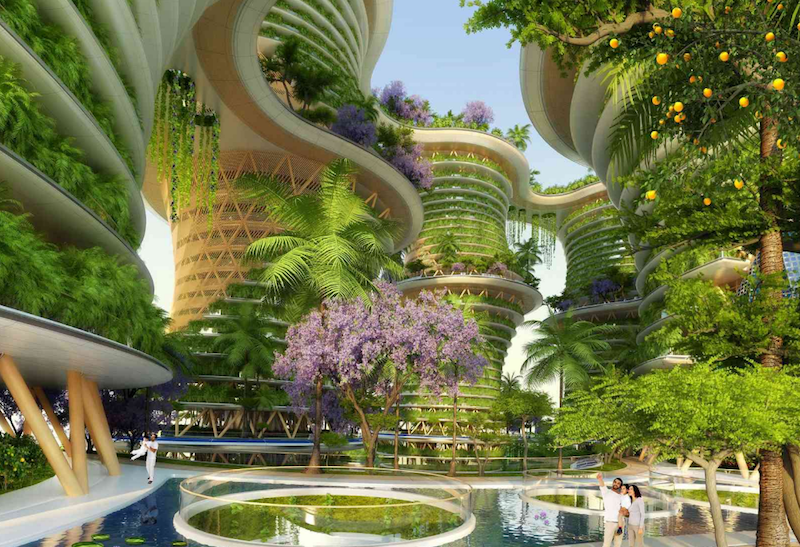
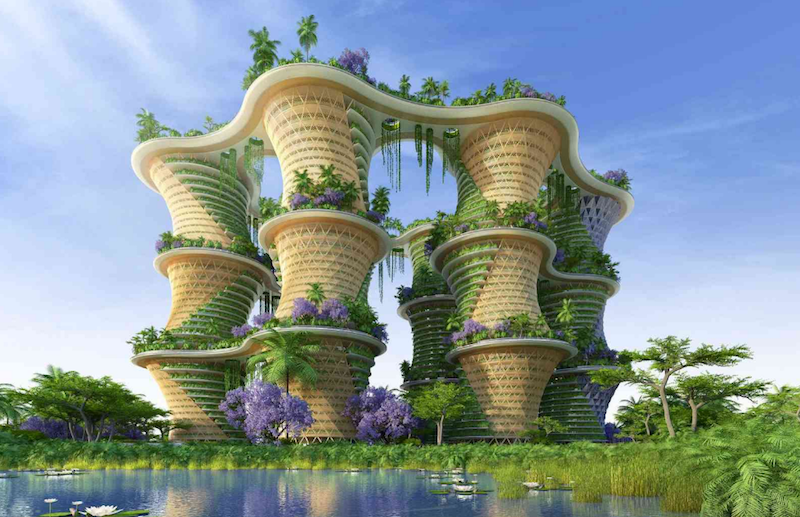
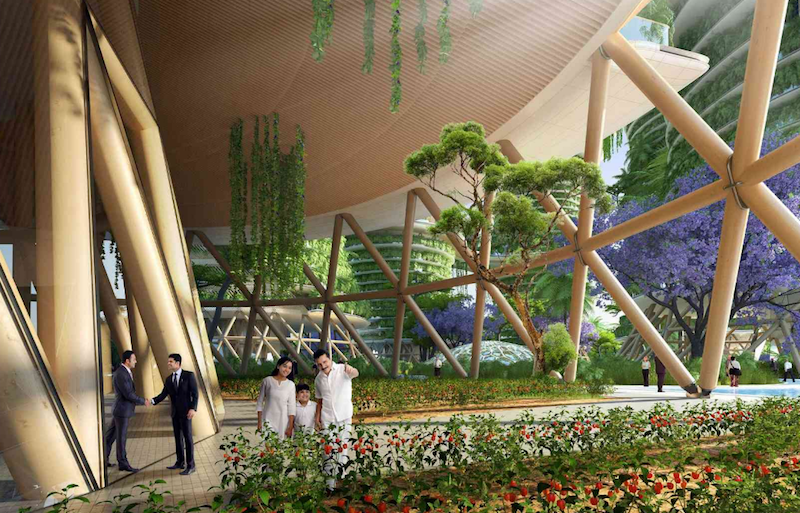
A new six-tower mixed-use project from Vincent Callebaut Architectures would incorporate community orchards, food gardens, and phytopurification lagoons in an attempt to build a sustainable and eco-friendly community. Named Hyperions after the world’s tallest tree (a Northern California Sequoia sempervirens that’s specific location is kept secret), the New Delhi-located project would be built out of cross-laminated timber (CLT) before being covered with food-producing gardens.
The wood required to build the towers would come from a sustainably managed Delhi forest. The buildings would be made from a superstructure of solid wood columns, beams, and walls and would be reinforced with steel blades where columns and beams meet. There would also be a steel and concrete substructure for earthquake resiliency. In total, Hyperions’ skeleton would be made of 25% inert materials and 75% bio-sourced materials.
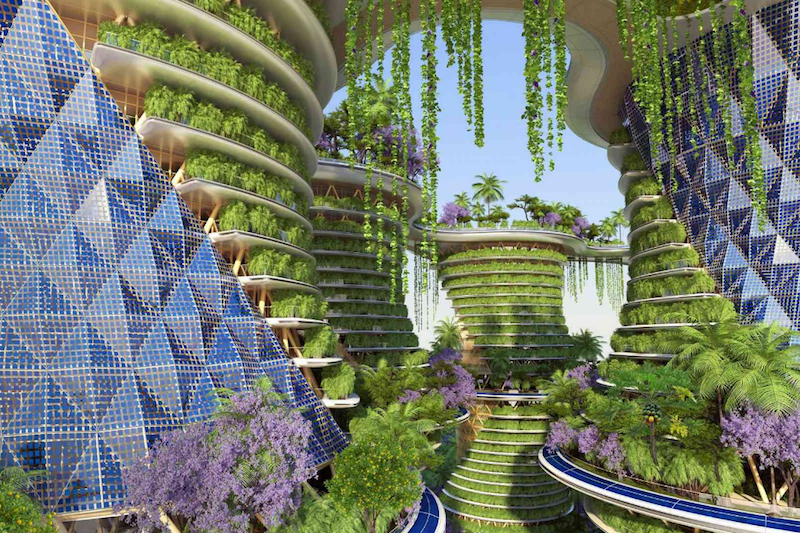
The buildings will use solar facades with photovoltaic and thermal scales that follow the course of the sun throughout the day to generate the towers; electricity needs. In addition, wind lampposts would be incorporated to produce electricity via magnetic-levitation, vertical-axis wind turbines integrated on their pole.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
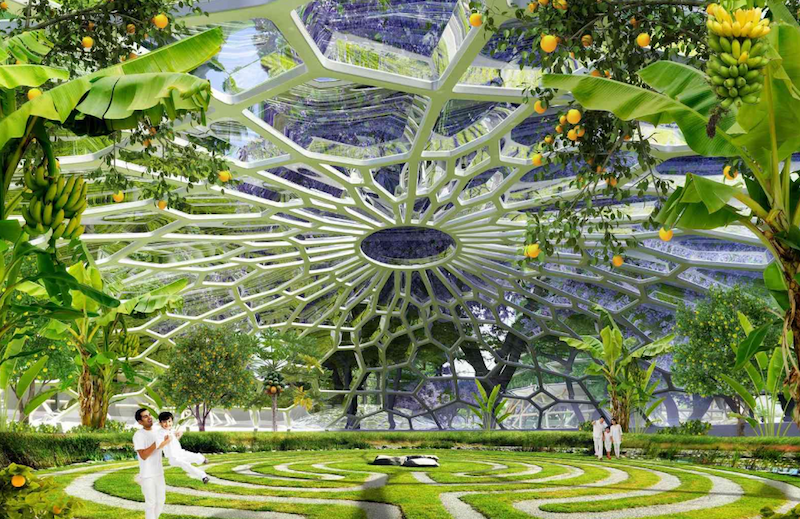
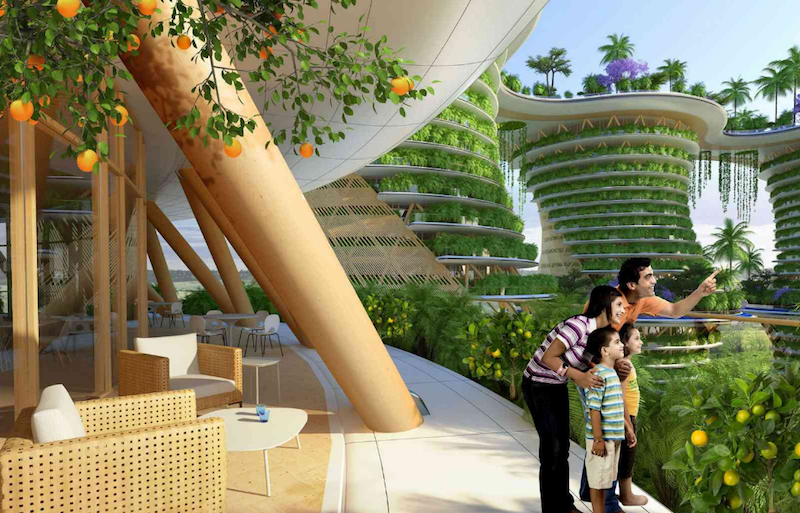
Each residential unit within the six towers would have vegetables and herbs such as carrots, tomatoes, spinach, saffron, and coriander growing on the balconies. There will also be an abundance of fruits and vegetables growing in hydroponic greenhouses. These plants will be irrigated with water from ponds housing several different species of fish. The waste from the fish, which is naturally rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, would help fertilize the plants. When accounting for plants in greenhouses, on balconies, and anywhere else they may be growing on the six towers (which is pretty much everywhere), the architects believe the buildings will be able to produce an annual output of four pounds of organic fruit and vegetables per square foot.
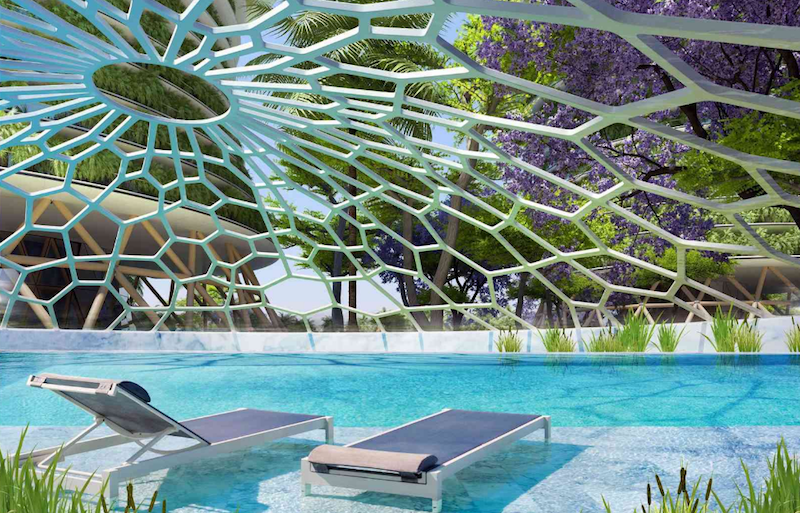
The roofs of each tower, joined together by skybridges, will be used as a large orchard space that doubles as a meeting space for the community. There will also be areas for sports, an organic pool, and playgrounds.
Heating and cooling is controlled via a natural climate control system articulated along the vertical circulation cores of wind chimneys. The system takes advantage of the earth’s thermal inertia under the foundations, which remains at a stable 64 degrees year round.
In addition to the residential spaces in each tower, business incubators, living labs, co-working spaces, and multipurpose rooms are all included. The project hopes to create more energy than it uses while also accomplishing its main objectives of energy decentralization and food deindustrialization.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
 Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Rendering courtesy of Vincent Callebaut Architectures.
Related Stories
Green | Nov 13, 2022
NREL report: Using photovoltaic modules with longer lifetimes is a better option than recycling
A new report from the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) says PV module lifetime extensions should be prioritized over closed-loop recycling to reduce demand for new materials.
Green | Nov 13, 2022
Global building emissions reached record levels in 2021
Carbon-dioxide emissions from building construction and operations hit an all-time high in 2021, according to the most recent data compiled by the Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction.
University Buildings | Nov 13, 2022
University of Washington opens mass timber business school building
Founders Hall at the University of Washington Foster School of Business, the first mass timber building at Seattle campus of Univ. of Washington, was recently completed. The 84,800-sf building creates a new hub for community, entrepreneurship, and innovation, according the project’s design architect LMN Architects.
Industry Research | Nov 8, 2022
U.S. metros take the lead in decarbonizing their built environments
A new JLL report evaluates the goals and actions of 18 cities.
Green | Nov 8, 2022
USGBC and IWBI will develop dual certification pathways for LEED and WELL
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) and the International WELL Building Institute (IWBI) will expand their strategic partnership to develop dual certification pathways for LEED and WELL.
Wood | Nov 1, 2022
A European manufacturer says its engineered wood products can store carbon for decades
Metsä Wood, a Finland-based manufacturer of engineered wood products, says its sustainable, material-efficient products can store carbon for decades, helping to combat climate change.
40 Under 40 | Oct 19, 2022
Meet the 40 Under 40 class of 2022
Each year, the editors of Building Design+Construction honor 40 architects engineers, contractors, and real estate developers as BD+C 40 Under 40 awards winners. These AEC professionals are recognized for their career achievements, passion for the AEC profession, involvement with AEC industry organizations, and service to their communities.
Green | Oct 5, 2022
In California, a public power provider’s new headquarters serves as a test case for an innovative microgrid and for reducing greenhouse gas emissions
Sonoma Clean Power (SCP), the public power provider for California’s Sonoma and Mendocino Counties, recently unveiled its new all-electric headquarters.
Resiliency | Sep 30, 2022
Designing buildings for wildfire defensibility
Wold Architects and Engineers' Senior Planner Ryan Downs, AIA, talks about how to make structures and communities more fire-resistant.
| Sep 23, 2022
High projected demand for new housing prompts debate on best climate-friendly materials
The number of people living in cities could increase to 80% of the total population by 2100. That could require more new construction between now and 2050 than all the construction done since the start of the industrial revolution.