of automated guided vehicles.
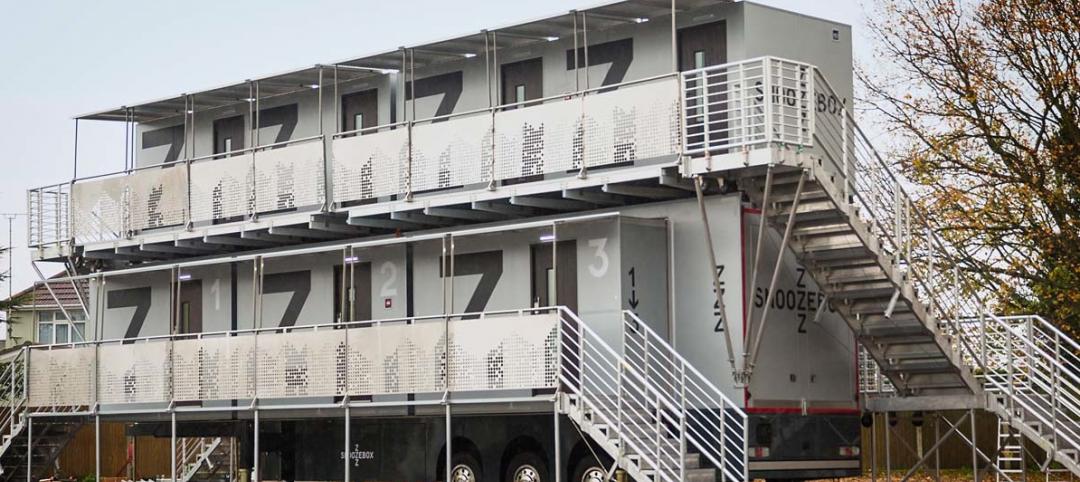
Great Solutions | Jan 4, 2016
Snoozebox’s portable hotel rooms make outside events more livable
Since 2011, the London-based company has thrived by creating portable hotels that are set up for the duration of open-air events (or longer), and offer many of the comforts of conventional hotels.