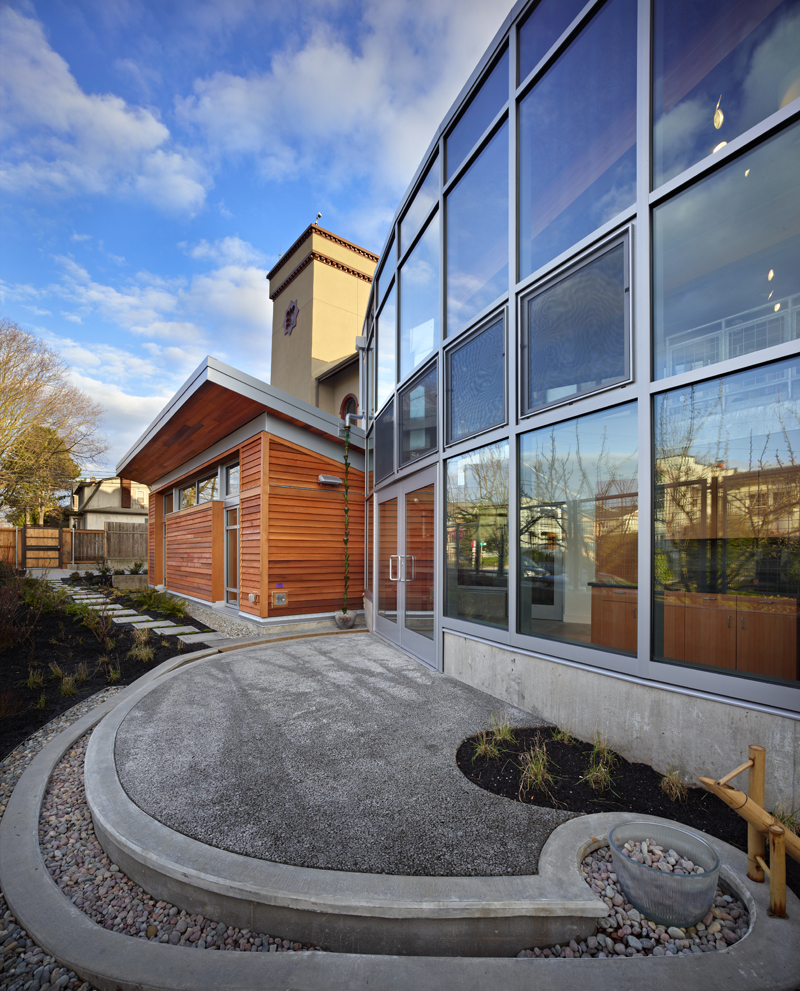
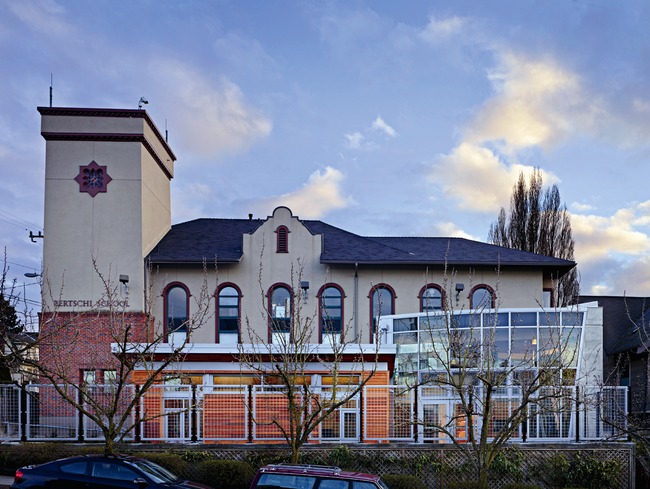
SEATTLE, WASH.—April 15, 2013— Bertschi School, an independent elementary school in the Capitol Hill neighborhood of Seattle, Wash., is now home to the first Living Building on the West Coast and the world’s fourth fully-certified Living Building. Completed in February 2011, Bertschi’s Living Building Science Wing is a 3,380 square foot interactive learning environment for students ages 5-11. It is the first built project to meet the standards of version 2.0 of the Living Building ChallengeSM, a green building certification program which integrates urban agriculture, social justice and universal access issues, and the use of healthy building materials.
A program of the International Living Future Institute, the Living Building Challenge(LBC) is widely considered the world’s most rigorous building performance standard. A Living Building generates all of its own energy through clean, renewable resources; captures and treats its own water; incorporates only non-toxic, appropriately sourced materials; and operates efficiently and for maximum beauty. A building must perform as designed for one full year of occupancy and pass a third-party audit before receiving certification as “Living.”
Conceptualized with significant teacher and student input, the Science Wing serves as the ultimate tool for teaching science and sustainability. Students participate in real-time monitoring of the building’s energy and water use to understand sustainable practices and witness the impact of their daily choices on the building’s performance.
"At Bertschi School, we are committed to educating children to become thoughtful stewards of their local and global communities,” said Brigitte Bertschi, Head of Bertschi School. “We are not simply teaching about how to responsibly manage resources. The Science Wing allows students to put our curriculum to authentic use. I am proud that our children are empowered to make a difference at a very young age — even if it is a small one."
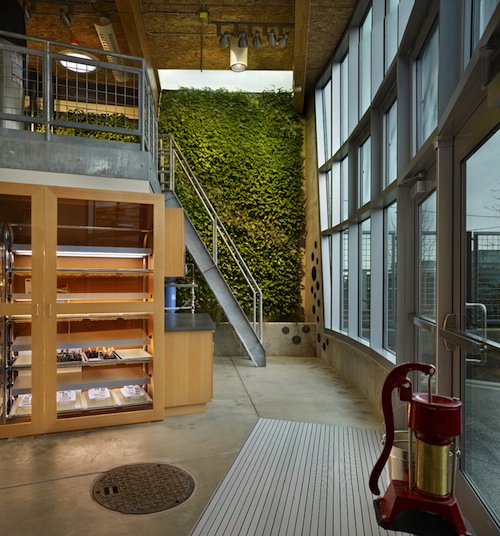
Bertschi School’s Science Wing sits on an urban site with an ethnobotanical garden that serves as an outdoor classroom. With its indigenous northwest plants, the garden enables students to learn about native culture and history, as well as use plant material in their art classes, such as berries for paint dyes and grasses used to fashion paint brushes. Food produced in this garden — and in the neighboring vegetable garden on-site — helps educate students about the values of organic farming and growing food.
The building’s sustainable features are visible and functional to foster dynamic learning opportunities. It is net-zero energy and water; a 20 kilowatt photovoltaic system provides all of the electricity, and cisterns collect rainwater that is used for irrigation and flushing the composting toilet. Excess captured water is absorbed by the on-site rain garden. Other water-saving features include a green roof and an interior living wall of tropical plants, which treats all of the building’s grey water.
The design of the Science Wing derived from a partnership between Bertschi School and the Restorative Design Collective, a multi-disciplinary team led by KMD Architects and comprised of leading Pacific Northwest green building professionals. The Collective contributed their design services pro-bono, with donations amounting to more than $500,000 in professional time and building materials.
“The challenges in creating truly net-zero energy and water buildings help all of us understand the integrative and continual efforts that are necessary to achieve the high-performance buildings that our changing planet requires,” said Stacy Smedley of KMD Architects, co-founder of the Restorative Design Collective.
In order to meet LBC standards, Skanska USA’s green building team navigated the strict material requirements to source building products that did not contain any of the materials or chemicals on the LBC Red List. One of the greatest challenges in this effort was finding local manufacturers and vendors who were fully transparent about the chemical makeup of their products. The use of healthy materials promotes better indoor air quality, as well as furthers transparency in the building materials industry.
“The Living Building Challenge is creating a major shift in the built environment — just as LEED did 10 years ago,” said Chris Toher, executive vice president and general manager at Skanska USA Building. “Thanks to the Restorative Design Collective, the Bertschi Living Building Science Wing is a model for sustainability in construction, and has challenged our industry to push for more net-zero buildings in our region and beyond.”
"The Bertschi School Science Wing has met the highest standard for sustainable performance, and is a powerful model for school additions all over the globe,” said Jason F. McLennan, CEO of the International Living Future Institute. “The International Living Future Institute is extremely proud of the huge accomplishments of this wonderful academic project."
Bertschi School is located at 2227 10th Ave. East in Seattle. Tours of the Living Science Building will be available to attendees of this year’s Living Future unConference, the International Living Future Institute’s 7th annual green building summit taking place May 15-17 at the Westin Seattle. Additional tours will be offered by the school throughout the year. More information is available in the International Living Future Institute’s Living Building case study.
About Bertschi School
An independent elementary school known for its integrated, innovative program, Bertschi School has a strong commitment to sustainability and incorporates this focus into both its curriculum and operations. In 2007, the school completed construction on its main building, The Bertschi Center, which is the first LEED Gold certified elementary classroom building in Washington State. www.bertschi.org
About the Restorative Design Collective
The Restorative Design Collective was founded in 2009 by Stacy Smedley and Chris Hellstern of KMD Architects. The Collective recognizes and endeavors to further the Living Building Challenge, which plays an essential role in raising green building standards, meeting the 2030 Challenge and creating net-zero buildings. Members of the Collective and its collaborators include: GGLO, landscape architect; 2020 Engineering, civil engineer; Back to Nature Design LLC, food systems consultant; GeoEngineers, geotechnical engineer; Morrison Hershfield, envelope consultant; O’Brien and Company, sustainable design consultant; Quantum Consulting Engineers, structural engineer; Rushing, mechanical-electrical-plumbing engineer; Skanska USA Building, general contractor; and Parsons Public Relations, as well as the City of Seattle and King County. KMD’s strong commitment to research-based design and collaboration fostered the opportunity to bring together a group of Seattle-area design professionals who share the desire to push themselves and their firms to the forefront of the sustainable building movement and create a built case study of a Living Building.
About the International Living Future InstituteSM and the Living Building ChallengeSM
The International Living Future Institute is an environmental NGO committed to catalyzing the transformation toward communities that are socially just, culturally rich and ecologically restorative. The Institute is premised on the belief that providing a compelling vision for the future is a fundamental requirement for reconciling humanity’s relationship with the natural world. The Institute operates the Living Building Challenge, the built environment’s most rigorous performance standard, and Declare, an ingredients label for building materials. It also houses the Cascadia Green Building Council and Ecotone Publishing.
The Living Building Challenge, the Institute’s best-known program, calls for the creation of a built environment that is as elegant and efficient as nature’s architecture. To be certified under the Challenge, a project must demonstrate that it has achieved 20 rigorous imperatives including net-zero energy, waste and water and alignment with a Red List of worst-in-class materials. The Challenge is the 2012 winner of the Buckminster Fuller Prize.
Related Stories
Building Technology | Jun 18, 2024
Could ‘smart’ building facades heat and cool buildings?
A promising research project looks at the possibilities for thermoelectric systems to thermally condition buildings, writes Mahsa Farid Mohajer, Sustainable Building Analyst with Stantec.
University Buildings | Jun 18, 2024
UC Riverside’s new School of Medicine building supports team-based learning, showcases passive design strategies
The University of California, Riverside, School of Medicine has opened the 94,576-sf, five-floor Education Building II (EDII). Created by the design-build team of CO Architects and Hensel Phelps, the medical school’s new home supports team-based student learning, offers social spaces, and provides departmental offices for faculty and staff.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Mass Timber | Jun 17, 2024
British Columbia hospital features mass timber community hall
The Cowichan District Hospital Replacement Project in Duncan, British Columbia, features an expansive community hall featuring mass timber construction. The hall, designed to promote social interaction and connection to give patients, families, and staff a warm and welcoming environment, connects a Diagnostic and Treatment (“D&T”) Block and Inpatient Tower.
Concrete Technology | Jun 17, 2024
MIT researchers are working on a way to use concrete as an electric battery
Researchers at MIT have developed a concrete mixture that can store electrical energy. The researchers say the mixture of water, cement, and carbon black could be used for building foundations and street paving.
Codes and Standards | Jun 17, 2024
Federal government releases national definition of a zero emissions building
The U.S. Department of Energy has released a new national definition of a zero emissions building. The definition is intended to provide industry guidance to support new and existing commercial and residential buildings to move towards zero emissions across the entire building sector, DOE says.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 14, 2024
AEC inspections are the key to financially viable office to residential adaptive reuse projects
About a year ago our industry was abuzz with an idea that seemed like a one-shot miracle cure for both the shockingly high rate of office vacancies and the worsening housing shortage. The seemingly simple idea of converting empty office buildings to multifamily residential seemed like an easy and elegant solution. However, in the intervening months we’ve seen only a handful of these conversions, despite near universal enthusiasm for the concept.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 13, 2024
Top 10 trends in the hospital facilities market
BD+C evaluated more than a dozen of the nation's most prominent hospital construction projects to identify trends that are driving hospital design and construction in the $67 billion healthcare sector. Here’s what we found.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 13, 2024
4 ways to transform old buildings into modern assets
As cities grow, their office inventories remain largely stagnant. Yet despite changes to the market—including the impact of hybrid work—opportunities still exist. Enter: “Midlife Metamorphosis.”
Affordable Housing | Jun 12, 2024
Studio Libeskind designs 190 affordable housing apartments for seniors
In Brooklyn, New York, the recently opened Atrium at Sumner offers 132,418 sf of affordable housing for seniors. The $132 million project includes 190 apartments—132 of them available to senior households earning below or at 50% of the area median income and 57 units available to formerly homeless seniors.