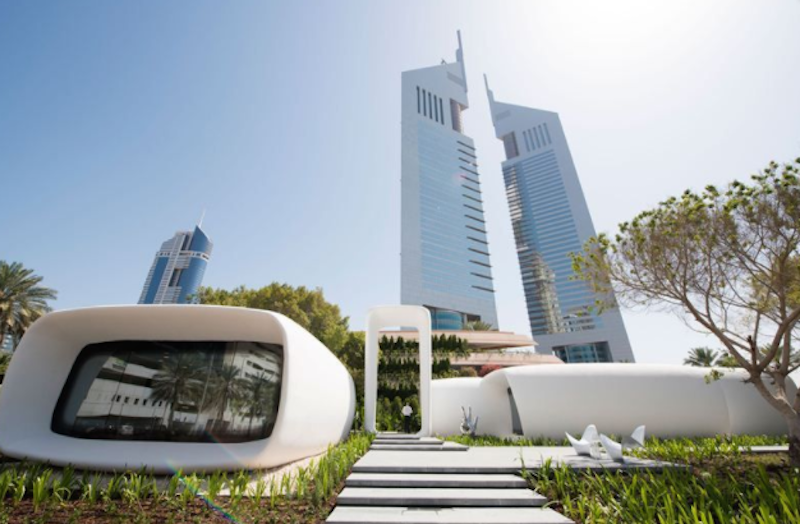
Last April, Dubai unveiled its 3D Printing Strategy, which calls for 25% of buildings in that city to be constructed using 3D printing technology by 2030. That strategy focuses on three major sectors: construction, medical products, and consumer products. The use of 3D printing in Dubai’s construction sector will increase by 2% starting in 2019.
One month after the strategy was publicized, Dubai completed what it asserts is the world’s first 3D-printed office, a 250-sm (2,691-sf) building made from a mixture of cement and other building materials, and assembled in 17 days by a 3D printer measuring 20 feet high, 120 feet long, and 40 feet wide, with a automated robotic arm.
Can a 3D-printed city be too far behind? The answer might lie in the Minitank, a 3D-printing crane under construction that its developer, a Silicon Valley startup called Cazza Construction Technologies, says can layer 2,153 sf of concrete per day, which would make it 50% faster than conventional construction methods.
Cazza’s 19-year-old CEO and co-founder Chris Kelsey tells CNN that construction is the natural progression for 3D printing. Last year, the Dubai Road and Transport Authority invited Cazza to present its technology to government officials overseeing the 3D Printing Strategy initiative. “Out of all of the groups they’d seen online or spoken with, they were most fascinated with the capabilities of our unique machines,” Kelsey told ConstructionWeekOnline.com.
It remains to be seen, though, whether this technology is practical for large-scale projects. There’s not much information about Cazza’s origins or its technology on its website, nor any images of the Minitank. (The site, however, is opening soliciting for partners and distributors for its technology.) Previously, Kelsey founded a company called Appsitude, an app development company. Part of Cazza’s funding came from proceeds of Appsitude’s sale last year.
Cazza, though, is undeniably following in the footsteps of pioneers who have tested the limits of 3D printing for construction. These include Behrokh Khoshnevis, a professor at the University of Southern California, who invented a concrete-extruding 3D printer in 2009 that could print a 2,500-sf structure in 20 hours; the construction firm WinSun, which in 2014 3D printed 10 one-story houses in a single day; and DUS Architects, which last year 3D printed a full canal house in Amsterdam.
Cazza’s process is relatively straightforward: an architect would upload blueprints onto a computer system, which transmits the information to the crane printer that layers the concrete in the shape of the design.
The Minitank, if it becomes operational, will be able to print on-site, and construct buildings up to three stories high. “The barrier to companies [printing on-site] so far has been that it’s extremely difficult to develop a machine with all of the factors needed,” Kelsey explained.
The Minitank would use cement made from 80% recycled materials. Cazza claims that its portable equipment can be set up within 30 minutes, and that its process would reduce labor and materials costs by up to 90%. Fernando De Los Rios, Cazza’s COO, said his company would soon bring its engineers from across the world to start working in Dubai and surrounding areas.
Dubai’s Roads and Transport Authority has several 3D printed projects in the works already, including the Museum of the Future, and DEWA’s labs in the Mohammed Bin Rashid Al-Maktoum Solar Park.
Related Stories
| Jan 23, 2014
Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill-designed Federation of Korean Industries tower opens in Seoul [slideshow]
The 50-story tower features a unique, angled building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) exterior designed to maximize the amount of energy collected.
| Jan 13, 2014
Custom exterior fabricator A. Zahner unveils free façade design software for architects
The web-based tool uses the company's factory floor like "a massive rapid prototype machine,” allowing designers to manipulate designs on the fly based on cost and other factors, according to CEO/President Bill Zahner.
| Jan 13, 2014
AEC professionals weigh in on school security
An exclusive survey reveals that Building Teams are doing their part to make the nation’s schools safer in the aftermath of the Sandy Hook tragedy.
| Jan 10, 2014
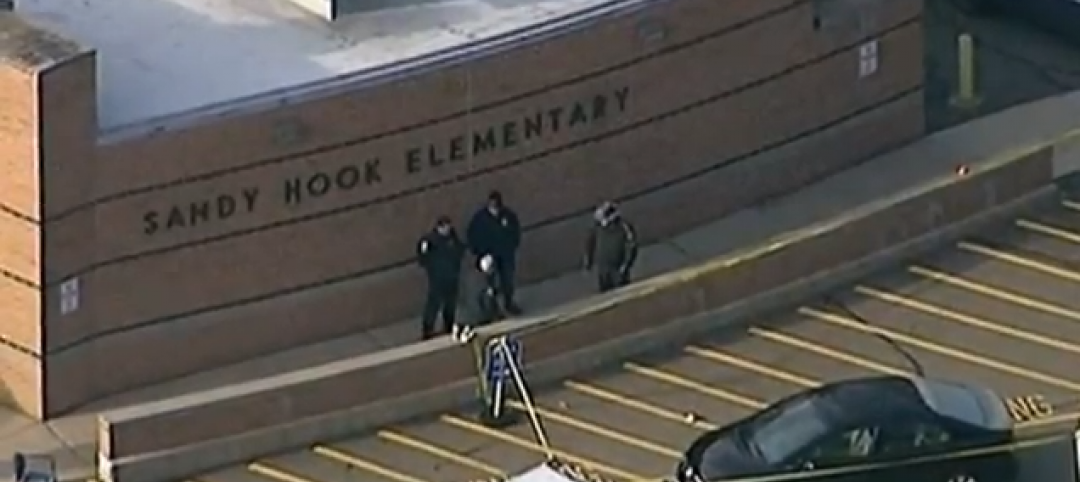
Special Report: K-12 school security in the wake of Sandy Hook
BD+C's exclusive five-part report on K-12 school security offers proven design advice, technology recommendations, and thoughtful commentary on how Building Teams can help school districts prevent, or at least mitigate, a Sandy Hook on their turf.
| Jan 9, 2014
How security in schools applies to other building types
Many of the principles and concepts described in our Special Report on K-12 security also apply to other building types and markets.
| Jan 9, 2014
16 recommendations on security technology to take to your K-12 clients
From facial recognition cameras to IP-based door hardware, here are key technology-related considerations you should discuss with your school district clients.
| Jan 6, 2014
What is value engineering?
If you had to define value engineering in a single word, you might boil it down to "efficiency." That would be one word, but it wouldn’t be accurate.
| Dec 23, 2013
MBI commends start of module setting at B2, world's tallest modular building
The first modules have been set at B2 residential tower at Atlantic Yards in New York, set to become the tallest modular building in the world.
| Dec 13, 2013
Safe and sound: 10 solutions for fire and life safety
From a dual fire-CO detector to an aspiration-sensing fire alarm, BD+C editors present a roundup of new fire and life safety products and technologies.
| Dec 10, 2013
16 great solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
From a crowd-funded smart shovel to a why-didn’t-someone-do-this-sooner scheme for managing traffic in public restrooms, these ideas are noteworthy for creative problem-solving. Here are some of the most intriguing innovations the BD+C community has brought to our attention this year.