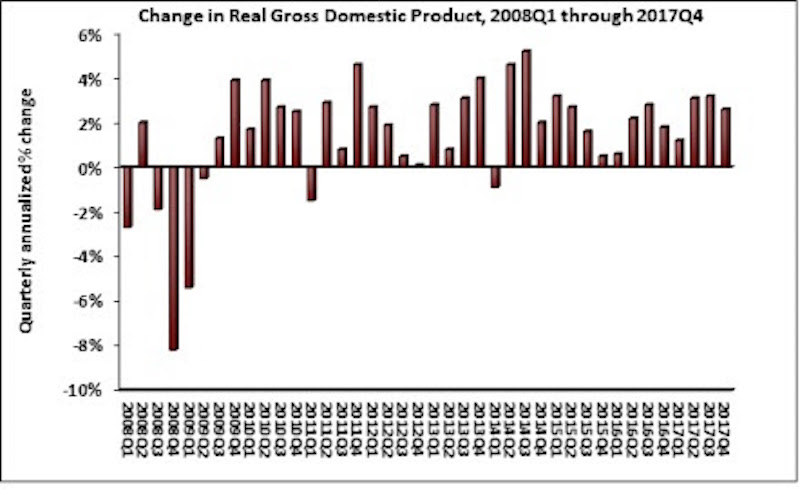
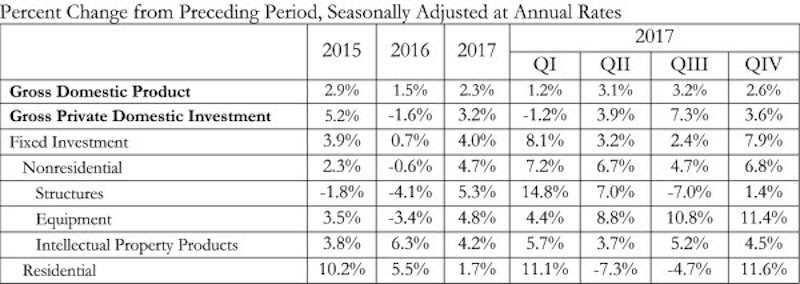
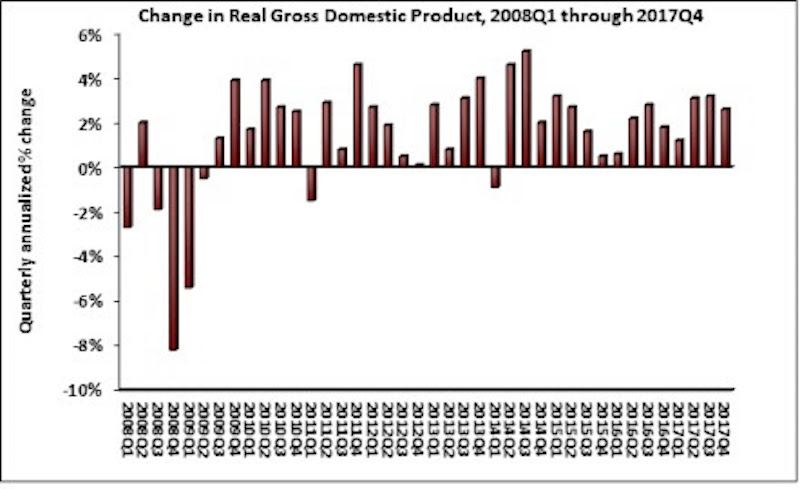
The U.S. economy grew by 2.3% in 2017, while fixed investment increased at a annual rate of 7.9%, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors (ABC) analysis of data released today by the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
The economy expanded at an annual rate of 2.6% during the fourth quarter of 2017 after expanding at a 3.2% rate during the third quarter. Nonresidential fixed investment performed similarly to overall fixed investment in the fourth quarter by increasing at a 6.8% rate. This represents the third time in the past four quarters that nonresidential fixed investment increased by at least 6.7%.
The year-end figure for GDP growth of 2.3% is up from 1.5% in 2016 but down from the 2.9% figure posted in 2015. Nonresidential fixed investment increased 4.7% in 2017, its best year since increasing 6.9% in 2014. This followed a 0.6% contraction in 2016.
“Many will look at this report and conclude that consumer spending, the largest component of the economy, drove fourth quarter growth by expanding at a 3.8% annual rate,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “Upon further inspection, however, the fourth quarter consumer spending missed its 3% expectation due to imports increasing at twice the rate of exports. This widening trade deficit subtracted 1.13 percentage points from fourth quarter GDP growth.
“The factors that have helped to accelerate economic growth in America remain in place, including a strengthening global economy, abundant consumer and business confidence, elevated liquidity flowing through the veins of the international financial system and deregulation,” said Basu. “Stakeholders should be aware that although many companies have announced big plans for stepped-up investment, staffing and compensation—due at least in part to the recently enacted tax cut—the plans have yet to fully manifest within the data. The implication is that the U.S. economy is set to roar in 2018.
“As always, contractors are warned to remain wary,” said Basu. “The combination of extraordinary confidence and capital can fuel excess financial leverage and spur asset price bubbles. The implication is that as contractors remain busy, there should be an ongoing stockpiling of defensive cash. That recommendation will be difficult for many contractors to implement, however, with labor shortages and materials costs rising more rapidly and slender profit margins in many construction segments.”
Related Stories
Market Data | Jan 6, 2022
A new survey offers a snapshot of New York’s construction market
Anchin’s poll of 20 AEC clients finds a “growing optimism,” but also multiple pressure points.
Market Data | Jan 3, 2022
Construction spending in November increases from October and year ago
Construction spending in November totaled $1.63 trillion at a seasonally adjusted annual rate.
Market Data | Dec 22, 2021
Two out of three metro areas add construction jobs from November 2020 to November 2021
Construction employment increased in 237 or 66% of 358 metro areas over the last 12 months.
Market Data | Dec 17, 2021
Construction jobs exceed pre-pandemic level in 18 states and D.C.
Firms struggle to find qualified workers to keep up with demand.
Market Data | Dec 15, 2021
Widespread steep increases in materials costs in November outrun prices for construction projects
Construction officials say efforts to address supply chain challenges have been insufficient.
Market Data | Dec 15, 2021
Demand for design services continues to grow
Changing conditions could be on the horizon.
Market Data | Dec 5, 2021
Construction adds 31,000 jobs in November
Gains were in all segments, but the industry will need even more workers as demand accelerates.
Market Data | Dec 5, 2021
Construction spending rebounds in October
Growth in most public and private nonresidential types is offsetting the decline in residential work.
Market Data | Dec 5, 2021
Nonresidential construction spending increases nearly 1% in October
Spending was up on a monthly basis in 13 of the 16 nonresidential subcategories.
Market Data | Nov 30, 2021
Two-thirds of metro areas add construction jobs from October 2020 to October 2021
The pandemic and supply chain woes may limit gains.