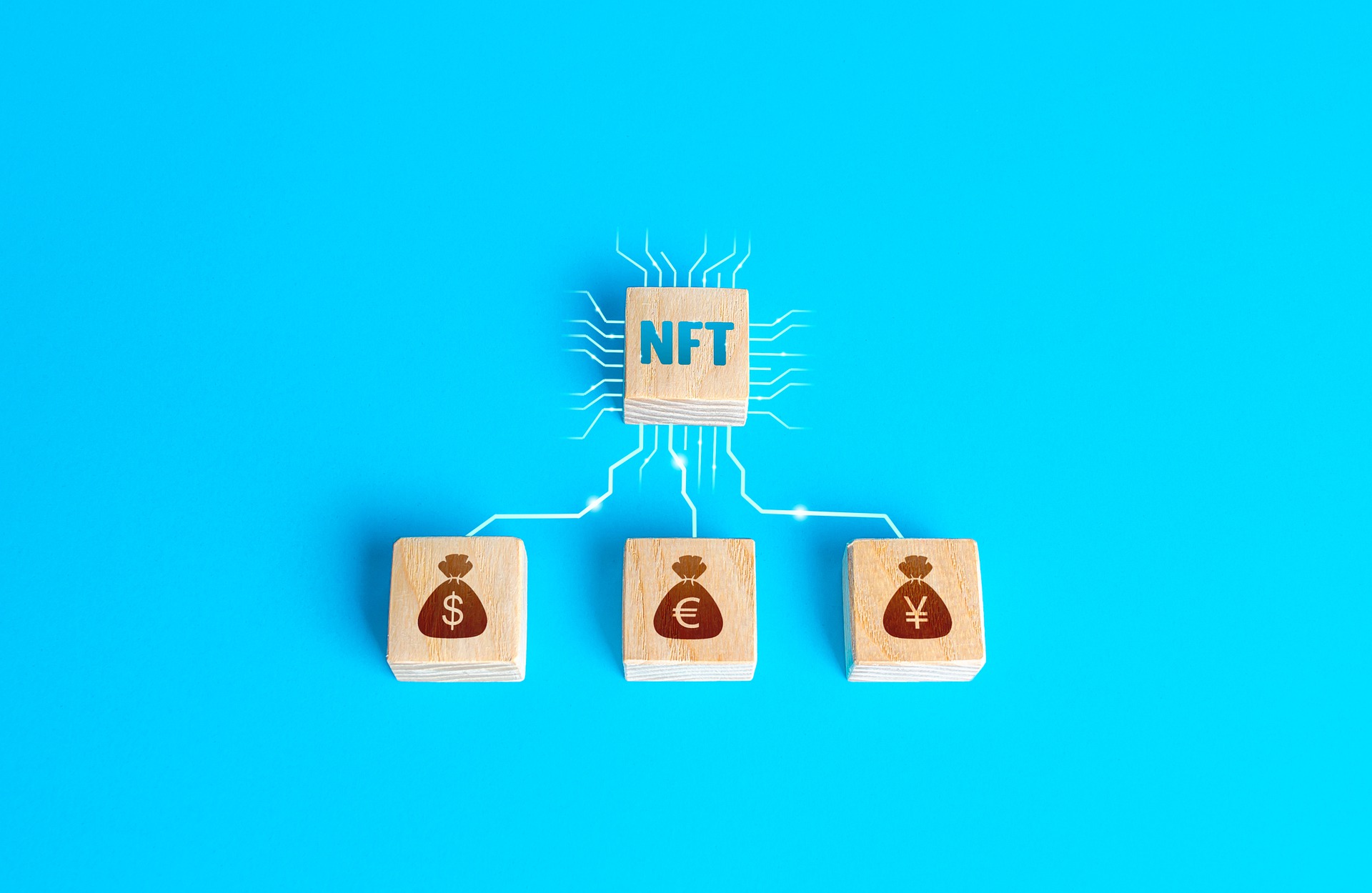
An NFT, or non-fungible token, is a digital object that cannot be duplicated. NFTs allow the owners of digital or intangible assets that can be replicated to assert ownership and, by extension, to commodify and trade those assets. For example, anyone can browse photography of the latest Anish Kapoor, but only one city can make a grand public artwork a tourist calling card. For anyone who has ever experienced the frustration of having an idea copied, NFTs offer a possible solution.
As we know them today, NFTs exist in a world far removed from everyday reality—belonging to an intangible fantasy land pioneered by connoisseurs of computer games and digital art. But the value placed on these digital objects, and the tokens associated, is as real as a coin in your pocket.
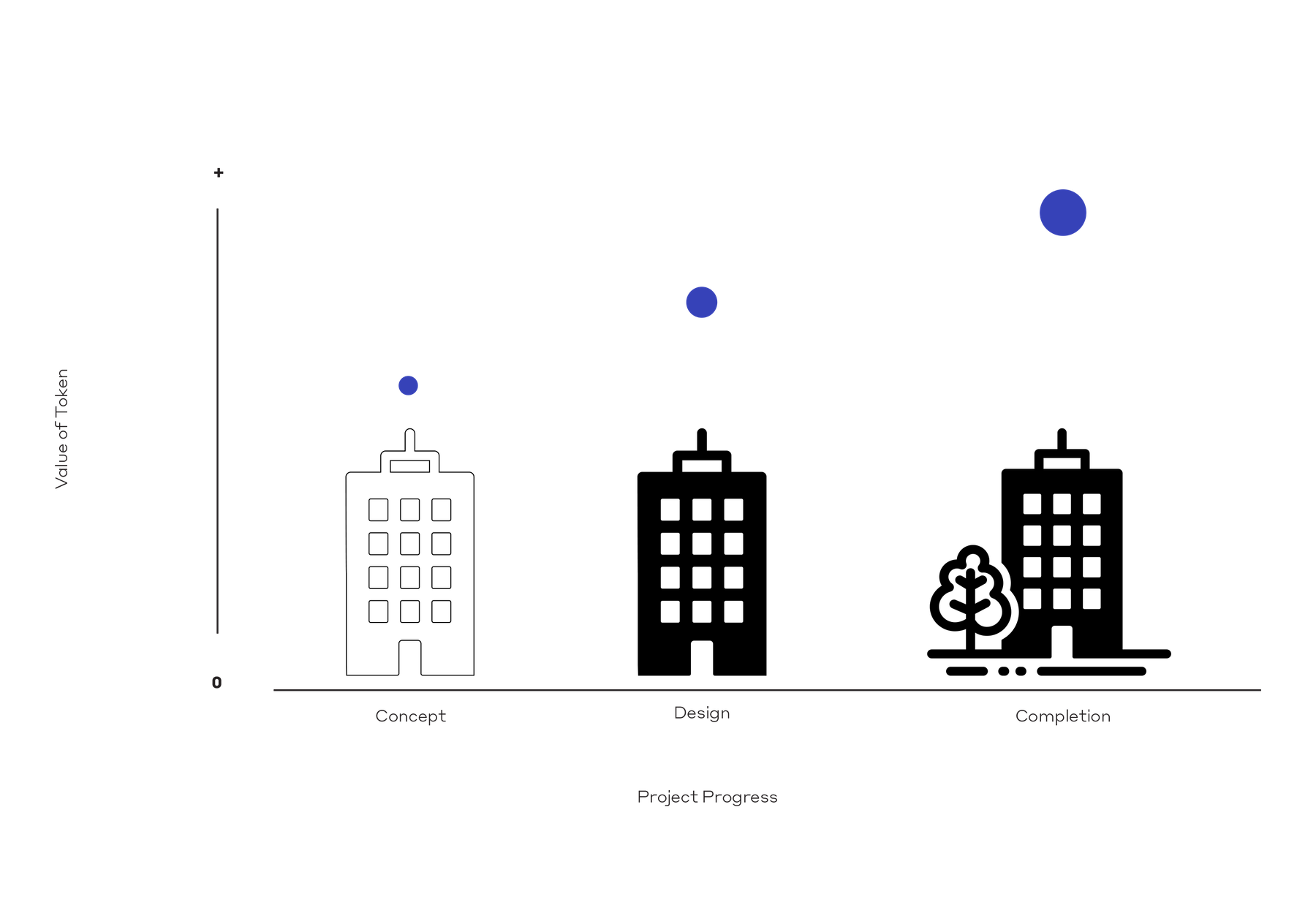
Where does design come into the NFT picture? A fundamental value of design is its ingenuity in reimagining a better future. Designs can be abstracted or copied, but the ingenuity lies in the process. The labor in design—the thinking, testing, and problem solving—is what clients are ultimately buying. The building or interior is the product of that process.
6 ways non-fungible tokens (NFTs) could transform the design industry
“Tokenizing” design labor would give clients the opportunity to bid for the time of a designer or firm. By placing a higher value on time, this Token Future would create six compelling outcomes:
1. Complimentary Investment.
When a client invests in design, they invest in the benefits expected from the finished building. Tokenizing design labor would mean that a complimentary investment in the designer’s time is also made. To explain, a labor token could appreciate in value and be traded for profit. A token will appreciate as market demand grows, which is itself fueled by public awareness of quality design. When a token appreciates, both designer and client/investor are rewarded with capital gain.
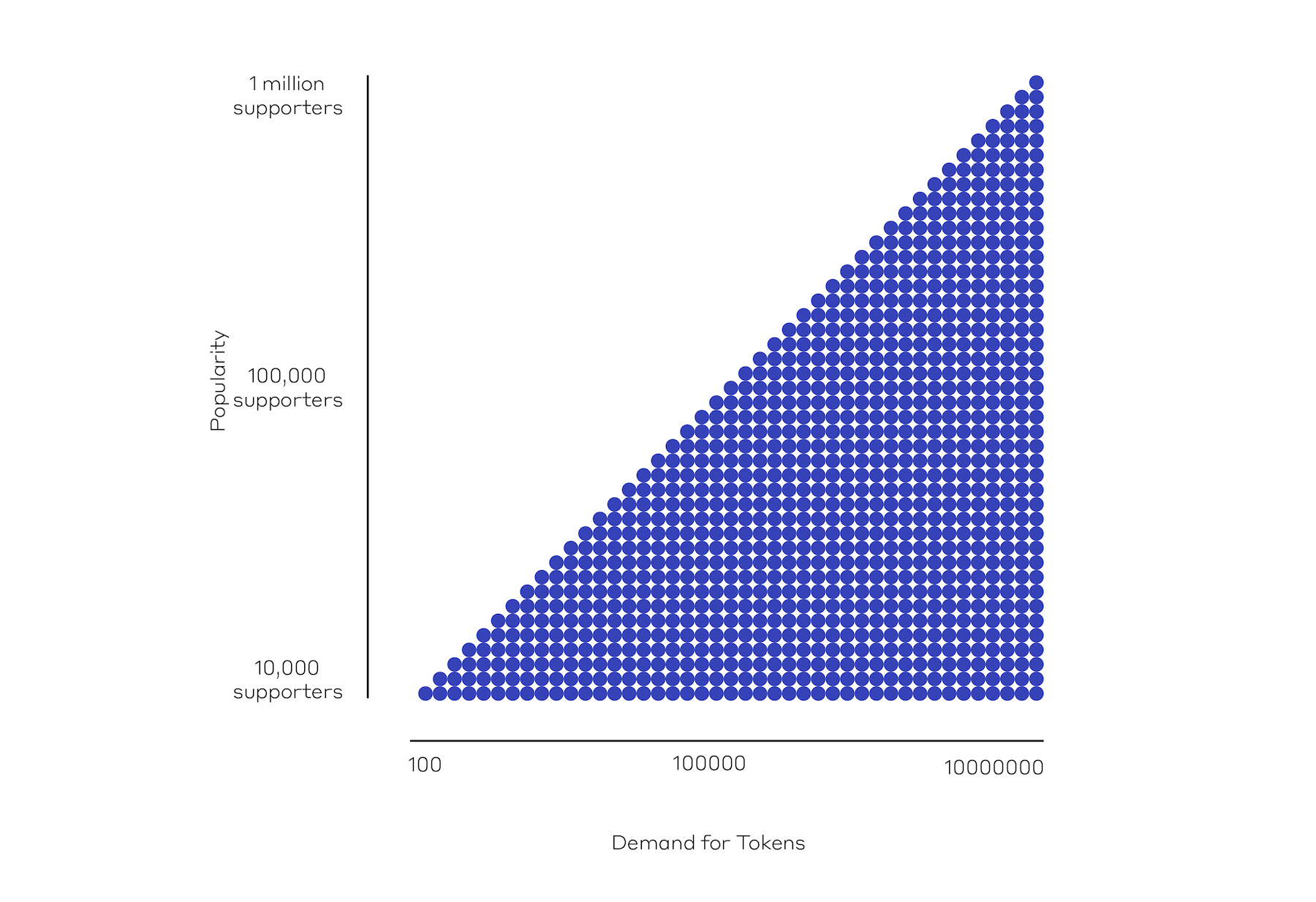
2. Mutually Beneficial Collaboration.
When a client purchases tokens from a designer, they become invested in the ongoing success of that token. The designer becomes a potential source of capital gain, like any other investment—something to be protected and nourished. For a designer, this means a client is more likely to support the process and capacity to perform.
3. Protection of Quality Design Time.
A Token Future should prevent design time from becoming overstretched. It would eliminate the fixed-fee contract, which sees designers at risk of shouldering disproportionate work without compensation—resulting in all-nighters, working weekends and, ultimately, a compromised design. Avoiding these pitfalls is in the best interests of all parties.
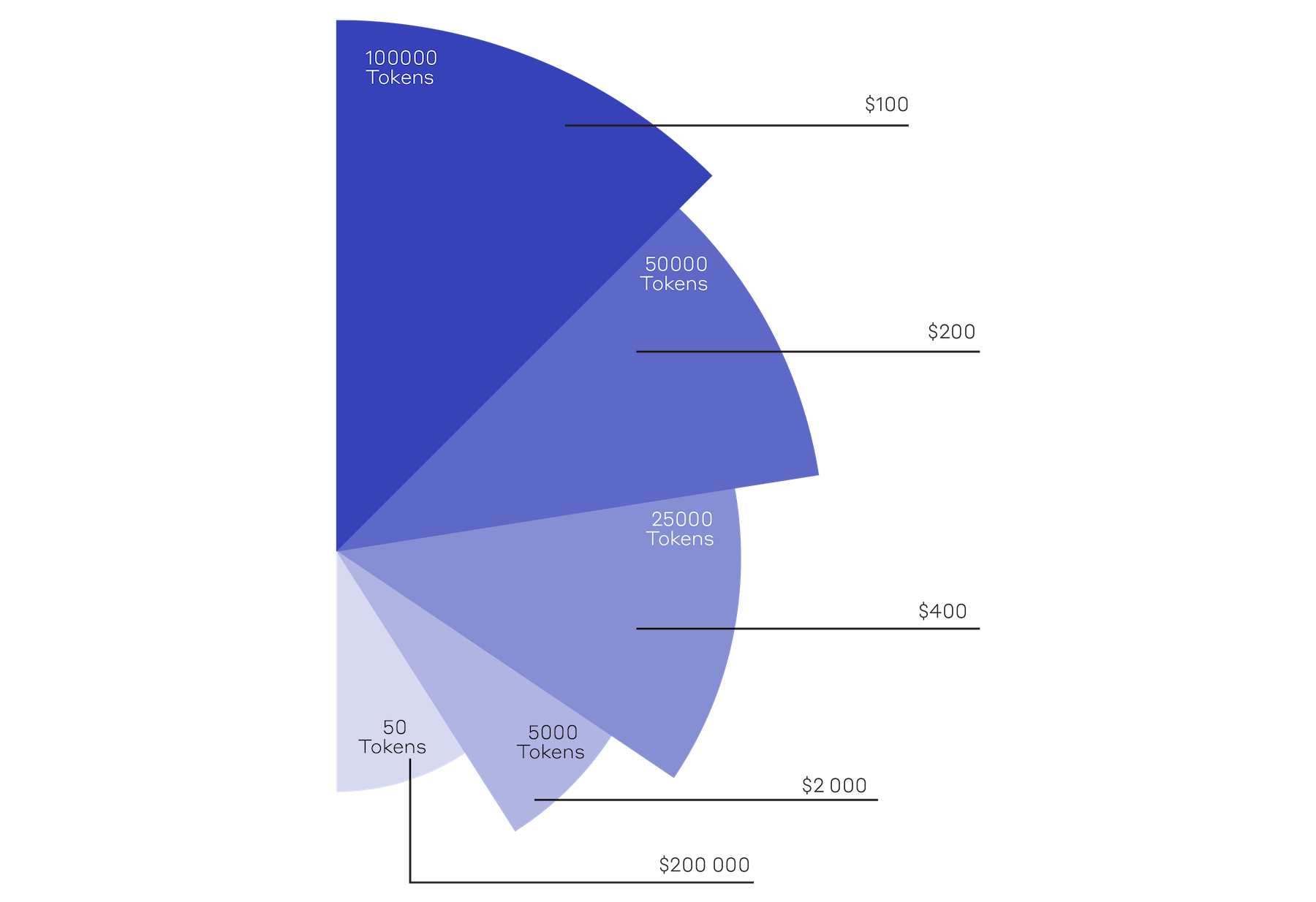
4. Less Money Wasted.
In a case where a client might need to cancel a project, good work and pursuant appreciation of the Token value may result in a financial return on their design investment rather than a write-off.
5. A Clearer and More Flexible Market.
The procurement of designers can be opaque and uncertain. Unfamiliar designers with hard-to-understand fee structures may be deemed a risk by clients. A project may need to be put on hold or cancelled. In both scenarios, a regulated and transparent token-based market would afford clients the opportunity to divest as they see fit, with the value of their original investment having appreciated.
6. An Equitable Market for Designers.
In such a system, a designer negotiates the supply of labor in a collaborative manner, only offering services in accordance with their resources. Managed professionally and systematically, design labor could be calibrated not only to a client’s requirements and the designer’s expertise, but also to the mutual financial and cultural benefit of each party—improving life for both parties.
The benefits of a Token Future currently contend with numerous uncertainties and challenges—much like any innovation. Though this concept remains a glimmer on the horizon, NFTs in the design industry promise better welfare, growth, and profit.
As the design industry continues to chart a course toward automated production and an acceleration of the service economy, the rewards of exploring a Token Future for design labor outweigh the risks.
About the author
Jet Geaghan is an Architect based in Woods Bagot’s Sydney studio. For Jet, every building should be conceived with purpose, expertise and wit. Clarity of communication is fundamental to his work, whether it be in a design gesture, construction detail, or cultural testimony. Having completed numerous additions and alterations projects, Jet relishes the complexity and challenges of adapting existing buildings to address evolving demands and unforeseen potential. His experience lends him a broad understanding of the myriad parameters involved in bringing buildings of differing scales to life, which have included the 275 Kent Street redevelopment and the refurbishment of InterContinental Hotel Sydney. Jet has extensive experience with planning approvals, design, documentation, construction delivery, digital modeling, as well as a passion for the written word.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Aug 24, 2017
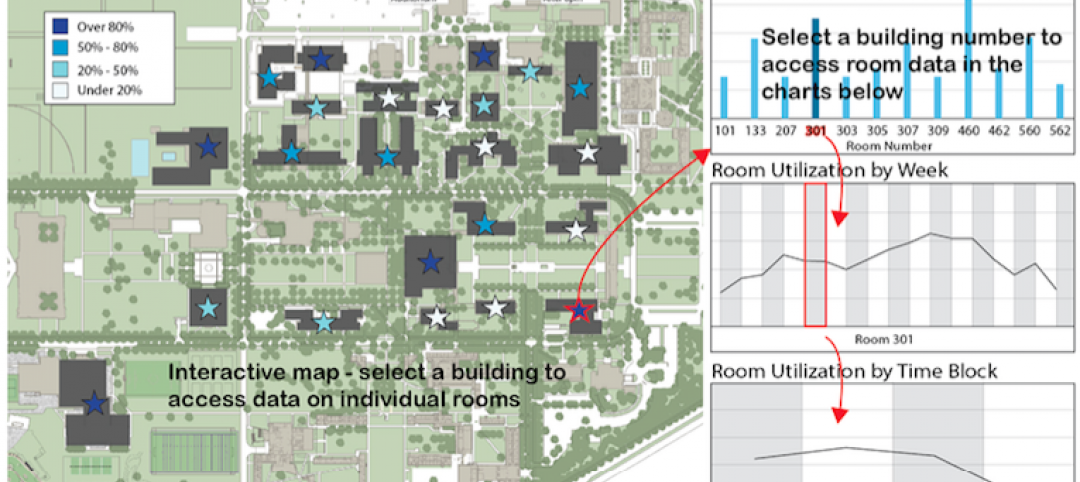
Big Data helps space optimization, but barriers remain
Space optimization is a big issue on many university campuses, as schools face increasing financial constraints, writes Hanbury’s Jimmy Stevens.
Lighting | Aug 2, 2017
Dynamic white lighting mimics daylighting
By varying an LED luminaire’s color temperature, it is possible to mimic daylighting, to some extent, and the natural circadian rhythms that accompany it, writes DLR Group’s Sean Avery.
Office Buildings | Jul 20, 2017
SGA uses virtual design and construction technology to redevelop N.Y. building into modern offices
287 Park Avenue South is a nine-story Classical Revival building previously known as the United Charities Building.
Accelerate Live! | Jul 6, 2017
Watch all 20 Accelerate Live! talks on demand
BD+C’s inaugural AEC innovation conference, Accelerate Live! (May 11, Chicago), featured talks on machine learning, AI, gaming in construction, maker culture, and health-generating buildings.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: Is the road to the future the path of least resistance? Sasha Reed, Bluebeam (sponsored)
Bluebeam’s Sasha Reed discusses why AEC leaders should give their teams permission to responsibly break things and create ecosystems of people, process, and technology.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: 3D laser scanning for the project lifecycle, FARO Technologies (sponsored)
Brent Slawnikowski of FARO Technologies and Jennifer Suerth of Pepper Construction discuss how implementation of laser scanning has helped Pepper become more successful in the completion of their projects.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: Incubating innovation through R&D and product development, Jonatan Schumacher, Thornton Tomasetti
Thornton Tomasetti’s Jonatan Schumacher presents the firm’s business model for developing, incubating, and delivering cutting-edge tools and solutions for the firm, and the greater AEC market.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: The future of computational design, Ben Juckes, Yazdani Studio of CannonDesign
Yazdani’s Ben Juckes discusses the firm’s tech-centric culture, where scripting has become an every-project occurrence and each designer regularly works with computational tools as part of their basic toolset.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: A case for Big Data in construction, Graham Cranston, Simpson Gumpertz & Heger
Graham Cranston shares SGH’s efforts to take hold of its project data using mathematical optimization techniques and information-rich interactive visual graphics.
| Jun 13, 2017
Accelerate Live! talk: Scaling change in a changing industry, Chris Mayer, Suffolk Construction
Suffolk’s CIO Chris Mayer talks about the firm’s framework for vetting and implementing new technologies and processes.