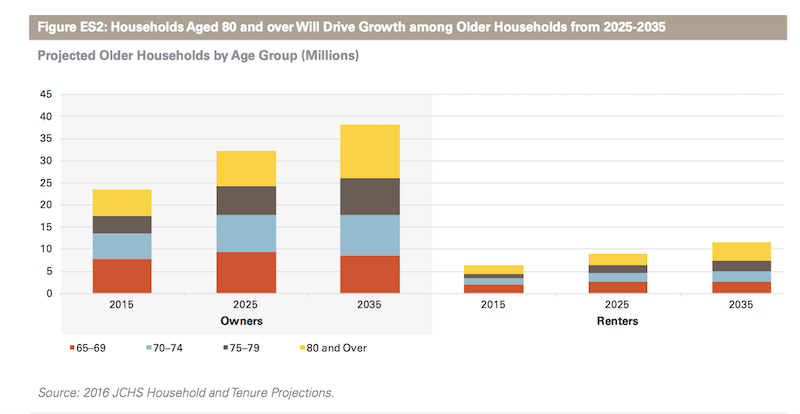
The nation is at the beginning stages of a 20-plus year surge in its older population. By 2035, one in five people in the U.S. will be aged 65 and over, up from one in seven today. By that same year, one in three households will be headed by someone aged 65 or older.
Those projections come from a new report published by the Harvard Joint Center of Housing Studies, which examines the challenges that lie ahead for a country where owners and renters are getting older, more diverse, but also more likely to be struggling with physical and mental infirmities that require regular care.
Will the housing sector be up to meeting the demands of an older population, many of whom prefer to age in their current residences? “A wider array of housing types can offer safer, more affordable, and lower-maintenance homes within existing communities,” the report states.
First, some statistics: The Census Bureau estimates the 65-and-over population will increase by more than 30 million people by 2035 and reach 79 million, with more than half that growth occurring in the next decade. The 80-and-over population alone will double between 2015 and 2035 to 24 million, with 70 percent of that growth occurring from 2025-2035.
The Joint Center projects that this population growth will translate into an increase of nearly 20 million older households, from 29.9 million in 2015 to 49.6 million by 2035. The number of owner households headed by a person aged 65 or over will soar from 24 million in 2015 to 32 million by 2025, and then to 38 million by 2035, an overall increase of 62%. Homeowner households headed by someone aged 80 or over will experience particularly steep growth, more than doubling from nearly 6 million to over 12 million within the next 20 years.
Over these two decades, the sheer growth in the older population will mean the number of renter households will expand from 6 million to more than 11 million households. Overall, the share of renters will increase slightly, from 21% of older households in 2015 to 23% in 2035.
Single-person households will grow slightly more quickly among older adults to total roughly 22 million households in 2035, barely outnumbering the 21 million projected married-couple households age 65 and over.
As the population ages, the home is an increasingly important setting for the delivery of long-term care, a trend likely to grow over the next two decades as millions more seek to remain in their current dwellings while coping with disabilities and health challenges.
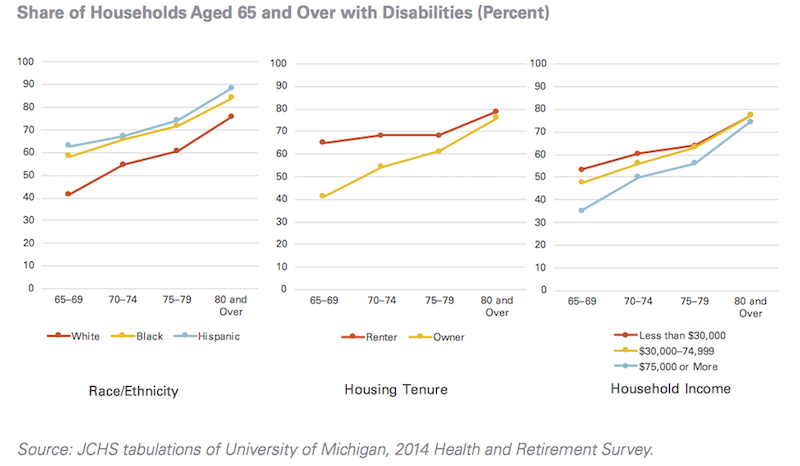 The home will increasingly become a setting for delivery of long-term care in the U.S., where older householders with a disability will grow by 76% to 31.2 milion by 2035. Image: Joint Center for Housing Studies
The home will increasingly become a setting for delivery of long-term care in the U.S., where older householders with a disability will grow by 76% to 31.2 milion by 2035. Image: Joint Center for Housing Studies
By 2035, older households with a disability will increase by 76 percent to reach 31.2 million. By that time, 17 million older households will include someone with a mobility disability, 12 million with a self-care disability, and 27 million with a household activity disability. Roughly half the anticipated increase of 13.4 million older households with disabilities will occur by 2025, with the remainder in the 2025-2035 decade.
By 2035, 17 million older adult households will have at least one person with a mobility disability, for whom stairs, narrow corridors and doorways, and traditional bathroom layouts will pose challenges to safety and independence. Over five million of these will be renter households. Renters are more likely than owners to have mobility disabilities, but also have less control over modifying their units.
The conundrum is that only 1 percent of the current housing stock offers the key accessibility features that people with disabilities require. And the financial wherewithal of older Americans to install those features or modify their houses themselves will be limited.
More than nine million older homeowners have less than $50,000 in non-housing assets. “Clearly, costs will pose challenges for many who will need to secure paid help to remain in their homes,” says the Joint Center. Renters’ assets are even more meager.
In the future, more women will be eligible for Social Security. But the Social Security Administration’s MINT (Modeling Incomes in the Near Term) model projects the share of all older adults having the means to maintain their pre-retirement lifestyle after they retire falling from 43% today to 39% in 2035. These trends together suggest a future widening in income distributions among older adults.
Households that pay more than half their income for housing costs are projected to reach 8.6 million by 2035. For both owners and renters, the numbers of severely cost-burdened households aged 80 and over will more than double.
In light of these trends and projections, the Joint Center recommends the following actions to ensure housing that provides adequate quality of life for an aging population:
•Increase accessible housing.
•Assist older owners with housing cost burdens.
•Increase subsidies to older renters.
•Strengthen ties between health care and housing.
•Increase public awareness.
•Expand housing options.
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | May 18, 2021
Multifamily housing sector sees near record proposal activity in early 2021
The multifamily sector led all housing submarkets, and was third among all 58 submarkets tracked by PSMJ in the first quarter of 2021.
Market Data | May 18, 2021
Grumman|Butkus Associates publishes 2020 edition of Hospital Benchmarking Survey
The report examines electricity, fossil fuel, water/sewer, and carbon footprint.
Market Data | May 13, 2021
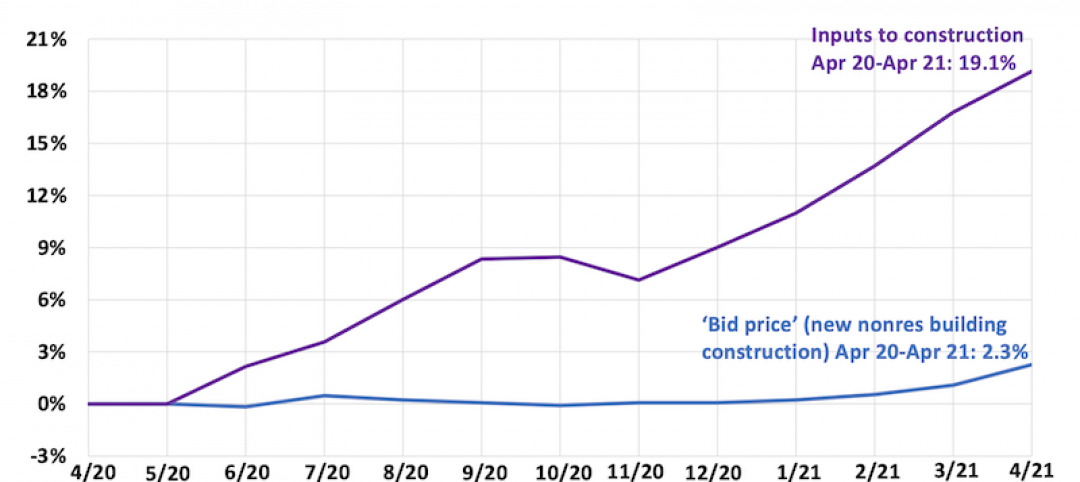
Proliferating materials price increases and supply chain disruptions squeeze contractors and threaten to undermine economic recovery
Producer price index data for April shows wide variety of materials with double-digit price increases.
Market Data | May 7, 2021
Construction employment stalls in April
Soaring costs, supply-chain challenges, and workforce shortages undermine industry's recovery.
Market Data | May 4, 2021
Nonresidential construction outlays drop in March for fourth-straight month
Weak demand, supply-chain woes make further declines likely.
Market Data | May 3, 2021
Nonresidential construction spending decreases 1.1% in March
Spending was down on a monthly basis in 11 of the 16 nonresidential subcategories.
Market Data | Apr 30, 2021
New York City market continues to lead the U.S. Construction Pipeline
New York City has the greatest number of projects under construction with 110 projects/19,457 rooms.
Market Data | Apr 29, 2021
U.S. Hotel Construction pipeline beings 2021 with 4,967 projects/622,218 rooms at Q1 close
Although hotel development may still be tepid in Q1, continued government support and the extension of programs has aided many businesses to get back on their feet as more and more are working to re-staff and re-open.
Market Data | Apr 28, 2021
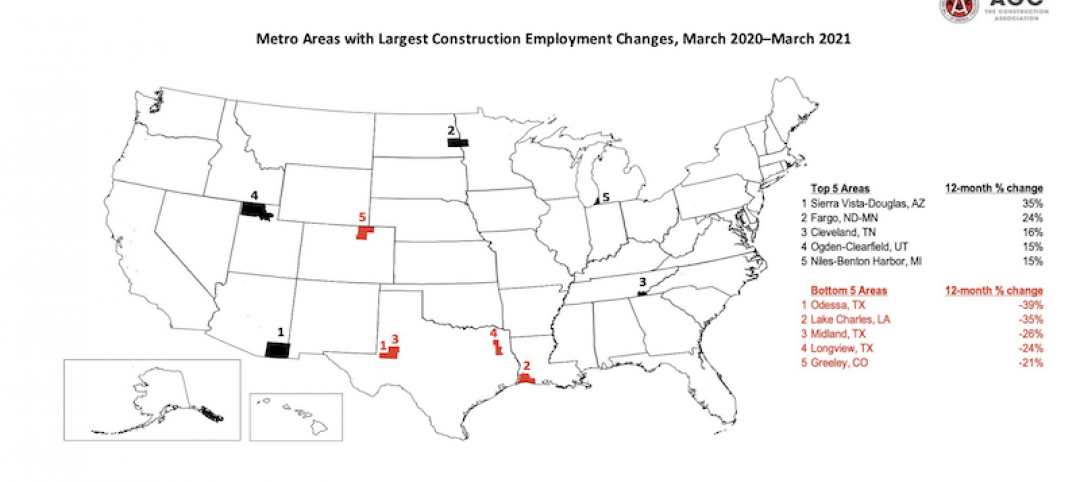
Construction employment declines in 203 metro areas from March 2020 to March 2021
The decline occurs despite homebuilding boom and improving economy.
Market Data | Apr 20, 2021
The pandemic moves subs and vendors closer to technology
Consigli’s latest market outlook identifies building products that are high risk for future price increases.