For years, MEP engineers have debated the untapped potential lying within the walls and ceilings of virtually every modern commercial building: fire protection piping. Building owners sink a hefty sum into fire sprinkler infrastructure. Why not tap into this water distribution network for other uses, like toilet flushing?
Until recently, code officials have told Building Teams “hands off,” for fear of jeopardizing the integrity of these critical systems. But they are slowly coming around.
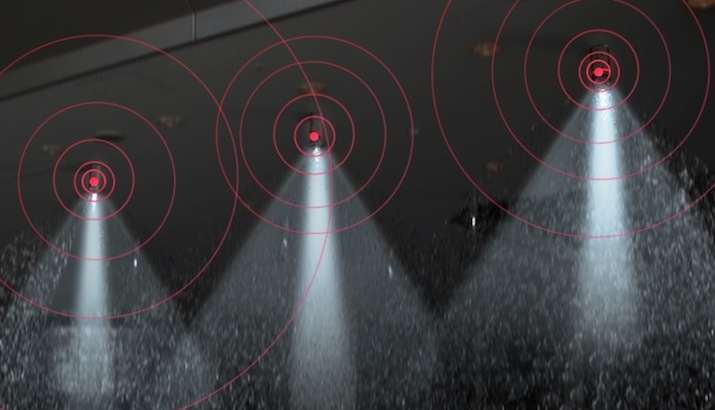
Two recent innovations are indicative of the trend. The first, the Fluid-Driven Sprinkler Light, utilizes a water turbine micro-generator with high-illumination LED light engines to provide emergency lighting without the need for batteries or other power sources (pictured above). Developed by the Industrial Technology Research Institute, the technology can provide for safer access and egress during fires, when buildings are engulfed by smoke.
High temperatures activate the sprinklers, and the flow of the water generates electricity to power the LEDs, which project a laser-based holography pattern light. The lights can be positioned to illuminate evacuation routes.
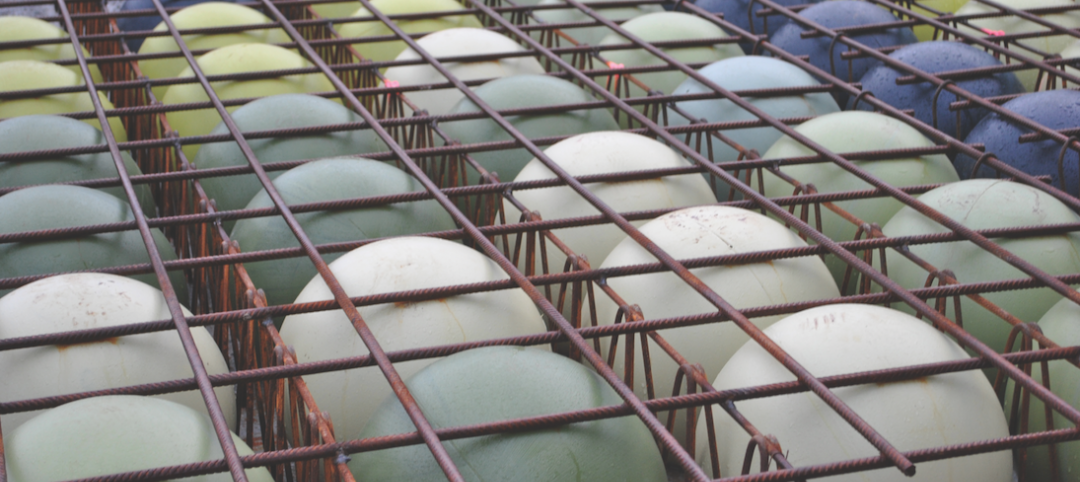
For the $29 million, four-level addition to the University of Michigan’s Institute for Social Research Expansion, in Ann Arbor, the engineering team, led by MEP engineer Peter Basso Associates, utilized the building’s fire protection piping system to distribute chilled water to the chilled beams (pictured, below). The dual-function design eliminated approximately 70% of the piping normally associated with a chilled beam system, and reduced first cost by an estimated $500,000.
It is the first installation of its kind in the U.S., and it required that all components of the combined fire protection/chilled beam system be rated for a minimum 175 PSIG (pounds per square inch gage) operating pressure, according to Brian Runde, PE, LEED AP, VP with Peter Basso Associates. He says using chilled beams helped the project reduce overall building energy use by 37.2% versus an ASHRAE 90.1-compliant building.
 Photo: Peter Basso Associates
Photo: Peter Basso Associates
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Jan 20, 2016
Skanska’s new app helps construction teams monitor and meet environmental quality standards while renovating hospitals
App allows users to track noise, differential pressure levels, vibration, and dust
Great Solutions | Jan 19, 2016
Concrete innovation: voided biaxial slab slashes weight, saves concrete
System reduces slab dead load by 30% on medical clinic project
Great Solutions | Jan 19, 2016
Healing garden doubles as therapy trails
A Boston-area hospital takes the healing garden to the next level.
Great Solutions | Jan 14, 2016
WWII watchtower turned into ‘land yacht’
Architect Siemasko + Verbridge and contractor Windover Construction transformed a coastal wartime observation post into an amenity-filled guesthouse.
Great Solutions | Jan 7, 2016
Bacteria-killing paint and magnetic wallcovering highlight innovations in surface materials
Sherwin-Williams recently introduced Paint Shield, the first EPA-registered microbicidal paint that kills virtually all infection-causing bacteria after two hours of exposure on painted surfaces.
Great Solutions | Jan 6, 2016
Shepley Bulfinch develops elegant design solution to address behavioral issues in emergency departments
ED scheme allows staff to isolate unruly patients and visitors in a secure area.
Great Solutions | Jan 6, 2016
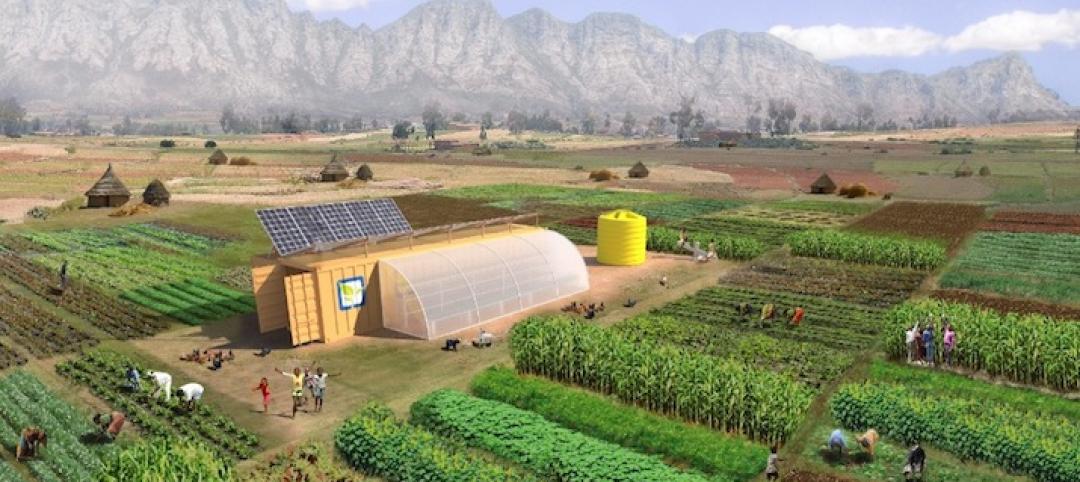
All-encompassing farming kit can provide communities with a sustainable food supply
Several manufacturers partnered with the group Farm from a Box to develop an off-the-grid farming solution for communities, all without the need for outside help.
Great Solutions | Jan 4, 2016
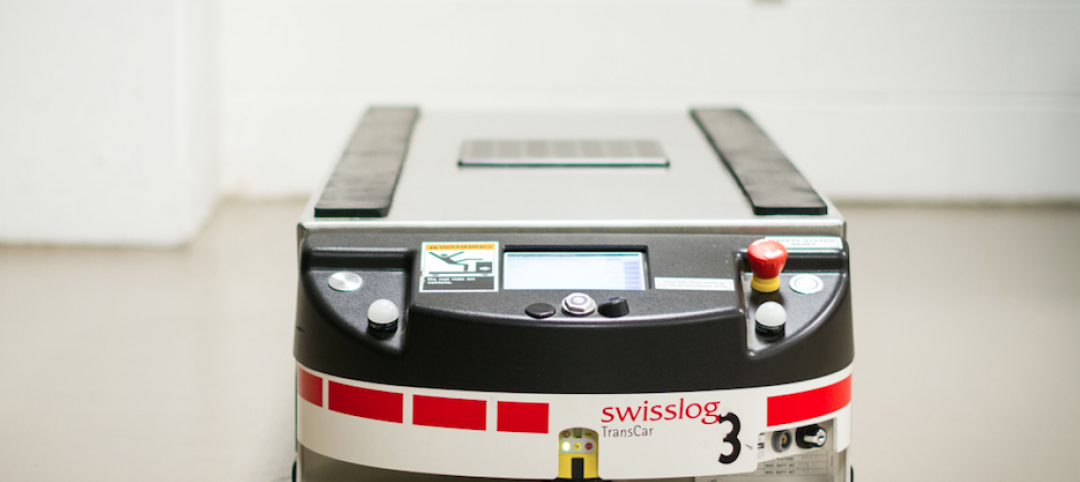
Toronto’s newest hospital employs 10 robots for moving food, supplies, and equipment
The 1.8 million-sf Humber River Hospital is loaded with high-tech gadgets. Its coolest innovation is the use of automated guided vehicles.
Great Solutions | Jan 4, 2016
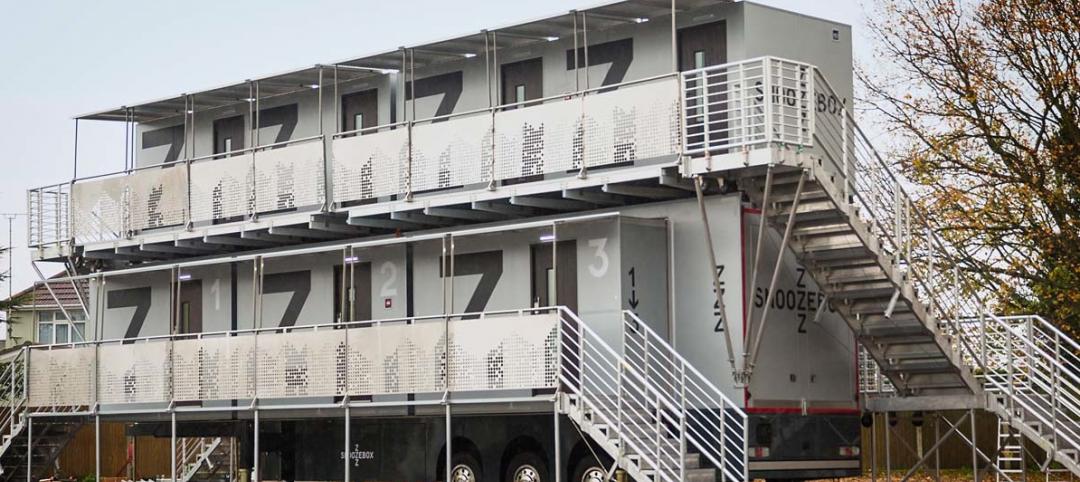
Snoozebox’s portable hotel rooms make outside events more livable
Since 2011, the London-based company has thrived by creating portable hotels that are set up for the duration of open-air events (or longer), and offer many of the comforts of conventional hotels.