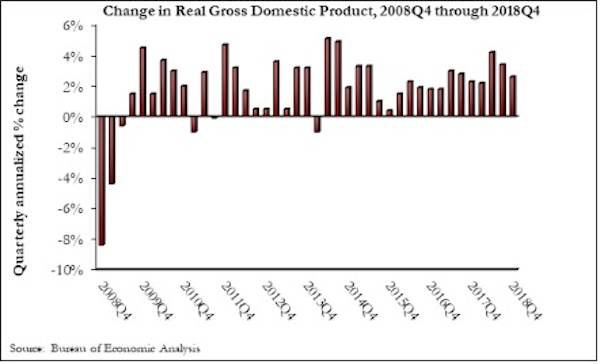
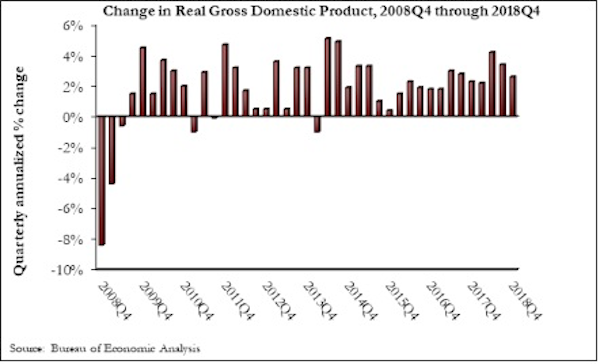
The U.S. economy grew at an annual rate of 2.6% in the fourth quarter of 2018, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data published today by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. Year-over-year GDP growth was 3.1%, while average growth for 2018 was 2.9%.
“Today’s GDP report confirms continued strong investment in nonresidential segments in America,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “Separately, construction spending data show significant expenditures on the construction of data centers, hotel rooms, theme parks and fulfillment centers. These data also indicate stepped up public construction spending in categories such as transportation, education, and water systems. Despite that, today’s GDP release indicated that investment in nonresidential structures actually declined 4.2% on an annualized basis during last year’s fourth quarter. Despite that setback, this form of investment was up by 5% for the entirety of 2018.
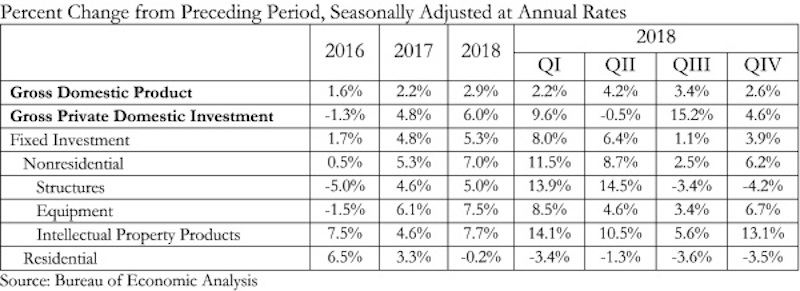
“Undoubtedly, some attention will be given to the fact that the U.S. economy expanded by just shy of 3% in 2018,” said Basu. “Unless that figure is revised upward in subsequent releases, it will mean that America has failed to reach the 3% annual threshold since 2005. But while much attention will be given to a perceived shortfall in growth, the fourth quarter figure of 2.6% signifies that the U.S. economy entered this year with substantial momentum. Were it not for a weak residential construction sector, 3% growth would have been attained. Moreover, the data indicate strength in disposable income growth and in business investment.
“It is quite likely that the U.S. economy will expand at around 2% this year,” said Basu. “Though interest rates remain low and hiring is still brisk, a number of leading indicators suggest that the nation’s economy will soften somewhat during the quarters ahead, which can be partly attributed to a weakening global economy. This won’t unduly impact nonresidential construction activity, however, since the pace of activity in this segment tends to lag the overall economy, and strong nonresidential construction spending expected in 2019. Finally, ABC’s Construction Backlog Indicator continues to reflect strong demand for contractors, which have nearly nine months of work lined up.”
Related Stories
Market Data | Aug 13, 2018
First Half 2018 commercial and multifamily construction starts show mixed performance across top metropolitan areas
Gains reported in five of the top ten markets.
Market Data | Aug 10, 2018
Construction material prices inch down in July
Nonresidential construction input prices increased fell 0.3% in July but are up 9.6% year over year.
Market Data | Aug 9, 2018
Projections reveal nonresidential construction spending to grow
AIA releases latest Consensus Construction Forecast.
Market Data | Aug 7, 2018
New supply's impact illustrated in Yardi Matrix national self storage report for July
The metro with the most units under construction and planned as a percent of existing inventory in mid-July was Nashville, Tenn.
Market Data | Aug 3, 2018
U.S. multifamily rents reach new heights in July
Favorable economic conditions produce a sunny summer for the apartment sector.
Market Data | Aug 2, 2018
Nonresidential construction spending dips in June
“The hope is that June’s construction spending setback is merely a statistical aberration,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu.
Market Data | Aug 1, 2018
U.S. hotel construction pipeline continues moderate growth year-over-year
The hotel construction pipeline has been growing moderately and incrementally each quarter.
Market Data | Jul 30, 2018
Nonresidential fixed investment surges in second quarter
Nonresidential fixed investment represented an especially important element of second quarter strength in the advance estimate.
Market Data | Jul 11, 2018
Construction material prices increase steadily in June
June represents the latest month associated with rapidly rising construction input prices.
Market Data | Jun 26, 2018
Yardi Matrix examines potential regional multifamily supply overload
Outsize development activity in some major metros could increase vacancy rates and stagnate rent growth.