While the Bird's Nest and Water Cube captured all the TV coverage during the Beijing Olympics in August, the Rem Koolhaas-designed CCTV Headquarters in Beijing—known as the “Drunken Towers” or “Big Shorts,” for its unusual shape—is certain to steal the show when it opens next year.
The Dutch architect's scheme for the $730 million, 4.8-million-sf building, which will serve as the new headquarters for China's state-run television network, essentially folds and twists the traditional skyscraper form into a parallelogram-like shape.
The result is a single loop composed of four horizontal and two vertical sections that connects CCTV's news, broadcasting, administration, and program production departments. Koolhaas's goal is to create an environment that forces everyone in the television business—creative types, producers, technicians, and administrators—to interact in hopes of producing better programming more efficiently and economically.
The novel design, with its large, nine-story base, also provides multiple social “touch points” with the public to encourage passersby to engage with the building, according to Ole Scheeren, Office for Metropolitan Architecture's partner-in-charge on the project.
Because OMA's unusual geometric scheme does not meet Chinese building code, the project structural engineering team, led by London-based Arup with the East China Architecture and Design Institute (ECADI) as local design institute of record, had to employ a performance-based design approach. As part of this process, engineers had to convince a panel of experts that the structure would not only withstand major seismic and wind events, but also hold up during construction—a significant challenge, given that the sloping vertical towers had to be connected at the top.
“The unprecedented structural design underwent the most rigorous internal and external scrutiny during a two-year span, including an expert panel review by China's Ministry of Construction,” says Rory McGowan, Arup's project director on the CCTV project.
Unlike traditional vertical high-rise construction, where the building's core serves as the primary support, Arup engineers had to utilize the building's external face as the superstructure, creating what is essentially a “continuous tube” composed of a series of steel diagonal braces, or X braces, that work in conjunction with a regular grid of columns and edge beams. This braced tube approach provides ample strength and stiffness in the towers to deliver the loads to the base, and the proper stiffness in the base to reinforce the lower tower levels and deliver loads to the foundation. It also accommodates forces from bending and twisting between the two towers, and provides the leaning towers ample stiffness during construction, allowing them to be safely constructed within tight tolerances before they were connected and propped off each other.
The distribution of the diagonal bracing is not uniform, however. Using 3D modeling software, engineers were able to make the structure as efficient as possible based on load calculations. For instance, the amount of X-bracing was doubled around heavy-loaded zones, such as the “armpits,” and halved around light-loaded zones, including the uppermost portion of the building.
“Varying the bracing density allowed us to fine-tune the structure to ensure it was not too stiff to minimize seismic loads,” says McGowan. The Arup team worked closely with OMA to express this optimized X-bracing pattern in the building's façade.
Internal steel columns extend from the foundation up to the furthest reaches of the building, providing support for the floor plates. Due to the slopping nature of the towers, the vertical columns could not extend continuously from top to bottom. To transfer the load from one series of columns to another, the team designed a system of two-story-deep transfer trusses located three-quarters of the way up the building. A similar approach was employed to support the floor plates in the cantilevered overhang.
Early on, the Building Team considered sloped vertical cores to provide a consistent floor plate layout. But finding a sloped elevator system for a building of this scale was difficult.
“We also learned that having different floor plans actually allowed more flexibility in terms of planning for studios, editing suites, and so on,” says McGowan. Therefore, the final scheme steps straight vertical cores so that they always sit within the footprint of the sloping towers.
The main towers sit on a hybrid piled raft foundation system that shares the total load coming from the superstructures between a 7½-meter-thick concrete platform, or “raft,” and a series of 1.2-meter-diameter piles that extend 52 meters into the soil. The foundation system is arranged so that the center of the raft is close to the center of load at the bottom of each tower, and no permanent tension is allowed in the piles. Limited tension in certain piles is permitted during a major seismic event.
For the nine-story base and three-story basement, a traditional raft foundation is used, with tension piles between column locations to resist uplift from water pressure acting on the deep basement. Fifteen- to 20-meter-long tension piles are arranged under the raft with additional piles under secondary cores and columns supporting large transfer trusses from the studio areas.
Related Stories
| Dec 29, 2014
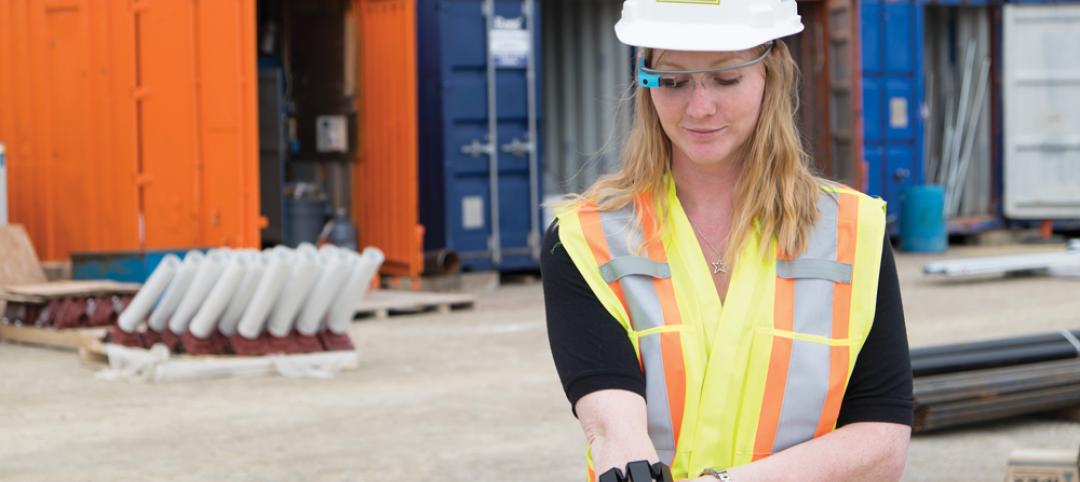
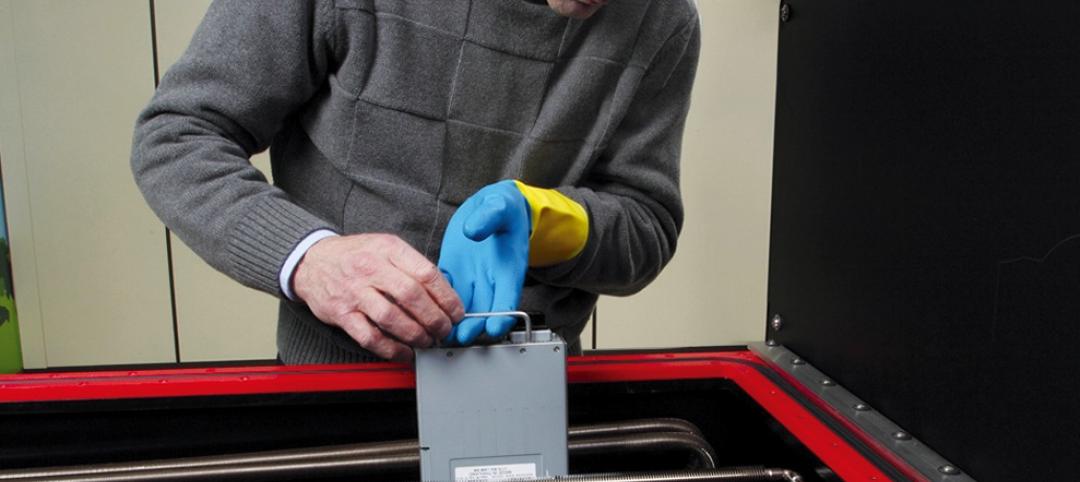
Wearable job site management system allows contractors to handle deficiencies with subtle hand and finger gestures [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
Technology combines a smartglass visual device with a motion-sensing armband to simplify field management work. The innovation was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 29, 2014
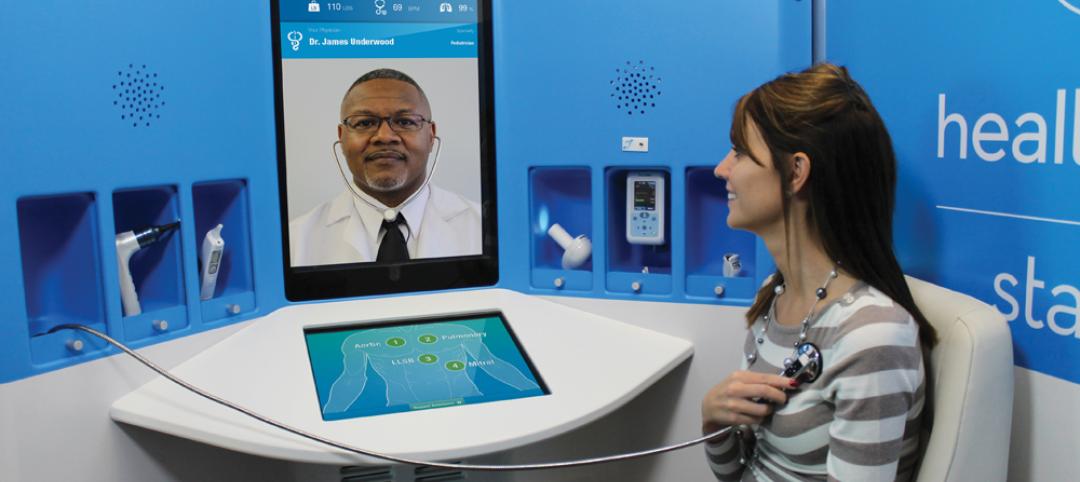
HealthSpot station merges personalized healthcare with videoconferencing [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
The HealthSpot station is an 8x5-foot, ADA-compliant mobile kiosk that lets patients access a network of board-certified physicians through interactive videoconferencing and medical devices. It was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 28, 2014
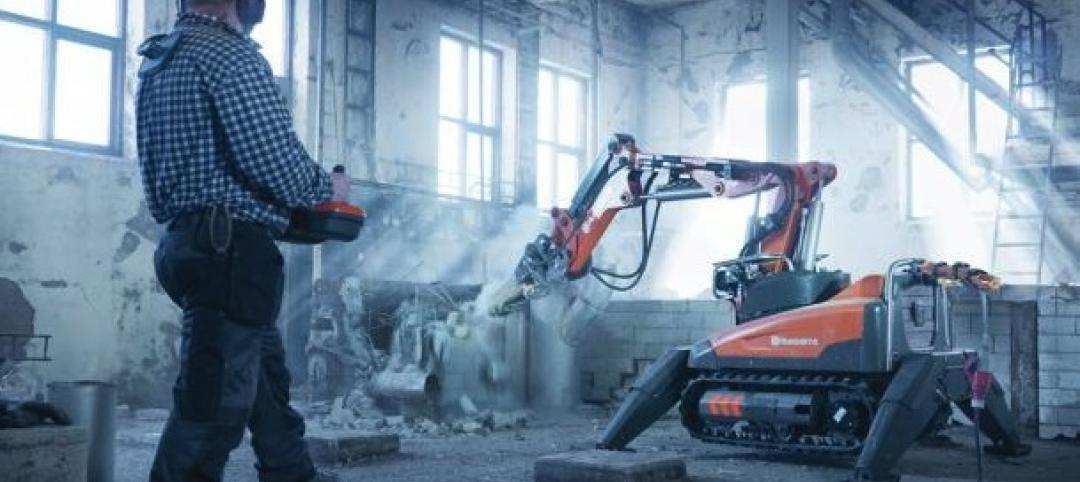
Robots, drones, and printed buildings: The promise of automated construction
Building Teams across the globe are employing advanced robotics to simplify what is inherently a complex, messy process—construction.
BIM and Information Technology | Dec 28, 2014
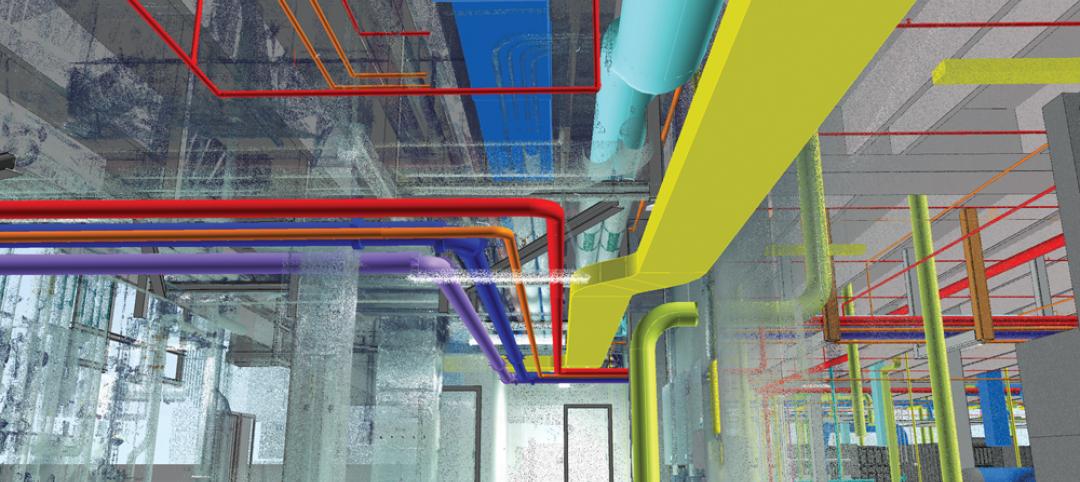
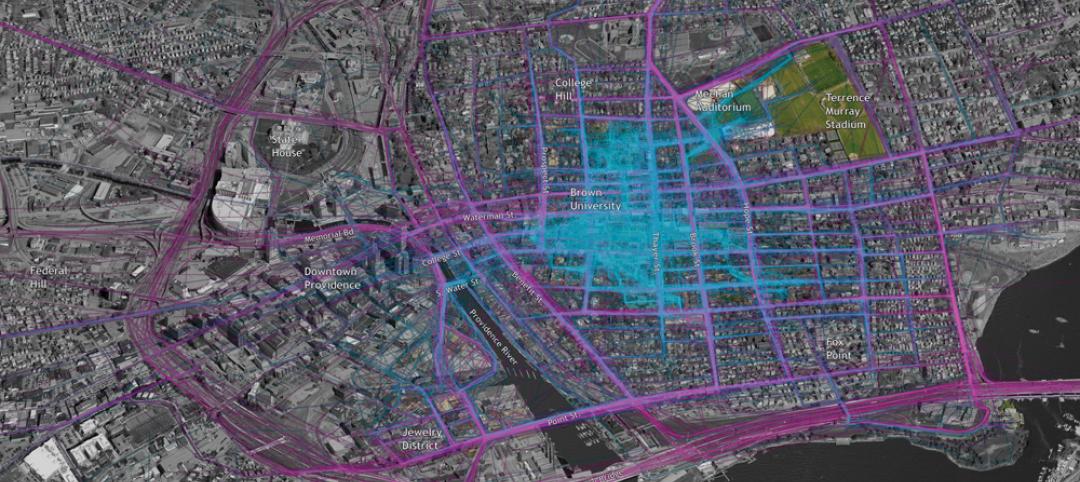
The Big Data revolution: How data-driven design is transforming project planning
There are literally hundreds of applications for deep analytics in planning and design projects, not to mention the many benefits for construction teams, building owners, and facility managers. We profile some early successful applications.
| Dec 23, 2014
5 tech trends transforming BIM/VDC
From energy modeling on the fly to prefabrication of building systems, these advancements are potential game changers for AEC firms that are serious about building information modeling.
| Dec 17, 2014
ULI report looks at growing appeal of micro unit apartments
New research from the Urban Land Institute suggests that micro units have staying power as a housing type that appeals to urban dwellers in high-cost markets who are willing to trade space for improved affordability and proximity to downtown neighborhoods.
| Nov 3, 2014
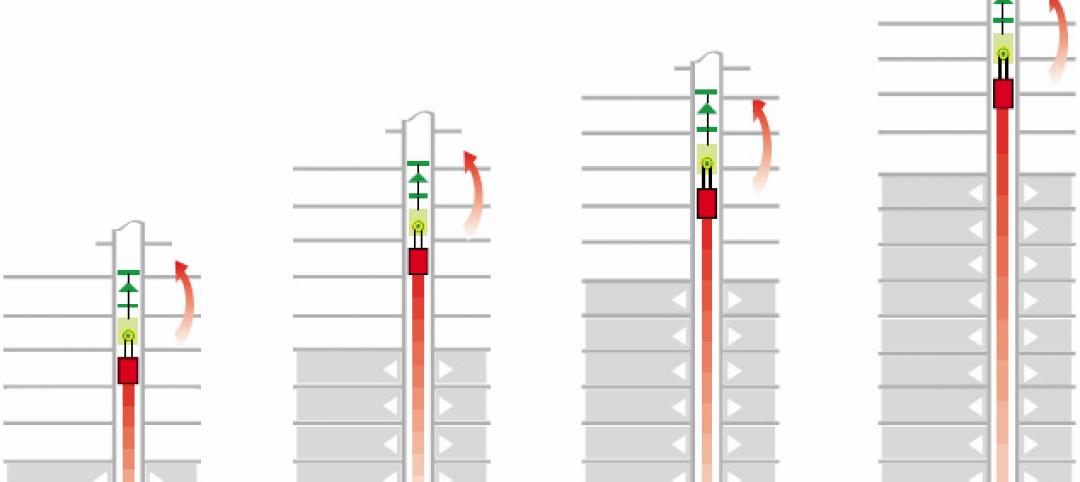
Novel 'self-climbing' elevator operates during construction of high-rise buildings
The JumpLift system from KONE uses a mobile machine room that moves upward as the construction progresses, speeding construction of tall towers.
| Oct 14, 2014
Slash energy consumption in data centers with liquid-based ‘immersive-cooling’ technology
A new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency by using liquid instead of air to cool the servers.
| Sep 10, 2014
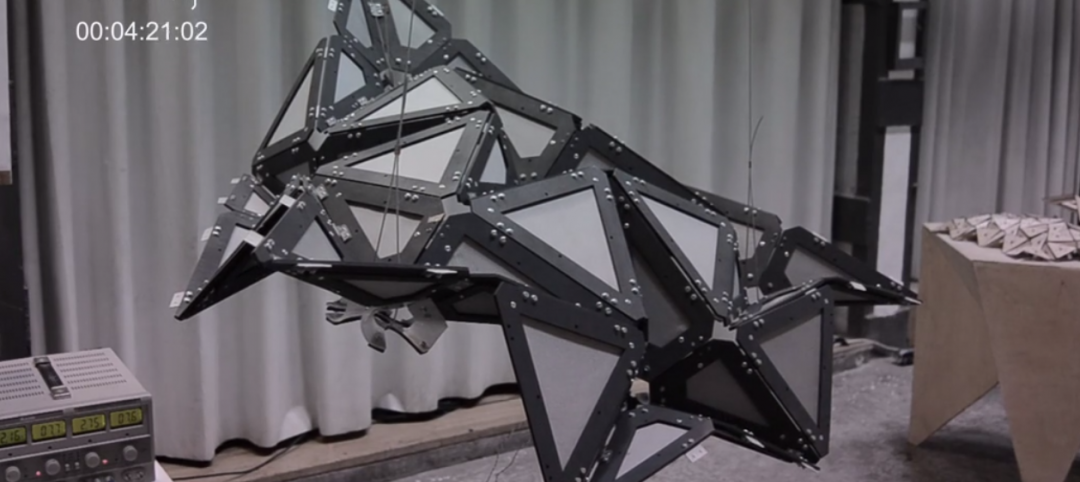
Must See: Shape-shifting architecture that responds to heat
Students in Barcelona have created a composite material using shape memory polymers that can deform and return to their original state when activated by cues like heat, humidity, and light.
| Aug 4, 2014
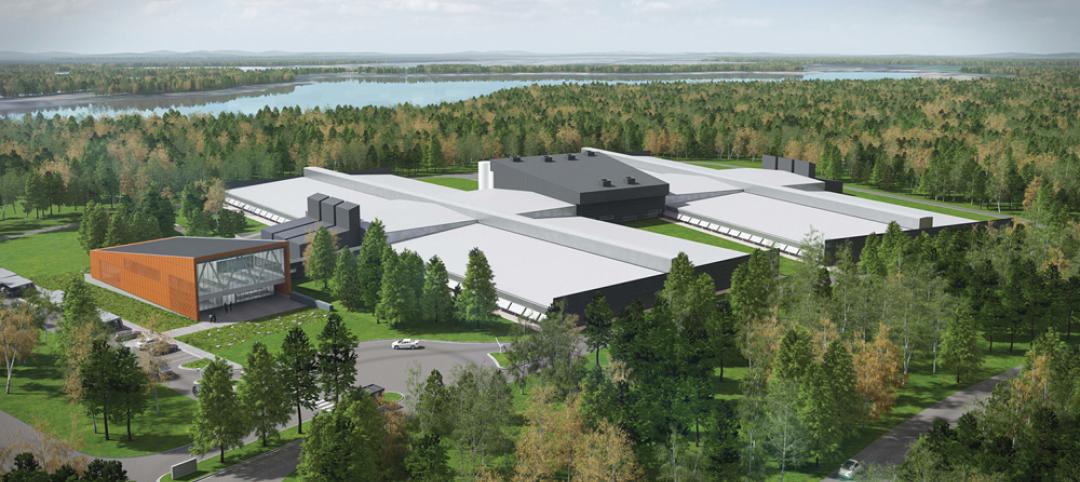
Facebook’s prefab data center concept aims to slash construction time in half
Less than a year after opening its ultra-green, hydropowered data center facility in Luleå, Sweden, Facebook is back at it in Mother Svea with yet another novel approach to data center design.