In the rush to slash energy consumption in power-hungry data centers, design teams, equipment manufacturers, and tech companies have been developing clever, low-energy cooling solutions—from Facebook’s open-rack server setup with exposed motherboards, to Skanska’s eOPTI-TRAX liquid refrigerant coil system, to Google’s evaporative cooling schemes.
Solutions like these have helped data center facility operators achieve unprecedented energy performance levels, with power utilization effectiveness (PUE) ratios dipping below 1.10 in some instances. This means that less than 10% of the total energy consumption in a facility is attributed to noncomputing functions, such as air-conditioning and lighting.
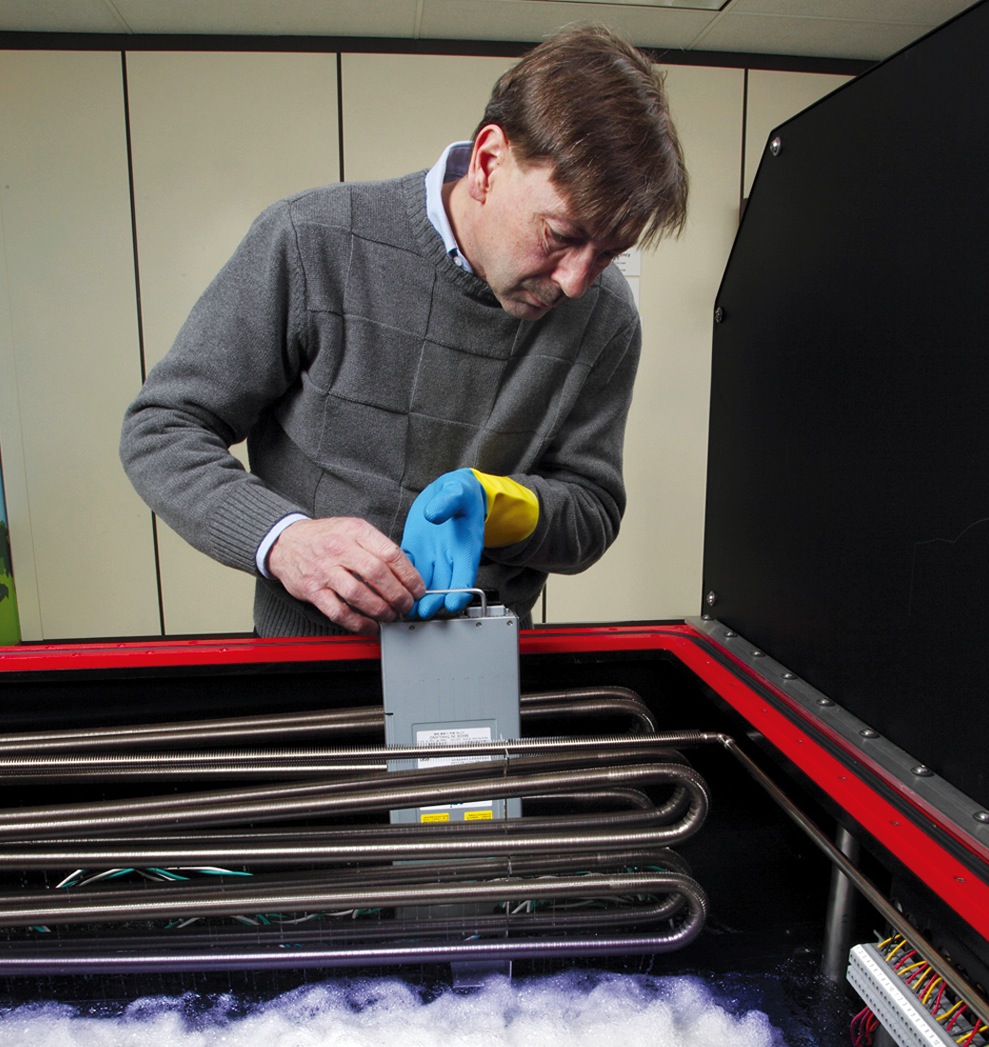
Now, a new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency even further. Called immersive cooling, it uses a liquid instead of air to cool the servers. LiquidCool Solutions, Green Revolution, and 3M are among the pioneers of this technology. Each system works a bit differently, but the basic idea is to submerge the motherboards in tanks filled with nonconductive fluid, which absorbs the heat generated by the processors.
LiquidCool Solutions, for example, uses an enclosed server module and pumps dielectric fluid through the server enclosure. Green Revolution uses a tub full of dielectric oil and circulates the liquid through the tubs. 3M also uses the tub approach, but the fluid boils and then is condensed to reject the heat.
By using liquid-based cooling at the server level, the need for air-conditioning is greatly reduced, or even eliminated in some climates. The same goes for traditional HVAC equipment and systems—chillers, fan units, raised floors, and so on.
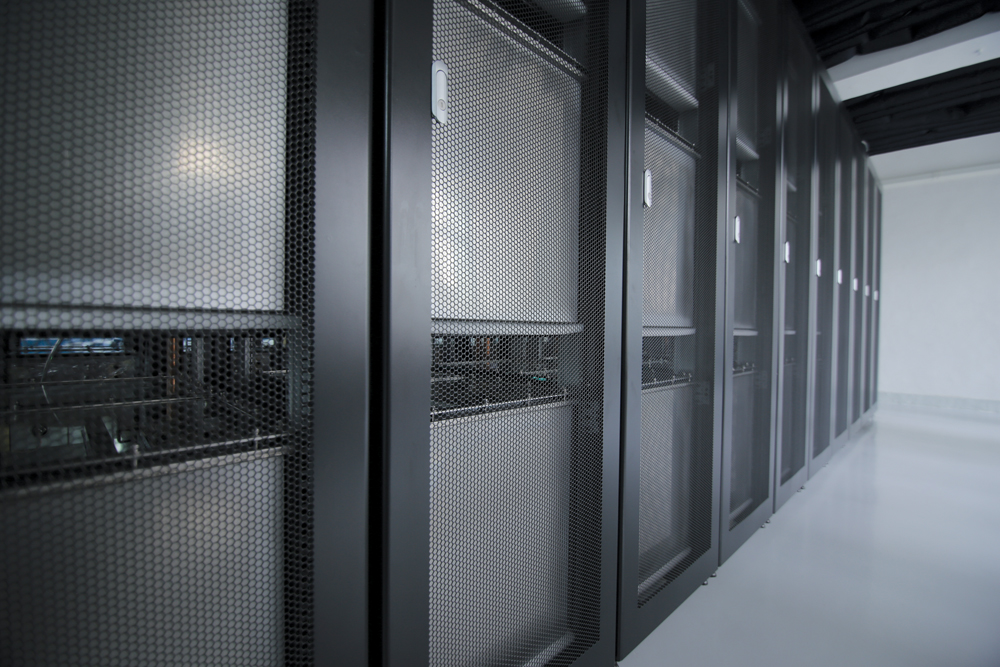

The Allied Control 500 kW immersion-cooled data center in Hong Kong is capable of delivering a PUE of just 1.02. The standard, 19-inch server racks use 3M Novec Engineered Fluids to enable tight component packaging for greater computing power in less space, according to Allied. Its open-bath design permits easy access to hardware and eliminates the need for pressure vessel enclosures and charging/recovery systems. PHOTO: COURTESY ALLIED CONTROL
“In most parts of the world, compressorized cooling would not be required with immersive cooling, since the liquid temperatures can be at a level where direct heat rejection using outdoor condensers or cooling towers would be sufficient,” says Thomas Squillo, PE, LEED AP, Vice President with Environmental Systems Design, who is currently researching the technology for the firm’s data center clients. “The fan energy is also eliminated, both in the HVAC system and in the server itself. Fluid pumping energy is very low.”
Other advantages of the cooling technology, according to Squillo:
• Increased performance and service life of the computer chips by eliminating heat buildup and problems related to contaminated air and dust.
• Ability to deploy data centers in extremely harsh environments without greatly impacting energy performance.
• Potential construction cost savings by downsizing or eliminating traditional HVAC systems.
Other than a few pilot projects, including a Bitcoin mining data center in Hong Kong and a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory-led installation in Chippewa Falls, Wis., immersive cooling technology is largely untested. A year into the Bitcoin pilot, the data center operator reported a 95% reduction in cooling costs.
AEC professionals are starting to realize the potential for immersive cooling, especially for high-performance computing centers and consolidated, high-density data centers.
“Large data centers that have many homogenous machines at high density—like those operated by Internet and cloud providers—are a good application,” says Squillo. “Small footprint and minimal energy use are very important due to the volume of servers. These can be deployed in remote areas where space and energy are cheap, but where air quality may be a concern, without having to worry about the data center air.”
TRICKY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Before the technology can be implemented, says Squillo, several nettlesome design factors specific to immersive cooling have to be addressed:
• Piping distribution to the racks and cooling units requires redundancy and valving to accommodate equipment maintenance without disrupting server performance.
• Additional equipment and space are needed to drain fluid from the tanks for server maintenance.
• Local code requirements may limit the amount of fluid that can be stored in a single room.
• For the foreseeable future, it’s unlikely that a large data center would be 100% liquid-immersion cooled. This means provisions will have to be made for both air- and liquid-cooling systems, which will require additional space in the data hall and mechanical room.
“I think that some form of this technology will definitely be the direction the data center market will take in the future,” says Squillo. “The market just needs to mature enough for owners to trust the technology and demand servers that are designed for a particular type of liquid cooling. In the short term, I see large companies and server manufacturers doing small-scale installations to test the concept, before wanting to implement it at a large scale.”
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 35 Veterans Affairs Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
LEO A DALY, Page Southerland Page, Guidon, and HDR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest Veterans Affairs facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 40 Military Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
Michael Baker International, HDR, Whitman, Requardt & Associates, and Stantec top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest military facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Office Buildings | Dec 12, 2023
Transforming workplaces for employee mental health
Lauren Elliott, Director of Interior Design, Design Collaborative, shares practical tips and strategies for workplace renovation that prioritizes employee mental health.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 150 Local Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HOK, Stantec, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest local government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 90 State Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Page Southerland Page, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Stantec, and NORR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest state government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Codes and Standards | Dec 11, 2023
Washington state tries new approach to phase out fossil fuels in new construction
After pausing a heat pump mandate earlier this year after a federal court overturned Berkeley, Calif.’s ban on gas appliances in new buildings, Washington state enacted a new code provision that seems poised to achieve the same goal.
Green | Dec 11, 2023
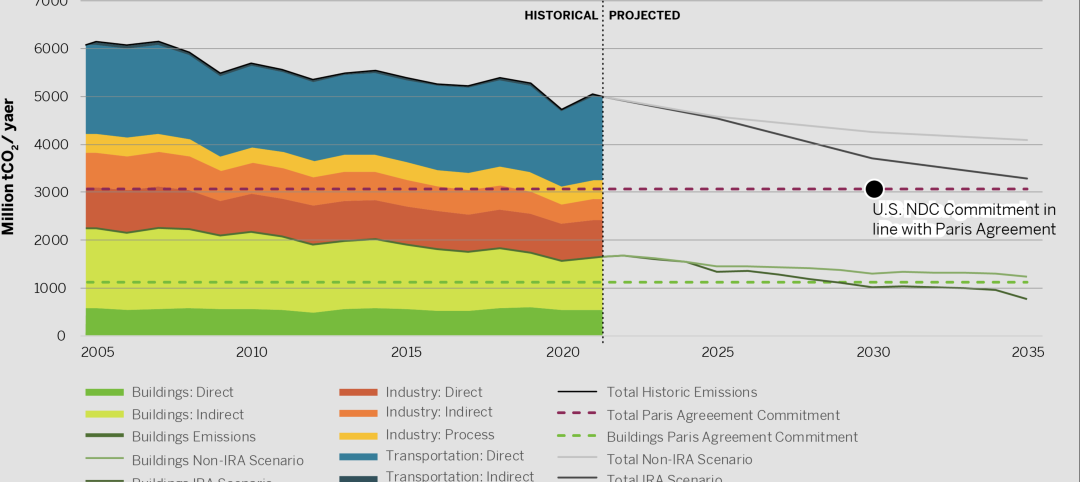
U.S. has tools to meet commercial building sector decarbonization goals early
The U.S. has the tools to reduce commercial building-related emissions to reach target goals in 2029, earlier than what it committed to when it signed the Paris Agreement, according to a report by the U.S. Green Building Council.
MFPRO+ News | Dec 11, 2023
U.S. poorly prepared to house growing number of older adults
The U.S. is ill-prepared to provide adequate housing for the growing ranks of older people, according to a report from Harvard University’s Joint Center for Housing Studies. Over the next decade, the U.S. population older than 75 will increase by 45%, growing from 17 million to nearly 25 million, with many expected to struggle financially.
Office Buildings | Dec 11, 2023
Believe it or not, there could be a shortage of office space in the years ahead
With work-from-home firmly established, many real estate analysts predict a dramatic reduction in office space leasing and plummeting property values. But the high-end of the office segment might actually be headed for a shortage, according to real estate intelligence company CoStar Group.
University Buildings | Dec 8, 2023
Yale University breaks ground on nation's largest Living Building student housing complex
A groundbreaking on Oct. 11 kicked off a project aiming to construct the largest Living Building Challenge-certified residence on a university campus. The Living Village, a 45,000 sf home for Yale University Divinity School graduate students, “will make an ecological statement about the need to build in harmony with the natural world while training students to become ‘apostles of the environment’,” according to Bruner/Cott, which is leading the design team that includes Höweler + Yoon Architecture and Andropogon Associates.