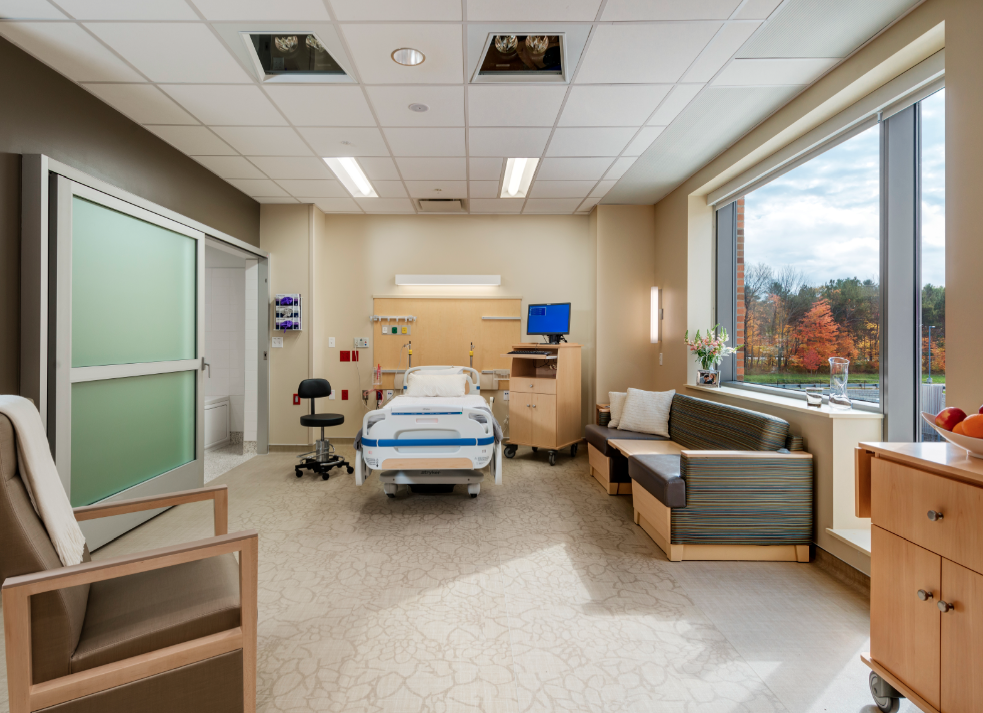
Hospital noise can be an insidious seed planted in a patient’s memory.
“They will recall extraordinary acts of kindness and consideration. However, they will also remember the agony of not being able to sleep, and hearing the nurses and others laughing just beyond their door,” says Chris Kay, ACHE, Managing Principal–National Healthcare & Science Buildings Practice at engineering giant Jacobs.
Some patients are bothered by noise that others shrug off. Volume isn’t necessarily the key factor. That’s the “noise conundrum,” says Kay. Every hospital has its own “culture” of loudness and quiet.
Kay says noise can impact patients through sleep deprivation, greater anxiety, and heightened blood pressure, respiration, and heart rates. It can also affect hospital workers, adding to their stress, lowering their ability to concentrate, and possibly leading to medical and nursing errors.
Kay offers steps to a therapeutic auditory environment:
1. Keep assessing your facility’s noise status. Hospital administrators and clinical staffs can become oblivious to daily noise patterns. They need to stop and listen to determine how loud is loud from the standpoint of patients, families, and visitors.
2. Establish relevant sound standards. EPA noise standards from the 1970s are out of date, says Kay. Any current sound standard needs to reflect the normal functioning of the facility and the needs of patients. That means going beyond decibel measurements and getting personnel involved in monitoring and modeling behavior that results in a healing environment.
3. Set noise impact standards for equipment purchases. For example, if a hospital plans to purchase a portable MRI, it should know beforehand where it’s going to be used, who will actually use it, and its impact on hospital noise.
4. Place nonclinical equipment in appropriate locations. In addition to the beep-beep of clinical and monitoring equipment, patients are bombarded with noise from vacuum cleaners, TVs, ice-making machines, and so on. Decide where and when such devices can be used around patients. “Housekeeping and nursing must bond to care for patients,” Kay notes.
5. Design spaces for sound control. Kay recommends that hospitals retain a noise control engineer to help find and mitigate “erratic” sounds. Spaces should also be retrofitted with acoustic materials that have high sound transmission ratings.
6. Engage and educate staff. Don’t blame the staff for being noisy; instead, make it a matter of patient care and professionalism. Emphasize that excessive noise shows a lack of respect for patients and their families. Whether it’s a door that slams or a cell phone that rings when it shouldn’t, hospitals need to “reclaim the sacred relationship and sacred space for healing,” says Kay.
7. Measure results. Collect data on how such metrics as patients’ complaints, calls for assistance at night, and request for pain medication correlate with noise levels on patient floors.
Related Stories
Daylighting | Aug 18, 2022
Lisa Heschong on 'Thermal and Visual Delight in Architecture'
Lisa Heschong, FIES, discusses her books, "Thermal Delight in Architecture" and "Visual Delight in Architecture," with BD+C's Rob Cassidy.
| Aug 16, 2022
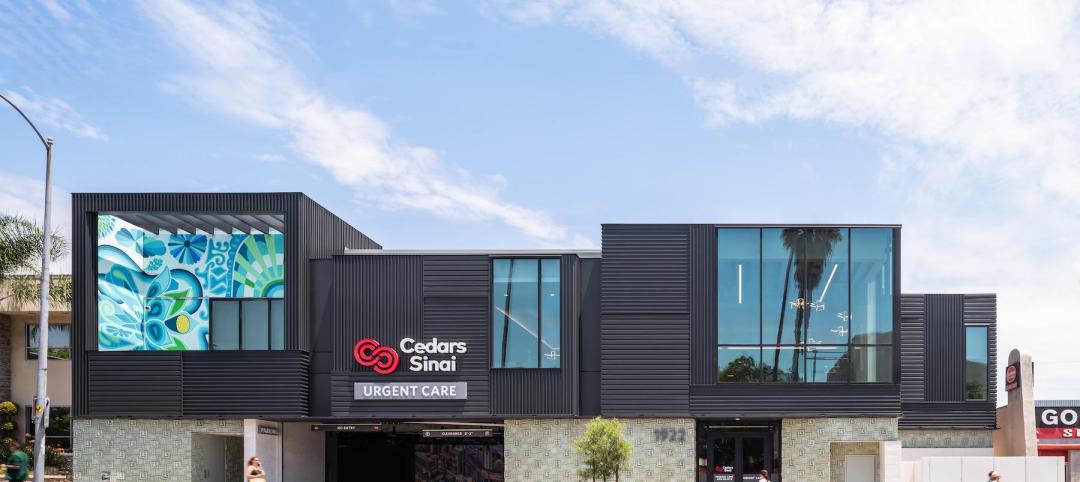
Cedars-Sinai Urgent Care Clinic’s high design for urgent care
The new Cedars-Sinai Los Feliz Urgent Care Clinic in Los Angeles plays against type, offering a stylized design to what are typically mundane, utilitarian buildings.
| Aug 15, 2022
IF you build it, will they come? The problem of staff respite in healthcare facilities
Architects and designers have long argued for the value of respite spaces in healthcare facilities.
AEC Tech | Aug 8, 2022
The technology balancing act
As our world reopens from COVID isolation, we are entering back into undefined territory – a form of hybrid existence.
| Aug 3, 2022
Designing learning environments to support the future of equitable health care
While the shortage of rural health care practitioners was a concern before the COVID-19 pandemic, the public health crisis has highlighted the importance of health equity in the United States and the desperate need for practitioners help meet the needs of patients in vulnerable rural communities.
Healthcare Facilities | Aug 1, 2022
New Phoenix VA outpatient clinic is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
The new Phoenix 32nd Street VA Clinic, spanning roughly 275,000 sf over 15 acres, is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
Building Team | Jul 12, 2022
10 resource reduction measures for more efficient and sustainable biopharma facilities
Resource reduction measures are solutions that can lead to lifecycle energy and cost savings for a favorable return on investment while simultaneously improving resiliency and promoting health and wellness in your facility.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 22, 2022
Arizona State University’s Health Futures Center: A new home for medical tech innovation
In Phoenix, the Arizona State University (ASU) has constructed its Health Futures Center—expanding the school’s impact as a research institution emphasizing medical technology acceleration and innovation, entrepreneurship, and healthcare education.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 20, 2022
Is telehealth finally mainstream?
After more than a century of development, telehealth has become a standard alternative for many types of care.
Codes and Standards | Jun 14, 2022
Hospitals’ fossil fuel use trending downward, but electricity use isn’t declining as much
The 2021 Hospital Energy and Water Benchmarking Survey by Grumman|Butkus Associates found that U.S. hospitals’ use of fossil fuels is declining since the inception of the annual survey 25 years ago, but electricity use is dipping more slowly.