In the rush to slash energy consumption in power-hungry data centers, design teams, equipment manufacturers, and tech companies have been developing clever, low-energy cooling solutions—from Facebook’s open-rack server setup with exposed motherboards, to Skanska’s eOPTI-TRAX liquid refrigerant coil system, to Google’s evaporative cooling schemes.
Solutions like these have helped data center facility operators achieve unprecedented energy performance levels, with power utilization effectiveness (PUE) ratios dipping below 1.10 in some instances. This means that less than 10% of the total energy consumption in a facility is attributed to noncomputing functions, such as air-conditioning and lighting.
Now, a new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency even further. Called immersive cooling, it uses a liquid instead of air to cool the servers. LiquidCool Solutions, Green Revolution, and 3M are among the pioneers of this technology. Each system works a bit differently, but the basic idea is to submerge the motherboards in tanks filled with nonconductive fluid, which absorbs the heat generated by the processors.
LiquidCool Solutions, for example, uses an enclosed server module and pumps dielectric fluid through the server enclosure. Green Revolution uses a tub full of dielectric oil and circulates the liquid through the tubs. 3M also uses the tub approach, but the fluid boils and then is condensed to reject the heat.
By using liquid-based cooling at the server level, the need for air-conditioning is greatly reduced, or even eliminated in some climates. The same goes for traditional HVAC equipment and systems—chillers, fan units, raised floors, and so on.

The Allied Control 500 kW immersion-cooled data center in Hong Kong is capable of delivering a PUE of just 1.02. The standard, 19-inch server racks use 3M Novec Engineered Fluids to enable tight component packaging for greater computing power in less space, according to Allied. Its open-bath design permits easy access to hardware and eliminates the need for pressure vessel enclosures and charging/recovery systems. PHOTO: COURTESY ALLIED CONTROL
“In most parts of the world, compressorized cooling would not be required with immersive cooling, since the liquid temperatures can be at a level where direct heat rejection using outdoor condensers or cooling towers would be sufficient,” says Thomas Squillo, PE, LEED AP, Vice President with Environmental Systems Design, who is currently researching the technology for the firm’s data center clients. “The fan energy is also eliminated, both in the HVAC system and in the server itself. Fluid pumping energy is very low.”
Other advantages of the cooling technology, according to Squillo:
• Increased performance and service life of the computer chips by eliminating heat buildup and problems related to contaminated air and dust.
• Ability to deploy data centers in extremely harsh environments without greatly impacting energy performance.
• Potential construction cost savings by downsizing or eliminating traditional HVAC systems.
Other than a few pilot projects, including a Bitcoin mining data center in Hong Kong and a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory-led installation in Chippewa Falls, Wis., immersive cooling technology is largely untested. A year into the Bitcoin pilot, the data center operator reported a 95% reduction in cooling costs.
AEC professionals are starting to realize the potential for immersive cooling, especially for high-performance computing centers and consolidated, high-density data centers.
“Large data centers that have many homogenous machines at high density—like those operated by Internet and cloud providers—are a good application,” says Squillo. “Small footprint and minimal energy use are very important due to the volume of servers. These can be deployed in remote areas where space and energy are cheap, but where air quality may be a concern, without having to worry about the data center air.”
TRICKY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Before the technology can be implemented, says Squillo, several nettlesome design factors specific to immersive cooling have to be addressed:
• Piping distribution to the racks and cooling units requires redundancy and valving to accommodate equipment maintenance without disrupting server performance.
• Additional equipment and space are needed to drain fluid from the tanks for server maintenance.
• Local code requirements may limit the amount of fluid that can be stored in a single room.
• For the foreseeable future, it’s unlikely that a large data center would be 100% liquid-immersion cooled. This means provisions will have to be made for both air- and liquid-cooling systems, which will require additional space in the data hall and mechanical room.
“I think that some form of this technology will definitely be the direction the data center market will take in the future,” says Squillo. “The market just needs to mature enough for owners to trust the technology and demand servers that are designed for a particular type of liquid cooling. In the short term, I see large companies and server manufacturers doing small-scale installations to test the concept, before wanting to implement it at a large scale.”
Related Stories
Cultural Facilities | Nov 21, 2023
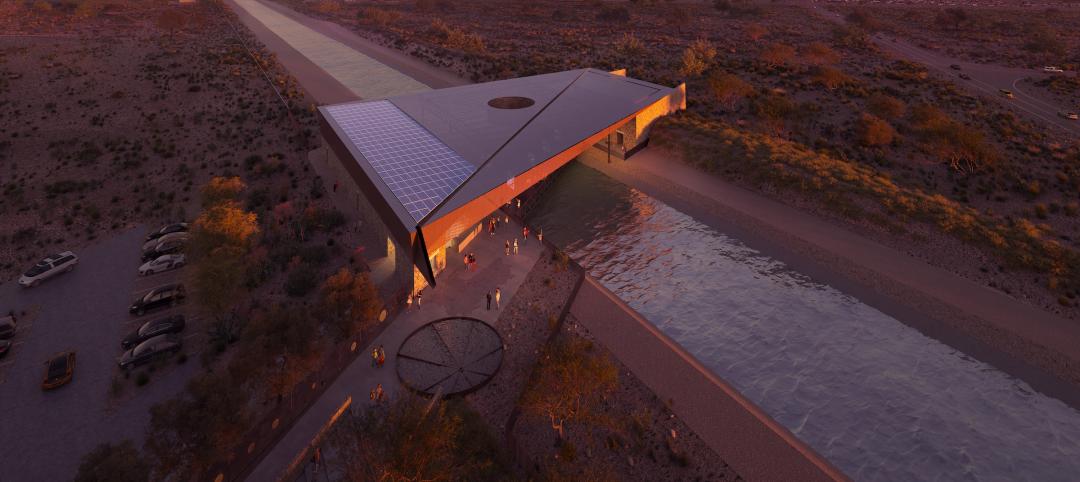
Arizona’s Water Education Center will teach visitors about water conservation and reuse strategies
Phoenix-based architecture firm Jones Studio will design the Water Education Center for Central Arizona Project (CAP)—a 336-mile aqueduct system that delivers Colorado River water to almost 6 million people, more than 80% of the state’s population. The Center will allow the public to explore CAP’s history, operations, and impact on Arizona.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Nov 21, 2023
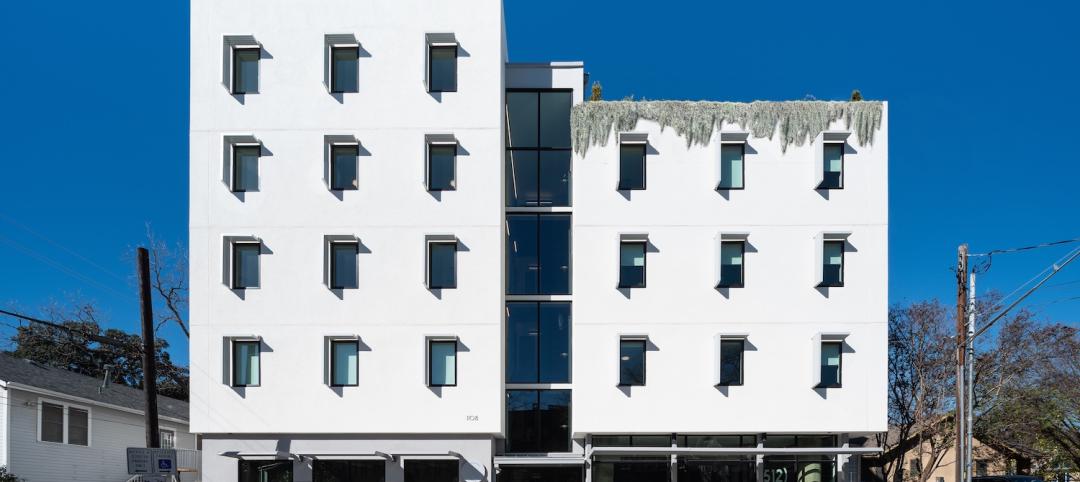
An 'eco-obsessed' multifamily housing project takes advantage of downtown Austin’s small lots
In downtown Austin, Tex., architecture firm McKinney York says it built Capitol Quarters to be “eco-obsessed, not just eco-minded.” With airtight walls, better insulation, and super-efficient VRF (variable refrigerant flow) systems, Capitol Quarters uses 30% less energy than other living spaces in Austin, according to a statement from McKinney York.
MFPRO+ News | Nov 21, 2023
California building electrification laws could prompt more evictions and rent increases
California laws requiring apartment owners to ditch appliances that use fossil fuels could prompt more evictions and rent increases in the state, according to a report from the nonprofit Strategic Actions for a Just Economy. The law could spur more evictions if landlords undertake major renovations to comply with the electrification rule.
Codes and Standards | Nov 21, 2023
Austin becomes largest U.S. city to waive minimum parking requirements
Austin, Texas recently became the largest city in the United States to stop requiring new developments to set a minimum amount of parking. The Austin City Council voted 8-2 earlier this month to eliminate parking requirements in an effort to fight climate change and spur more housing construction as Texas’s capitol grapples with a housing affordability crisis.
MFPRO+ News | Nov 21, 2023
Underused strip malls offer great potential for conversions to residential use
Replacing moribund strip malls with multifamily housing could make a notable dent in the housing shortage and revitalize under-used properties across the country, according to a report from housing nonprofit Enterprise Community Partners.
Giants 400 | Nov 16, 2023
Top 100 Science + Technology Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HDR, Page Southerland Page, Flad Architects, and DGA top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest science and technology (S+T) facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report. Note: This ranking factors revenue from all science and technology (S+T) buildings work, including laboratories, research buildings, technology/innovation buildings, pharmaceutical production facilities, and semiconductor production facilities.
Resiliency | Nov 16, 2023
How inclusive design supports resilience and climate preparedness
Gail Napell, AIA, LEED AP BD+C, shares five tips and examples of inclusive design across a variety of building sectors.
Retail Centers | Nov 15, 2023
Should retail developers avoid high crime areas?
For retailers resolute to operating in high crime areas, design elements exist to mitigate losses and potentially deter criminal behavior.
MFPRO+ News | Nov 15, 2023
Average U.S multifamily rents drop $3 to $1,718 in October 2023: Yardi Matrix
Multifamily fundamentals continued to soften and impact rents last month, according to the latest Yardi Matrix National Multifamily Report. The average U.S. asking rent dropped $3 to $1,718 in October, with year-over-year growth moderating to 0.4%, down 40 basis points from September. Occupancy slid to 94.9%, marking the first decline in four months.
MFPRO+ Special Reports | Nov 14, 2023
Register today! Key trends in the multifamily housing market for 2024 - BD+C Live Webinar
Join the BD+C and Multifamily Pro+ editorial team for this live webinar on key trends and innovations in the $110 billion U.S. multifamily housing market. A trio of multifamily design and construction experts will present their latest projects, trends, innovations, and data/research on the three primary multifamily sub-sectors: rental housing, senior living, and student housing.