For many of us who have participated in the rapid growth of BIM, It is tempting to see it as just one more technology development in the project delivery process, but its real impact is quickly accelerating beyond that. More accurately, the growth of BIM is heralding a true disruption in the construction industry. It is transforming markets, and revolutionizing expectations.
In fact, it is increasingly apparent that BIM fits a well-known pattern familiar to business scholars, a pattern known as disruptive innovation and made famous by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen in his best-selling book The Innovator’s Dilemma.
In innovation theory, a disruptive technology is one that creates entirely new “value networks”––a combination of capabilities and expectations––for a given process or technology.
For example, 2D CAD simply computerized the production of drawings. Before CAD, designers produced drawings; after CAD, we still produced drawings, just differently and with more flexibility. CAD was a “sustaining technology”––something that simply improved an existing market proposition.
BIM also started out as a sustaining technology, as many disruptions do. The notion was that 3D models would be an efficient way to produce 2D documents, the next evolution of CAD enhancement. But it quickly morphed to a point where the model created brand new value networks: clash detection, quantity takeoffs, field BIM, direct fabrication, energy analysis––and, ultimately, BIM models as a store of myriad facility information.
Enter the Contractor: BIM becomes VDC
The disruptive growth of BIM has been largely due to the unanticipated interest contractors would take in the technology, and in this respect it is clearly a “new market disruption” in the terminology of disruption. By any measure, contractors have grasped the power of BIM with far more vigor than design professionals, who tend to see it as sustaining, and have failed to perceive its disruptive trajectory. Contractors looked at BIM models and immediately understood how they could be used for virtual design and construction (VDC) tasks.
Many leading design firms have come to realize that BIM’s disruption means developing new ways to work with savvy contractors and owners. At our firm, design teams now routinely exchange BIM files with contractors during and after design for purposes that are entirely unprecedented in our previous experience.
Further fueling the disruption, many savvy clients now contractually require that we work closely with the contractor and owner on BIM development and file exchange. Penn State University, for example, has some of the most detailed and well-developed processes for designers and contractors in BIM implementation.
The rumblings of disruption were becoming apparent to our firm almost as soon as contractors first learned we were creating BIM files. One of our first structural BIM projects was (somewhat hesitantly) transferred to the contractors so they could use it to quantify the lengths of steel members for a mill order. It proved useful, but it was unfamiliar to us, and a first brush with the emerging uses of BIM.
Since then we have become accustomed to our clients (both private and governmental) making BIM submission a requirement. Somewhere along the way, we began to realize that expectations were changing dramatically. It is now relatively routine for the BIM files to get substituted or supplemented with subcontractor 3D fabrication files for on-site, real-time coordination.
Enter the Owner: BIM in Real Time
More recently, another development has increased the pace of disruption-––the addition of the owner to the BIM design process. Smart owners quickly began to realize how these information-rich 3D models could be useful as an active decision-making tool during construction, and then used as stores of information for facility operations purposes. Many adopted detailed protocols for how BIM should be used on their projects.
In a subsequent development, our firm has begun to experience owners now sitting in on the fast-track design for a large high-tech facility and expecting to see 3D models they can query at any point. Our design team sits with the owner, contractor, and facility personnel to review BIM models in real time as they develop. This is a huge departure from our previous workflow, where owners received progress paper sets, carefully controlled for output. Now the process is open, active, and raw.
Embrace the Strange
For those of us using BIM, it’s important to fully understand BIM as a disruption and avoid getting caught up comparing CAD and BIM software as two different, but comparable, approaches. Such a perspective would focus on BIM’s sustaining effects and totally miss its disruptive potential.
BIM shows all the signs of a classic market disruption, and like other disruptions its ultimate destination is not yet clear, except that it will certainly change markets and expectations.
Our best strategy is to embrace the full power of BIM, to recognize its disruptive potential, and to explore its power to address many of the issues we currently face as we attempt to reImagine design and construction. +
--
John Tobin is Director of Architecture at EYP Architecture & Engineering, Albany, N.Y.
Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Nov 3, 2015
How virtual and augmented reality can shape architecture and design
Gensler's Alan Robles examines a few ways VR and AR could create value for architecture and design professionals.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 29, 2015
MIT develops ‘river of 3D pixels’ to assemble objects
The Kinetic Blocks can manipulate objects into shapes without human interference.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 27, 2015
Magic Leap's breakthrough augmented reality project continues to generate support
The company is developing the Dynamic Digitized Lightfield Signal. It projects images onto the retina, giving users an interactive 3D experience.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 26, 2015
Tableau’s new app, Vizable, converts spreadsheets into charts and graphs
Everyday users can simplify large amounts of data and sift through it interactively.
Architects | Oct 20, 2015
Four building material innovations from the Chicago Architecture Biennial
From lightweight wooden pallets to the largest lengths of CLT-slabs that can be shipped across North America
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 19, 2015
A robotic arm can 3D print, etch, solder, and carve from a desktop
It’s not just a 3D printer. The creators say Makerarm can also etch, solder, and put icing on cake.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 19, 2015
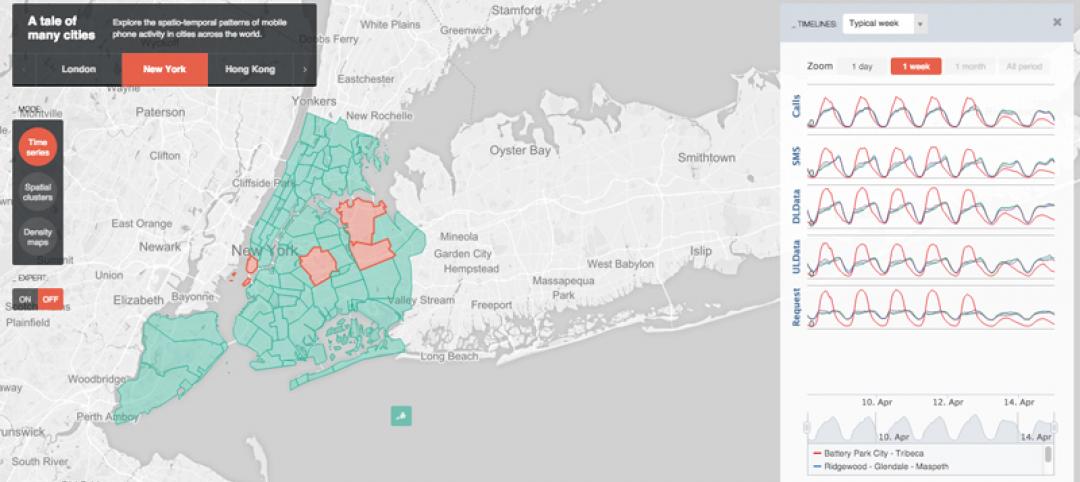
New web tool from MIT organizes human movement in interactive graphs
Users can explore the mobile phone activities in London, New York, Los Angeles, and Hong Kong.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 12, 2015
NIBS launches effort to develop BIM guideline for owners
Aim is to provide uniformity in the delivery of BIM projects.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 11, 2015
VR for all: How AEC teams are benefiting from the commercialization of virtual reality tools
AEC teams are using gaming engines to not just showcase their projects, but to immerse their clients, end users, and Building Team members in highly detailed, fully lit environments that simulate the final structure.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 9, 2015
Facebook’s data center complex has become economic engine for one North Carolina town
Cities are now vying for these facilities with sizable tax incentives.