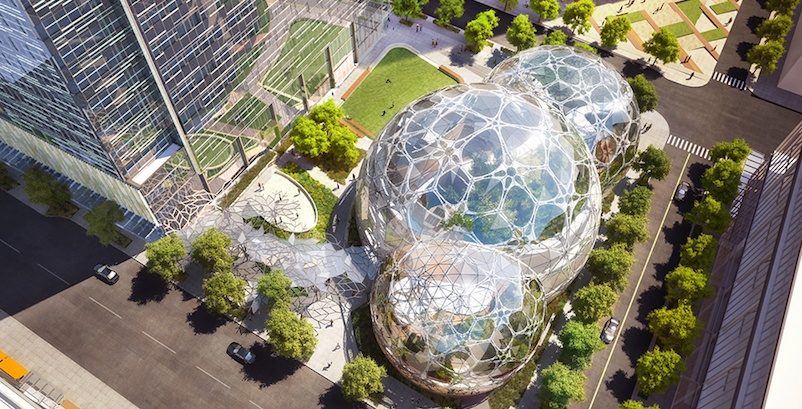
Next month, Amazon.com is scheduled to open the first phase of its massive Denny Triangle campus in Seattle. Through a unique partnership, the spheres and towers that comprise Amazon’s four-block, 4-million-sf campus will be heated by waste heat recovered from the 34-story Westin Building Exchange across the street.
The Seattle Times reports that 70% of the Westin Building Exchange’s 400,000 sf is dedicated to data centers that are throwing off tremendous amounts of excess heat.
The building produces heat equivalent to 11 megawatts per day. Through an agreement with Pacific Northwest, which routes nearly all of its Internet traffic through the data centers in Westin, the building will transfer up to five megawatts to Amazon, which is purchasing the energy at a discounted rate. Recapturing this waste heat is expected to save about 4 million kilowatt-hours of energy per year.
Here’s how this system will work, according to the Times and the Seattle Post-Intelligencer: When the Amazon buildings need heat, that will signal two heat pumps that collect heat from the data centers in the Westin Building Exchange, and use it to heat water traveling via pipes from the roof of the Westin building and through its floors to a refrigerator-sized steel-plated heat exchanger in Westin’s basement.
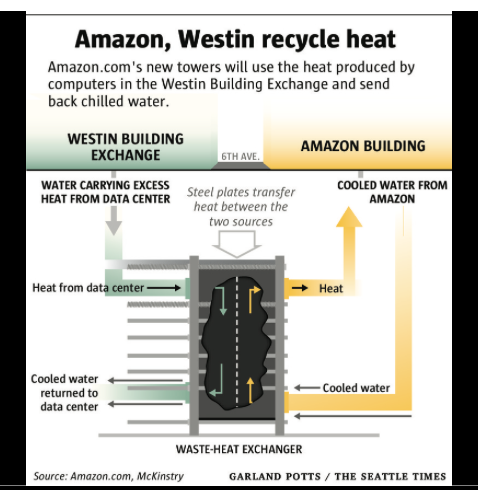 Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
By the time that water reaches the exchanger, its temperature exceeds 70 degrees Fahrenheit. The exchanger transfers that heat through pipes running under the street to Amazon’s campus, which returns cooler water via the exchanger to the data centers.
When this system is fully functional, it will be circulating up to 3,000 gallons of water per minute.
Several entities collaborated on this project, which has been in the works for three years. They include McKinstry, which designed the heat-exchange system; and Clise Development, which co-owns the Westin Building Exchange with Digital Realty Trust, and sold Amazon the four blocks for its campus. Clise and McKinstry formed a partnership called Eco District for this project.
The agreement also involved several city agencies including its office of sustainability and environment. The Post-Intelligencer reports that one of Amazon’s building is already using this so-called district heating system that will ultimately provide heat for more than 3 million sf of office space.
Richard Stevenson, Clise Properties’ president, estimates the cost of this system in “the low millions” that would pay for itself in energy savings.
While heat exchange isn’t a new concept, it usually involves only one building, and rarely on the scale of this project. The Times quotes Susan Wickwire, executive director of the Seattle 2030 District—which aims to significantly reduce energy and water use in buildings in Seattle by 2030—who believes the arrangement between Amazon and Pacific Northwest could provide “a smooth path” for similar agreements where building occupants work together to save energy and make their operations more efficient.
“We’re showing people it can be done,” John Schoettler, Amazon’s director of global real estate, told the Times. “If other developments can model this, that’s a win-win.”
Amazon’s Denny Triangle campus, designed by NBBJ, will include three intersecting glass spheres that form a five-story office building, a 38-story tower, and 18,000 sf of retail. Amazon expects to be fully moved into these buildings in a couple of years.
Related Stories
| Mar 1, 2012
AIA: A clear difference, new developments in load-bearing glass
Earn 1.0 AIA/CES learning units by studying this article and successfully completing the online exam.
| Mar 1, 2012
7 keys to ‘Highest value, lowest cost’ for healthcare construction
The healthcare design and construction picture has been muddied by uncertainty over the new healthcare law. Hospital systems are in a bind, not knowing what levels of reimbursement to expect. Building Teams serving this sector will have to work even harder to meet growing client demands.
| Feb 28, 2012
Roofing contractors recognized for workmanship
Sika Sarnafil announces Project of the Year winners; competition highlights visually stunning, energy efficient, and sustainable roofs.
| Feb 28, 2012
LUMEnergi names Weinbaum president and CEO
Weinbaum’s experience spans communications, nanotechnology, electronics components, consumer products, semiconductors, software, wireless and lighting.
| Feb 28, 2012
Griffin Electric completes Medical University of South Carolina project
The 210,000-sf complex is comprised of two buildings, and houses research, teaching and office areas, plus conference spaces for the University.
| Feb 22, 2012
Siemens earns LEED certification for Maryland office
The Beltsville facility, which also earned the ENERGY STAR Label for energy performance, implemented a range of energy efficiency, water conservation and sustainable operations measures as part of the certification process.
| Feb 21, 2012
SMPS announces Build Business 2012 keynote speakers
National conference set for July 11–13 in San Francisco.
| Feb 20, 2012
Comment period for update to USGBC's LEED Green Building Program now open
This third draft of LEED has been refined to address technical stringency and rigor, measurement and performance tools, and an enhanced user experience.
| Feb 17, 2012
Tremco Inc. headquarters achieves LEED Gold certification
Changes were so extensive that the certification is for new construction and not for renovation; officially, the building is LEED-NC.