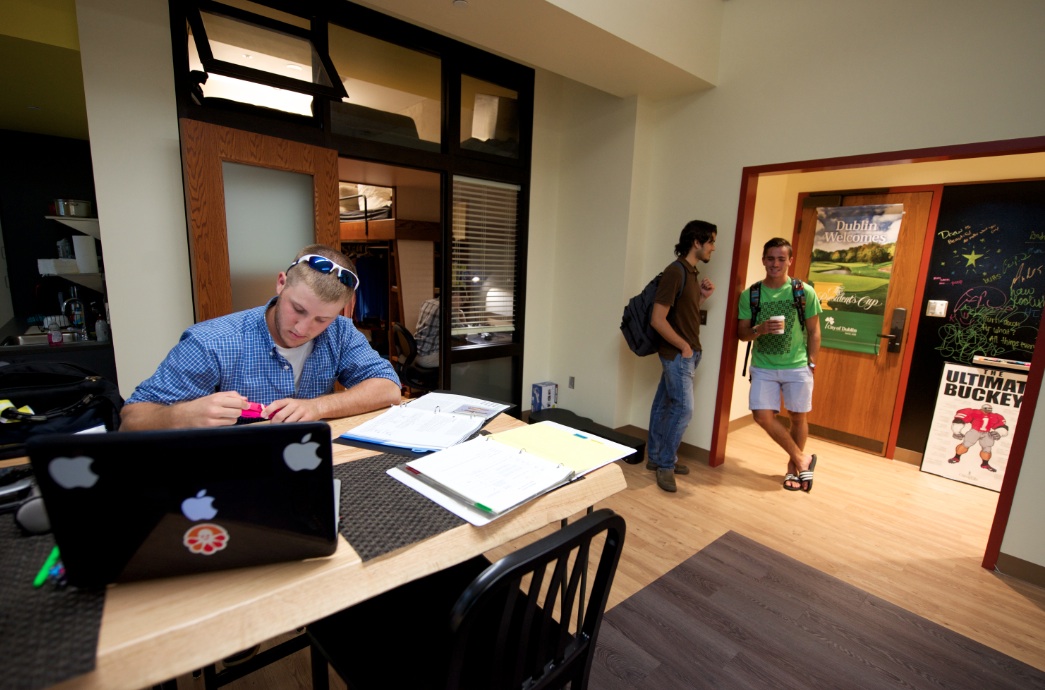
University officials and design firms are struggling to understand how rapidly changing student habits are altering how they use living spaces. To get a better feel for that phenomenon, Little Diversified Architectural Consulting earlier this year conducted a daylong student housing symposium at its Durham and Charlotte locations to pick the brains of 62 students from a dozen North Carolina institutions. The firm recapped the findings in a recent report, called "What Students Want."
“We were surprised at how much time students are spending in housing facilities,” says Thomas Carlson-Reddig, AIA, LEED AP, Global Practice Leader for Little's Community team. The discussion revealed that half the students surveyed studied in their rooms, while half “escaped” to other spaces to study, eat, and relax.
Here are highlights of the comments from 62 college students that participated in Little’s workshops:
What students want in their rooms:
• Ability to reconfigure the room
• Built-in furniture that defines the space (but is still reconfigurable)
• Mobile beds with a cushion seat that could rest below the desk
• “Work surface” desk space with a comfortable chair
• Ability to create a private zone in rooms with multiple students
• More storage, such as built-in closets (not wardrobes)
• A sink—accessible outside the bathroom—in the room
• No old-school “dorm furniture”
• Option to paint one wall in the room
• Rooms with some color and texture—not all gray, tan, or white walls
• Translucent divider wall along the bed
• “Murphy beds” or loft beds as options, but no bunk beds
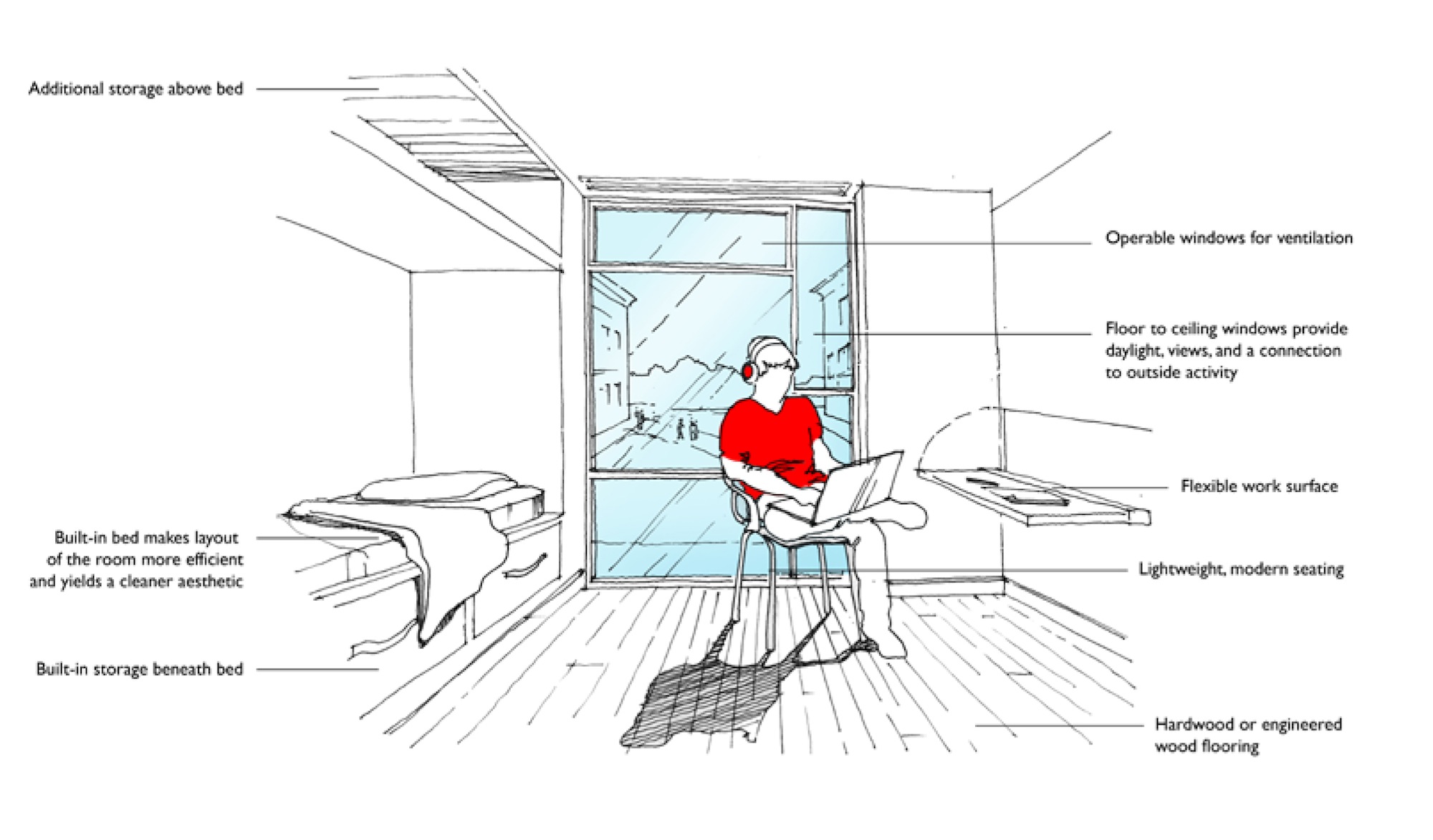
During the symposium, Little asked the students a variety of questions pertaining to their dorm room experiences. There was a broad consensus that traditional dorm furniture frequently impedes their optimal use of the space. Their responses generated ideas ranging from a multi-purpose wall where a bed, desk and storage can be easily reconfigured to moveable partitions that could help define living and sleeping spaces and provide privacy between roommates. What Little learned is that the efficiency of the room can be greatly improved without increasing floor area.
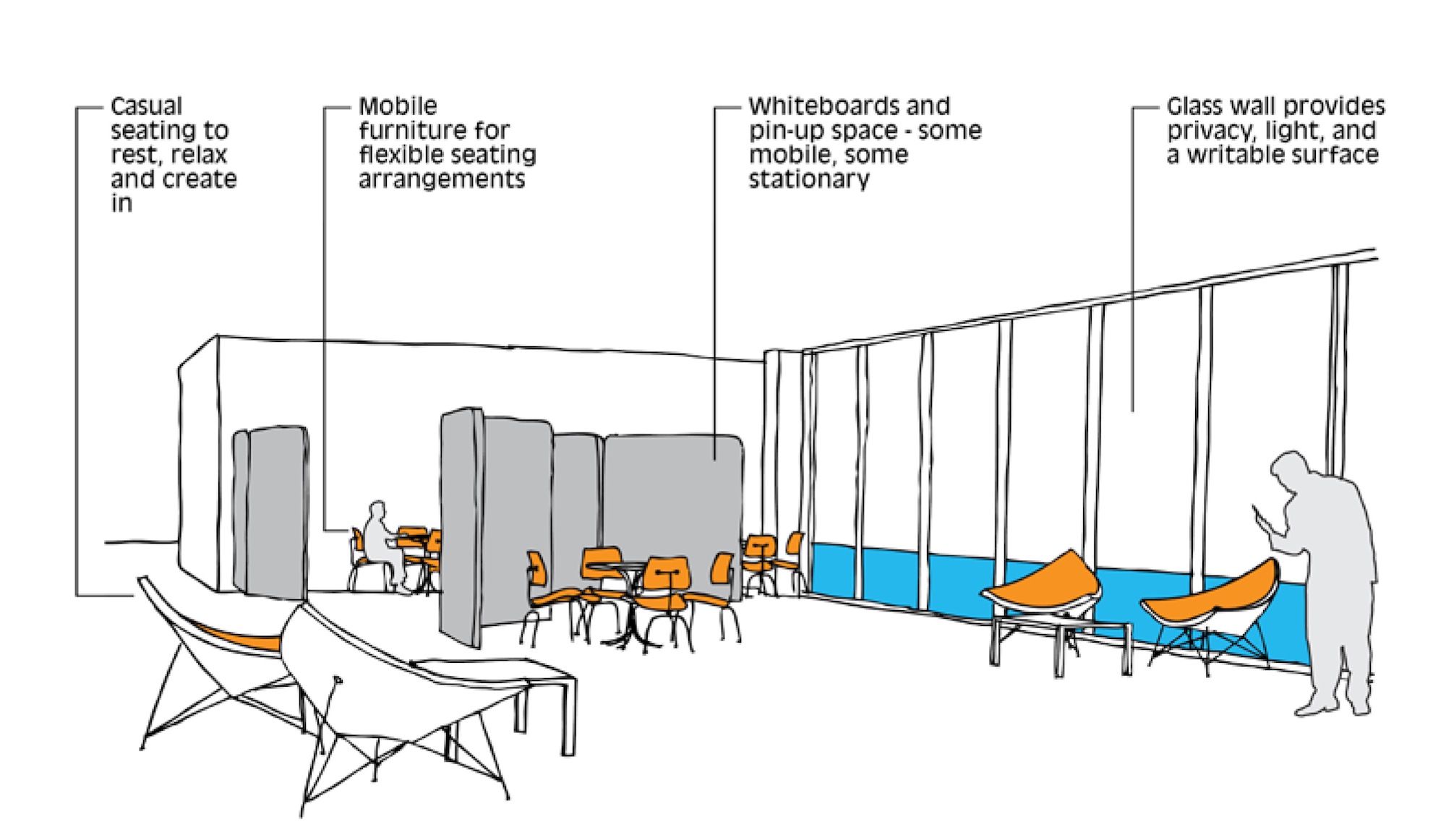
What students want in their study spaces:
• Small, individual study nooks scattered throughout the residence hall (and other buildings as well)
• Comfortable seating that is playful, whimsical, and relaxed
• Spaces that are full of light, with views of outdoors
• Quality of light is important, but avoid glare and heat gain
• Small study areas adjacent to stairs/elevators (to allow students to monitor activity, meet friends)
• Group study and collaboration areas
• Flexible furniture options, from small group tables to lounge seating
• Outdoor study space, where feasible
Over the course of a day, students find opportunities to study in various locations throughout campus. Little wanted to understand the characteristics of what makes a good study spot. The firm learned it should be bright and comfortable. It should be fairly quiet, yet visually connected to the more active spaces. Larger group study areas should be complemented by cozier individual study nooks. A student that chooses to study outside of his or her room doesn’t want to feel isolated.
What students want in their social lives:
• Learning spaces that can dovetail into “chill” spaces
• Laundry facilities that create an opportunity for social interaction
• Community lounges located in vertical circulation zones so that students can see others coming and going
• Kitchens that serve a smaller “community” are preferred over those that serve an entire building
• Chill spaces that provide as much variety as possible
• Active outdoor zones adjacent to housing for group-based casual fitness (e.g., Frisbee, volleyball)
• Rooftop gardens, green roofs, “working green spaces,” outdoor benches, and outdoor eating areas with picnic tables and barbecue grilles
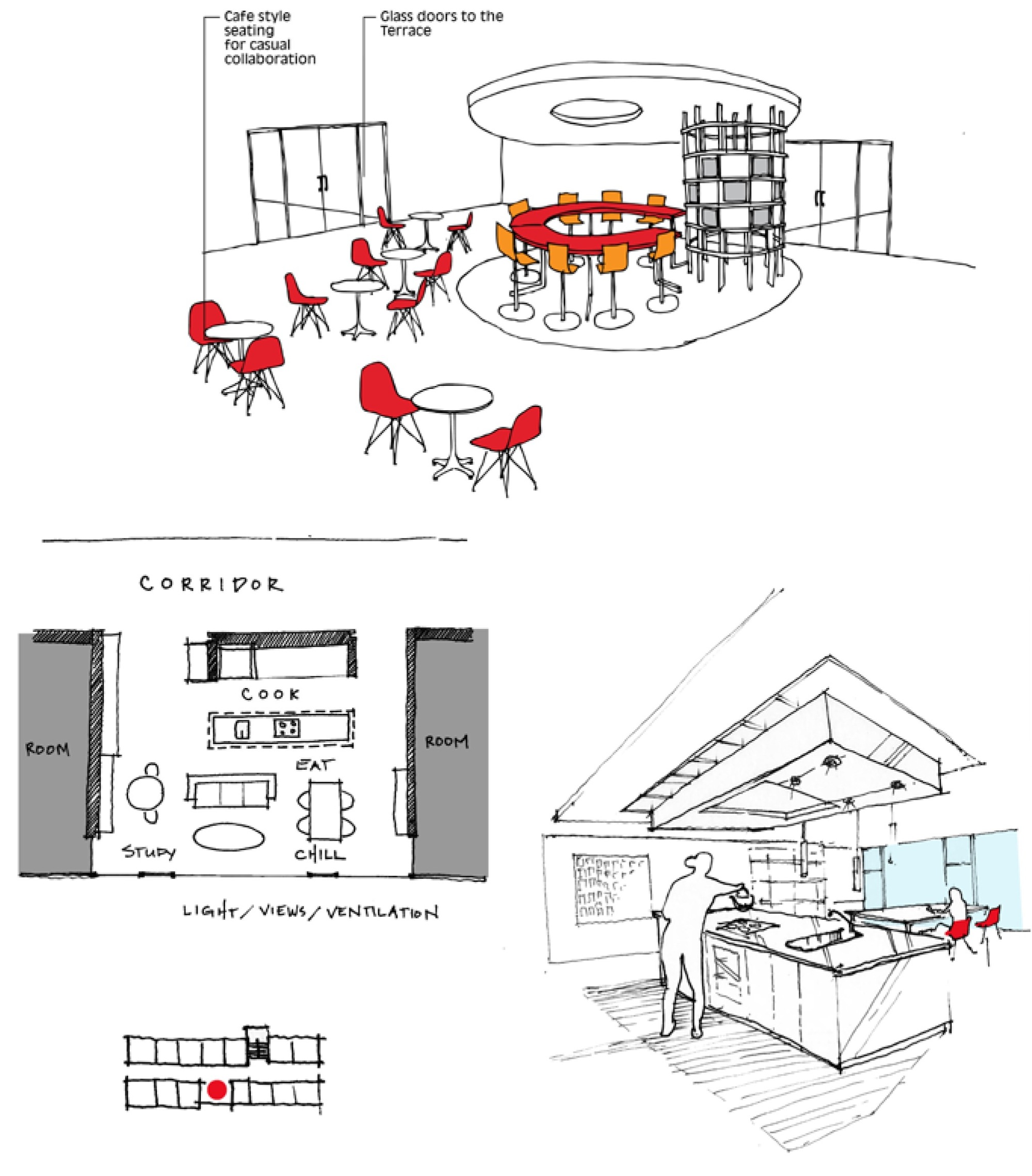
A sense of community is what students seek when they arrive on campus and it is what will keep them there for the course of their studies. Little defined the community as a relatively small group (16-32 students) that can take ownership of common areas, such as kitchens or lounges. In order to be activated, gathering areas should be located along the horizontal and vertical circulation paths, have access to light and views, and connect various communities to each other.
Download the complete "What Students Want" report from Little.
Related Stories
| Jan 4, 2011
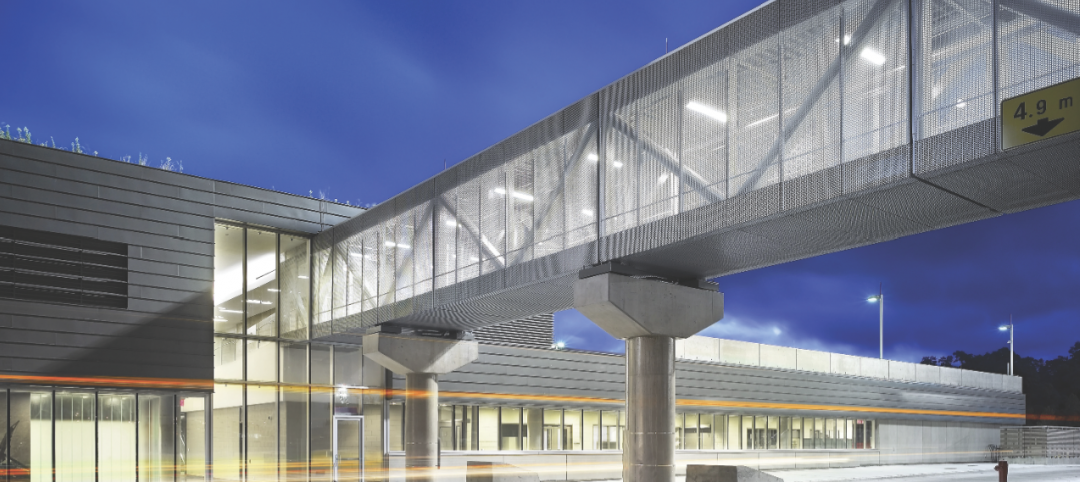
Product of the Week: Zinc cladding helps border crossing blend in with surroundings
Zinc panels provide natural-looking, durable cladding for an administrative building and toll canopies at the newly expanded Queenstown Plaza U.S.-Canada border crossing at the Niagara Gorge. Toronto’s Moriyama & Teshima Architects chose the zinc alloy panels for their ability to blend with the structures’ scenic surroundings, as well as for their low maintenance and sustainable qualities. The structures incorporate 14,000 sf of Rheinzink’s branded Angled Standing Seam and Reveal Panels in graphite gray.
| Jan 4, 2011
6 green building trends to watch in 2011
According to a report by New York-based JWT Intelligence, there are six key green building trends to watch in 2011, including: 3D printing, biomimicry, and more transparent and accurate green claims.
| Jan 4, 2011
LEED standards under fire in NYC
This year, for the first time, owners of 25,000 commercial properties in New York must report their buildings’ energy use to the city. However, LEED doesn’t measure energy use and costs, something a growing number of engineers, architects, and landlords insist must be done. Their concerns and a general blossoming of environmental awareness have spawned a host of rating systems that could test LEED’s dominance.
| Jan 4, 2011
LEED 2012: 10 changes you should know about
The USGBC is beginning its review and planning for the next version of LEED—LEED 2012. The draft version of LEED 2012 is currently in the first of at least two public comment periods, and it’s important to take a look at proposed changes to see the direction USGBC is taking, the plans they have for LEED, and—most importantly—how they affect you.
| Jan 4, 2011
California buildings: now even more efficient
New buildings in California must now be more sustainable under the state’s Green Building Standards Code, which took effect with the new year. CALGreen, the first statewide green building code in the country, requires new buildings to be more energy efficient, use less water, and emit fewer pollutants, among many other requirements. And they have the potential to affect LEED ratings.
| Jan 4, 2011
New Years resolutions for architects, urban planners, and real estate developers
Roger K. Lewis, an architect and a professor emeritus of architecture at the University of Maryland, writes in the Washington Post about New Years resolutions he proposes for anyone involved in influencing buildings and cities. Among his proposals: recycle and reuse aging or obsolete buildings instead of demolishing them; amend or eliminate out-of-date, obstructive, and overly complex zoning ordinances; and make all city and suburban streets safe for cyclists and pedestrians.
| Jan 4, 2011
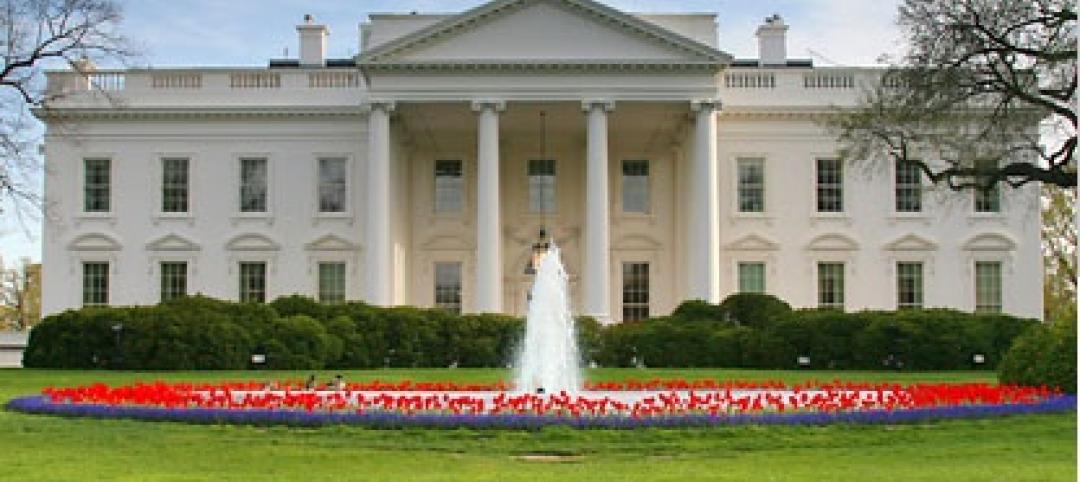
An official bargain, White House loses $79 million in property value
One of the most famous office buildings in the world—and the official the residence of the President of the United States—is now worth only $251.6 million. At the top of the housing boom, the 132-room complex was valued at $331.5 million (still sounds like a bargain), according to Zillow, the online real estate marketplace. That reflects a decline in property value of about 24%.
| Jan 4, 2011
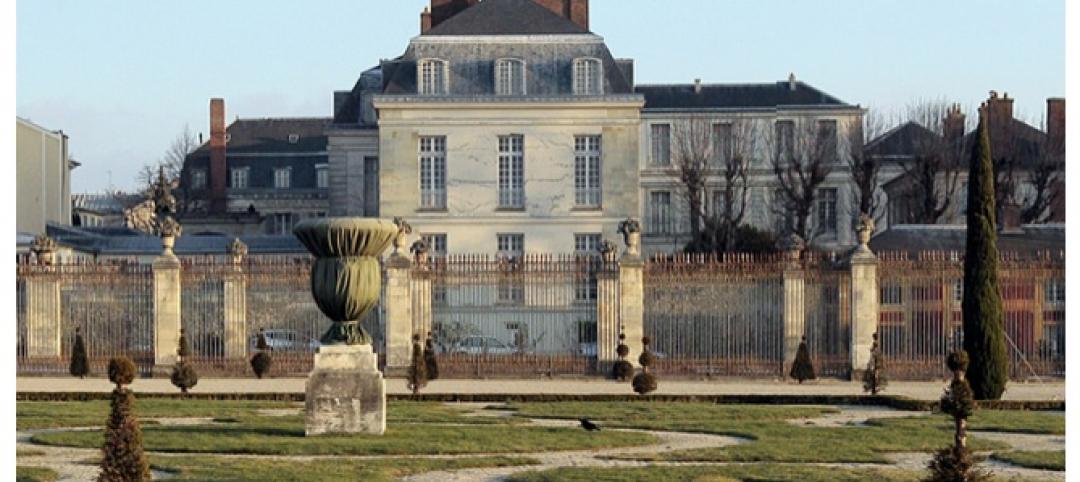
Luxury hotel planned for Palace of Versailles
Want to spend the night at the Palace of Versailles? The Hotel du Grand Controle, a 1680s mansion built on palace grounds for the king's treasurer and vacant since the French Revolution, will soon be turned into a luxury hotel. Versailles is partnering with Belgian hotel company Ivy International to restore the dilapidated estate into a 23-room luxury hotel. Guests can live like a king or queen for a while—and keep their heads.
| Jan 4, 2011
Grubb & Ellis predicts commercial real estate recovery
Grubb & Ellis Company, a leading real estate services and investment firm, released its 2011 Real Estate Forecast, which foresees the start of a slow recovery in the leasing market for all property types in the coming year.
| Jan 4, 2011
Furniture Sustainability Standard - Approved by ANSI and Released for Distribution
BIFMA International recently announced formal American National Standards Institute (ANSI) approval and release of the ANSI/BIFMA e3-2010 Furniture Sustainability Standard. The e3 standard represents a structured methodology to evaluate the "sustainable" attributes of furniture products and constitutes the technical criteria of the level product certification program.