Today is Earth Day, and this morning, Turner Construction made public an ambitious program that could burnish its standing as a green builder.
This three-pronged initiative starts with Turner reaffirming its commitment, made in 2004, to “build green.” Over the past 15 years, Turner has worked on more than $60 billion of green building projects. The company has 1,500 LEED-accredited employees. It now diverts, on average, 75% of jobsite waste from landfills. And three years ago, it formed a National Sustainability Committee, currently comprised of 16 people who look for innovative strategies to apply to the company’s various projects.
Turner is taking this commitment to another level today, as it will monitor the activities on certain jobsites to see where water and energy consumption can be lowered. It has selected 30 projects, across different building typologies, to participate in a pilot program that, over the next 18 months, will meter those projects on all forms of C02 emissions and water use, including onsite fuel use.
The company will compile these data through the end of 2020, it which point it hopes to have a normalized average for emissions and water use per building. Using those averages, Turner will then devise a strategy to reduce water and energy use by 50% on all of its projects by 2030. (To see images of a project being metered—the Natural Resources Agency headquarters for the California Department of General Services, in Sacramento, Calif.—go to https://app.oxblue.com/open/Turner/NNRHPROJECT)
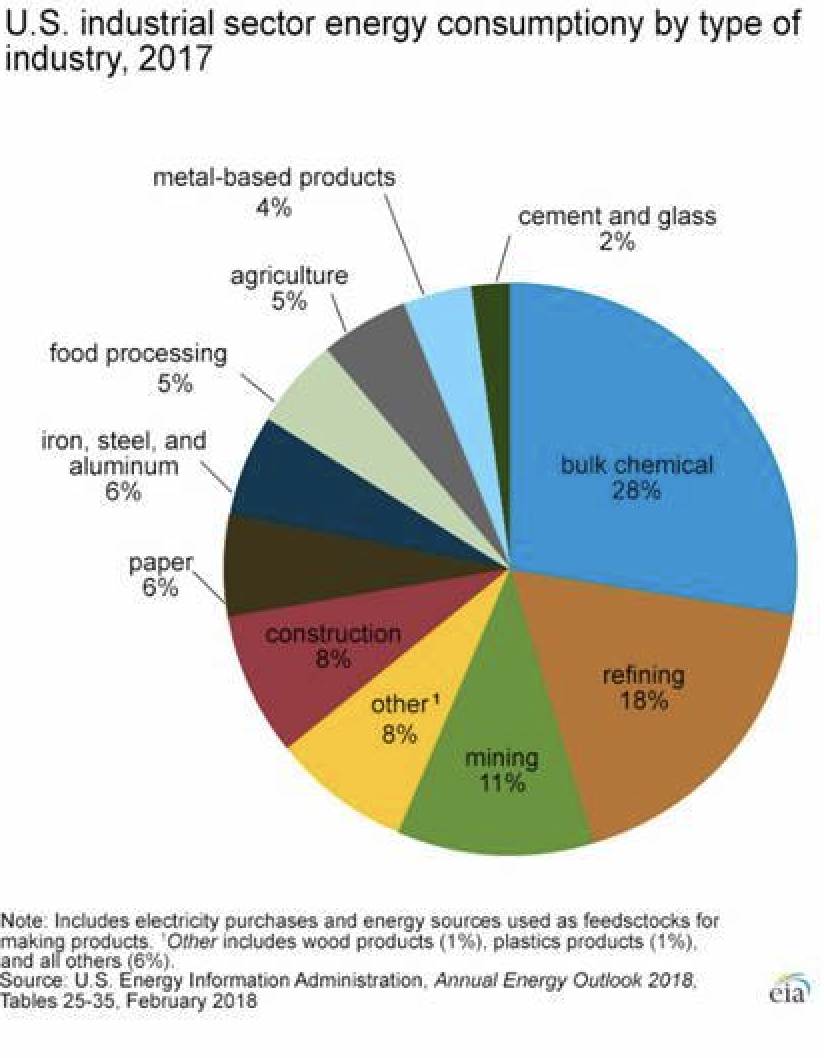
Construction activities account for 8% of industrial sector's energy use. Turner is monitoring select jobsites to determine how they can reduce water and energy use. Image: U.S. Energy Information Administration
The company also has about 40 sustainability managers who provide technical support and guidance to its regional offices. They are “our green ambassadors,” and “eyes and ears on the ground,” says Julia Gisewite, whom Turner promoted to Director of Sustainability last September. Gisewite is spearheading the company’s initiative with Tom Gerlach, an Executive Vice President who has been with Turner Construction since 1977; and Peter Davoren, the company’s President and CEO.
The third pillar of Turner’s initiative focuses on resilience. Turner is responding to the threats from natural disasters such as flooding and fires that “are getting bigger and bigger,” and “are becoming more intense,” says Christopher McFadden, a company spokesman. He explains that Turner is now looking closer at the welfare and safety of its workers under those conditions, as well as “the range of resilience for the built environment,” with the goal being to develop ways that it can strengthen buildings’ resistance.
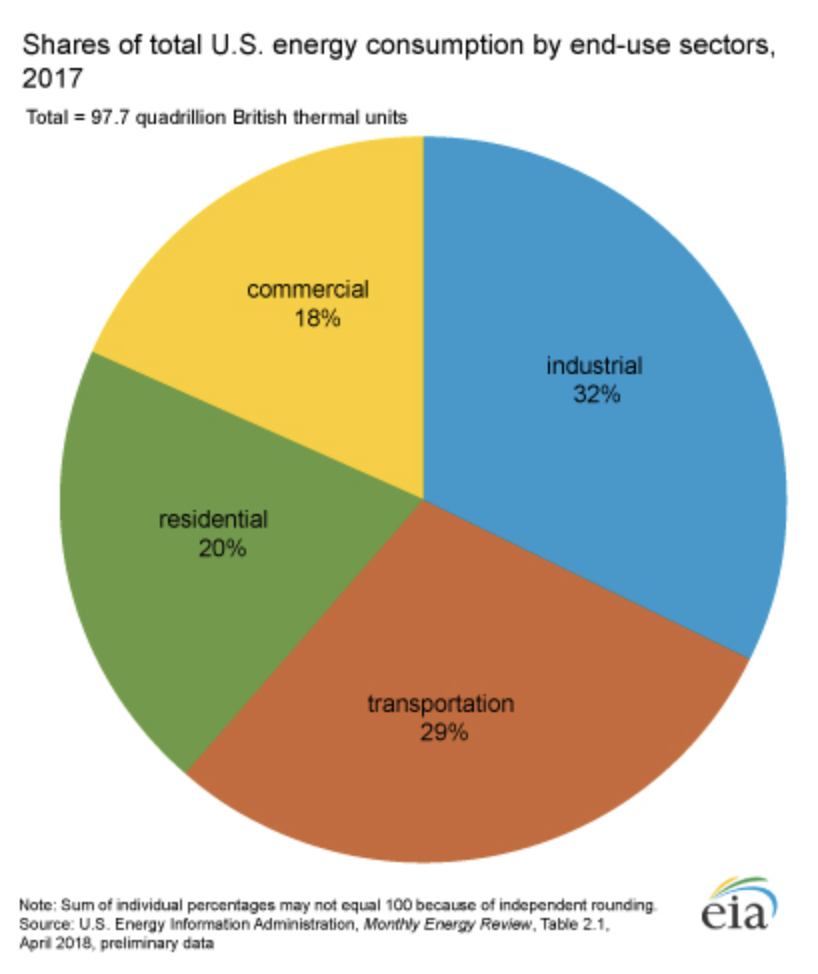
The built environment continues to be a massive energy user. Image: U.S. Energy Information Administration
“We want to be a voice at the table, and a stronger, better partner,” especially during preconstruction discussions with owners, developers, and AEC partners. Gisewite adds that Turner has started to insinuate resilience and resource awareness into its orientation of workers and subcontractors.
Getting back to its construction activities, Turner already has some baseline data: its annual Turner Green Zone survey, which it has conducted for the last seven years, and which guides how the company sets up its offices. That survey “has given us the confidence to move forward” with its initiative, says McFadden.
Gisewite says that some of the activities monitored will be “low-hanging fruit,” like turning off lights and equipment in jobsite trailers every night. She adds, too, that Turner is now committed to installing LEDs for those sites’ temporary lighting.
“We’re looking at what we can control,” says McFadden.
Gisewite envisions holding meetings with subcontractors and suppliers about jobsite efficiency. Nothing’s been scheduled yet, but she expects these meetings will most likely happen regionally, and some could also be project-by-project.
The Turner execs agree that technology will play a role in the company’s program. “The conversation around carbon has elevated so quickly,” she says, “and I’m most excited about the technology” that might provide answers. McFadden adds that Turner recently completed its 5th annual Innovation Summit, and that its jobsites are already using augmented and virtual reality tools to help reduce waste by using fewer materials.
He recalls that in the early 1900s, Turner Construction made a name for itself by building with steel-reinforced concrete as an alternative to lumber at a time when wood-made factories were burning down. Today, that same mentality of taking the lead is what’s driving Turner’s environmental stewardship as well as efforts to make buildings better able to withstand the ravages of nature.
“We’re asking ‘what can we be doing?’ because we should be doing more,” McFadden says.
Related Stories
Resiliency | Feb 15, 2022
Design strategies for resilient buildings
LEO A DALY's National Director of Engineering Kim Cowman takes a building-level look at resilient design.
Sponsored | Steel Buildings | Jan 25, 2022
Multifamily + Hospitality: Benefits of building in long-span composite floor systems
Long-span composite floor systems provide unique advantages in the construction of multi-family and hospitality facilities. This introductory course explains what composite deck is, how it works, what typical composite deck profiles look like and provides guidelines for using composite floor systems. This is a nano unit course.
Sponsored | Reconstruction & Renovation | Jan 25, 2022
Concrete buildings: Effective solutions for restorations and major repairs
Architectural concrete as we know it today was invented in the 19th century. It reached new heights in the U.S. after World War II when mid-century modernism was in vogue, following in the footsteps of a European aesthetic that expressed structure and permanent surfaces through this exposed material. Concrete was treated as a monolithic miracle, waterproof and structurally and visually versatile.
Sponsored | Resiliency | Jan 24, 2022
Norshield Products Fortify Critical NYC Infrastructure
New York City has two very large buildings dedicated to answering the 911 calls of its five boroughs. With more than 11 million emergency calls annually, it makes perfect sense. The second of these buildings, the Public Safety Answering Center II (PSAC II) is located on a nine-acre parcel of land in the Bronx. It’s an imposing 450,000 square-foot structure—a 240-foot-wide by 240-foot-tall cube. The gleaming aluminum cube risesthe equivalent of 24 stories from behind a grassy berm, projecting the unlikely impression that it might actually be floating. Like most visually striking structures, the building has drawn as much scorn as it has admiration.
Sponsored | Resiliency | Jan 24, 2022
Blast Hazard Mitigation: Building Openings for Greater Safety and Security
Microgrid | Jan 16, 2022
Resilience is what makes microgrids attractive as back-up energy controls
Jacobs is working with clients worldwide to ensure mission critical operations can withstand unexpected emergencies.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Jan 12, 2022
Total steel project performance
This instructor-led video course discusses actual project scenarios where collaborative steel joist and deck design have reduced total-project costs. In an era when incomplete structural drawings are a growing concern for our industry, the course reveals hidden costs and risks that can be avoided.
Resiliency | Oct 19, 2021
Achieving resiliency through integrated design
Planning for and responding to the effects of adverse shocks and stresses is typically what architects and engineers have always thought of as good standard design practices.
Resiliency | Aug 19, 2021
White paper outlines cost-effective flood protection approaches for building owners
A new white paper from Walter P Moore offers an in-depth review of the flood protection process and proven approaches.
Resiliency | Aug 19, 2021
White paper outlines cost-effective flood protection approaches for building owners
A new white paper from Walter P Moore offers an in-depth review of the flood protection process and proven approaches.