The Q3 2018 USG Corporation + U.S. Chamber of Commerce Commercial Construction Index (Index) released today indicates skilled labor shortages will have the greatest impact on commercial construction businesses over the next three years. The report revealed 88% of contractors expect to feel at least a moderate impact from the workforce shortages in the next three years with over half (57%) expecting the impact to be high/very high.
The skilled labor shortage has been consistently identified as a major issue facing the industry, but it is now reported by 80% of contractors to be impacting worker and jobsite safety. In fact, the Q3 report found that a lack of skilled workers was the number one factor impacting increased jobsite safety risks (58%).
"The commercial construction industry is growing but the labor shortage remains unresolved," said Jennifer Scanlon, president and CEO of USG Corporation. "As contractors are forced to do more with less, a renewed emphasis on safety is imperative to the strength and health of the industry. It continues to be important for organizations to build strong and comprehensive safety programs."
As contractors grapple with a scarcity of skilled workers, findings show a majority are working to improve the overall safety culture on the jobsite (63%) and at their firm's offices (58%). However, the indicators that were reported to have the highest impact on improving safety culture and outcomes are those that engage employees throughout the organization. This includes developing training programs for all levels of workers (67%), ensuring accountability across the organization (53%), empowering and involving employees (48%). Other indicators reported include improving communication (46%), demonstrating management's commitment to safety (46%), improving supervisory leadership (43%) and aligning and integrating safety as a value (42%).
In addition to the skilled labor shortage, the report found addiction and substance abuse issues are a factor in worker and jobsite safety. Nearly 40% of contractors are highly concerned over the safety impacts of worker use/addiction to opioids, followed by alcohol (27%) and marijuana (22%). Notably, the report showed that while nearly two-thirds of contractors have strategies in place to reduce the safety risks presented by alcohol (62%) and marijuana (61%), only half have strategies to address their top substance of concern: opioids, which is a newer growing concern. The opioid epidemic cost our economy $95 billion in 2016, and could account for approximately 20% of the observed decline in men's labor force participation.
"The opioid crisis has both human and economic costs," said Neil Bradley, chief policy officer of the U.S. Chamber. "The U.S. Chamber of Commerce remains committed to helping combat the opioid epidemic, which continues to devastate too many families, communities, and industries every day. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, a multipronged legislative approach is a critical first step."
Overall contractor sentiment saw a slight boost in optimism with an Index score of 75 in the third quarter – up two points from Q2 2018. The Index looks at the results of three leading indicators to gauge confidence in the commercial construction industry - backlog levels, new business opportunities and revenue forecasts – generating a composite index on the scale of 0 to 100 that serves as an indicator of health of the contractor segment on a quarterly basis.
The Q3 2018 results from the three key drivers were:
— Backlog: Optimal backlog rose from 73 to 81, the largest change in any of the three components of the CCI in the last six quarters. The average current backlog was 10.3 months, up from 9.3 last quarter.
— New Business: The level of overall confidence was 74, relatively steady quarter-over-quarter (75 in Q2 2018) but down two points since Q1 (76).
— Revenues: Expectations slipped from 72 to 69, the most notable change coming in a decrease in the percentage of contractors who now expect an increase in revenues, which dropped from 83% to 72%.
The research was developed with Dodge Data & Analytics (DD&A), the leading provider of insights and data for the construction industry, by surveying commercial and institutional contractors.
Related Stories
Market Data | Apr 20, 2021
Demand for design services continues to rapidly escalate
AIA’s ABI score for March rose to 55.6 compared to 53.3 in February.
Market Data | Apr 16, 2021
Construction employment in March trails March 2020 mark in 35 states
Nonresidential projects lag despite hot homebuilding market.
Market Data | Apr 13, 2021
ABC’s Construction Backlog slips in March; Contractor optimism continues to improve
The Construction Backlog Indicator fell to 7.8 months in March.
Market Data | Apr 9, 2021
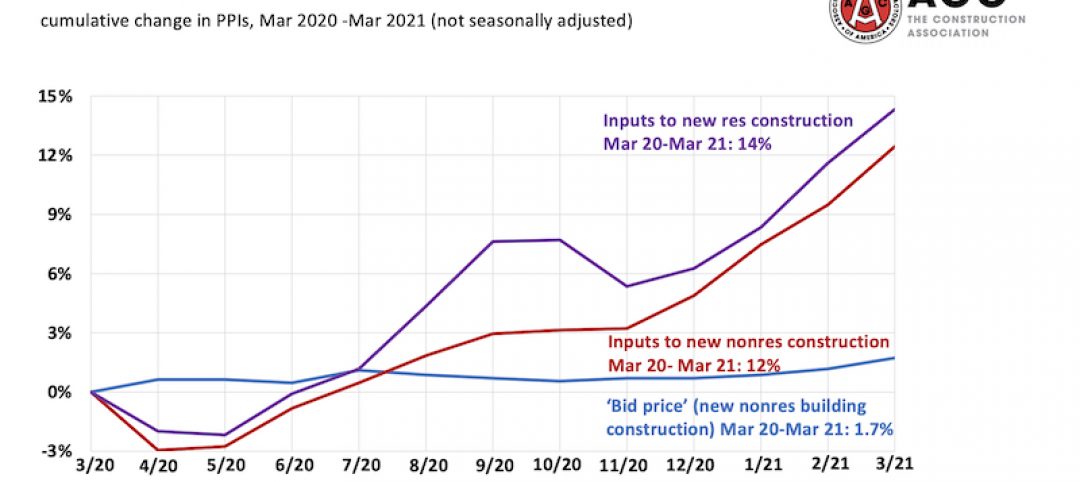
Record jump in materials prices and supply chain distributions threaten construction firms' ability to complete vital nonresidential projects
A government index that measures the selling price for goods used construction jumped 3.5% from February to March.
Contractors | Apr 9, 2021
Construction bidding activity ticks up in February
The Blue Book Network's Velocity Index measures month-to-month changes in bidding activity among construction firms across five building sectors and in all 50 states.
Industry Research | Apr 9, 2021
BD+C exclusive research: What building owners want from AEC firms
BD+C’s first-ever owners’ survey finds them focused on improving buildings’ performance for higher investment returns.
Market Data | Apr 7, 2021
Construction employment drops in 236 metro areas between February 2020 and February 2021
Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land and Odessa, Texas have worst 12-month employment losses.
Market Data | Apr 2, 2021
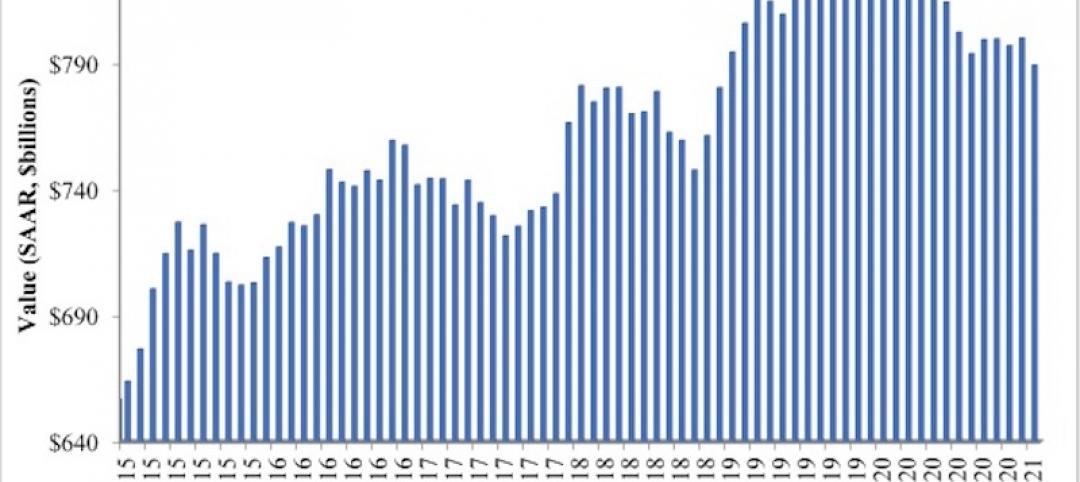
Nonresidential construction spending down 1.3% in February, says ABC
On a monthly basis, spending was down in 13 of 16 nonresidential subcategories.
Market Data | Apr 1, 2021
Construction spending slips in February
Shrinking demand, soaring costs, and supply delays threaten project completion dates and finances.
Market Data | Mar 26, 2021
Construction employment in February trails pre-pandemic level in 44 states
Soaring costs, supply-chain problems jeopardize future jobs.