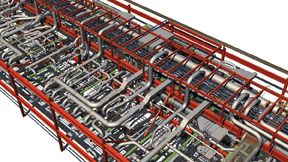
For many of us who have participated in the rapid growth of BIM, It is tempting to see it as just one more technology development in the project delivery process, but its real impact is quickly accelerating beyond that. More accurately, the growth of BIM is heralding a true disruption in the construction industry. It is transforming markets, and revolutionizing expectations.
In fact, it is increasingly apparent that BIM fits a well-known pattern familiar to business scholars, a pattern known as disruptive innovation and made famous by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen in his best-selling book The Innovator’s Dilemma.
In innovation theory, a disruptive technology is one that creates entirely new “value networks”––a combination of capabilities and expectations––for a given process or technology.
For example, 2D CAD simply computerized the production of drawings. Before CAD, designers produced drawings; after CAD, we still produced drawings, just differently and with more flexibility. CAD was a “sustaining technology”––something that simply improved an existing market proposition.
BIM also started out as a sustaining technology, as many disruptions do. The notion was that 3D models would be an efficient way to produce 2D documents, the next evolution of CAD enhancement. But it quickly morphed to a point where the model created brand new value networks: clash detection, quantity takeoffs, field BIM, direct fabrication, energy analysis––and, ultimately, BIM models as a store of myriad facility information.
Enter the Contractor: BIM becomes VDC
The disruptive growth of BIM has been largely due to the unanticipated interest contractors would take in the technology, and in this respect it is clearly a “new market disruption” in the terminology of disruption. By any measure, contractors have grasped the power of BIM with far more vigor than design professionals, who tend to see it as sustaining, and have failed to perceive its disruptive trajectory. Contractors looked at BIM models and immediately understood how they could be used for virtual design and construction (VDC) tasks.
Many leading design firms have come to realize that BIM’s disruption means developing new ways to work with savvy contractors and owners. At our firm, design teams now routinely exchange BIM files with contractors during and after design for purposes that are entirely unprecedented in our previous experience.
Further fueling the disruption, many savvy clients now contractually require that we work closely with the contractor and owner on BIM development and file exchange. Penn State University, for example, has some of the most detailed and well-developed processes for designers and contractors in BIM implementation.
The rumblings of disruption were becoming apparent to our firm almost as soon as contractors first learned we were creating BIM files. One of our first structural BIM projects was (somewhat hesitantly) transferred to the contractors so they could use it to quantify the lengths of steel members for a mill order. It proved useful, but it was unfamiliar to us, and a first brush with the emerging uses of BIM.
Since then we have become accustomed to our clients (both private and governmental) making BIM submission a requirement. Somewhere along the way, we began to realize that expectations were changing dramatically. It is now relatively routine for the BIM files to get substituted or supplemented with subcontractor 3D fabrication files for on-site, real-time coordination.
Enter the Owner: BIM in Real Time
More recently, another development has increased the pace of disruption-––the addition of the owner to the BIM design process. Smart owners quickly began to realize how these information-rich 3D models could be useful as an active decision-making tool during construction, and then used as stores of information for facility operations purposes. Many adopted detailed protocols for how BIM should be used on their projects.
In a subsequent development, our firm has begun to experience owners now sitting in on the fast-track design for a large high-tech facility and expecting to see 3D models they can query at any point. Our design team sits with the owner, contractor, and facility personnel to review BIM models in real time as they develop. This is a huge departure from our previous workflow, where owners received progress paper sets, carefully controlled for output. Now the process is open, active, and raw.
Embrace the Strange
For those of us using BIM, it’s important to fully understand BIM as a disruption and avoid getting caught up comparing CAD and BIM software as two different, but comparable, approaches. Such a perspective would focus on BIM’s sustaining effects and totally miss its disruptive potential.
BIM shows all the signs of a classic market disruption, and like other disruptions its ultimate destination is not yet clear, except that it will certainly change markets and expectations.
Our best strategy is to embrace the full power of BIM, to recognize its disruptive potential, and to explore its power to address many of the issues we currently face as we attempt to reImagine design and construction. +
--
John Tobin is Director of Architecture at EYP Architecture & Engineering, Albany, N.Y.
Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Jul 1, 2015
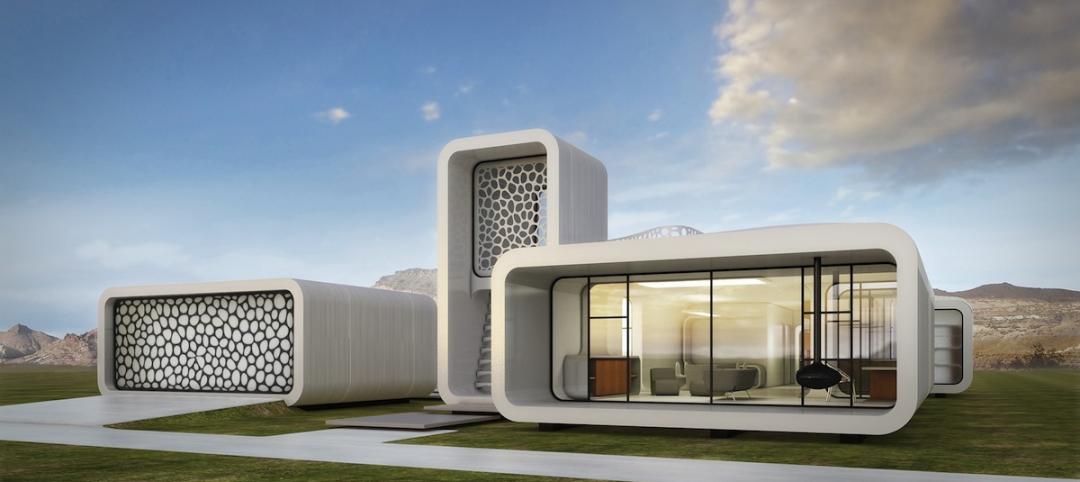
World’s first fully 3D-printed office to be produced in Dubai
A 20-foot-tall printer will be needed for the project, spewing out construction material consisting of special reinforced concrete, fiber reinforced plastic, and glass fiber reinforced gypsum.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Jun 23, 2015
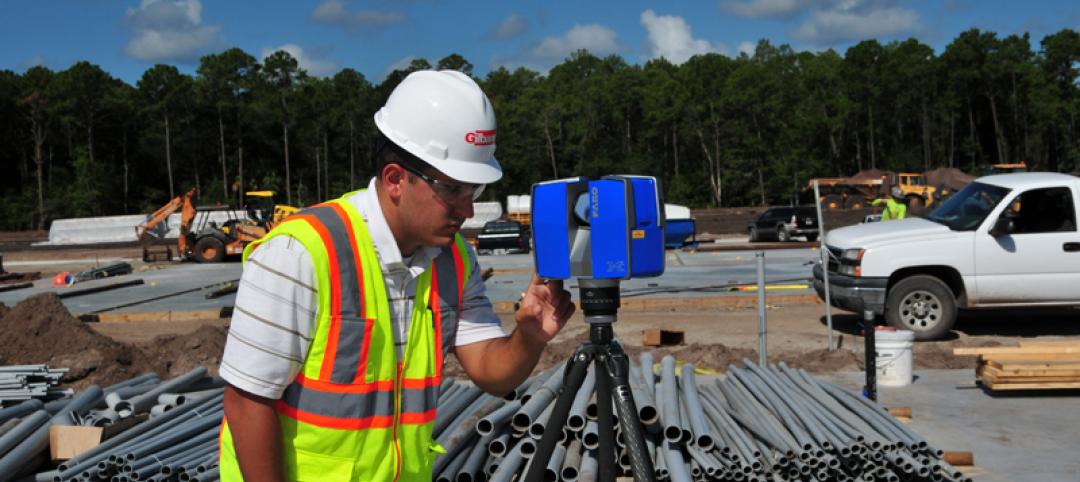
Emerging technology reinvents construction principals
Gilbane discovered the anecdotal side of laser scanning pales in comparison to the dramatic ROI story.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 23, 2015
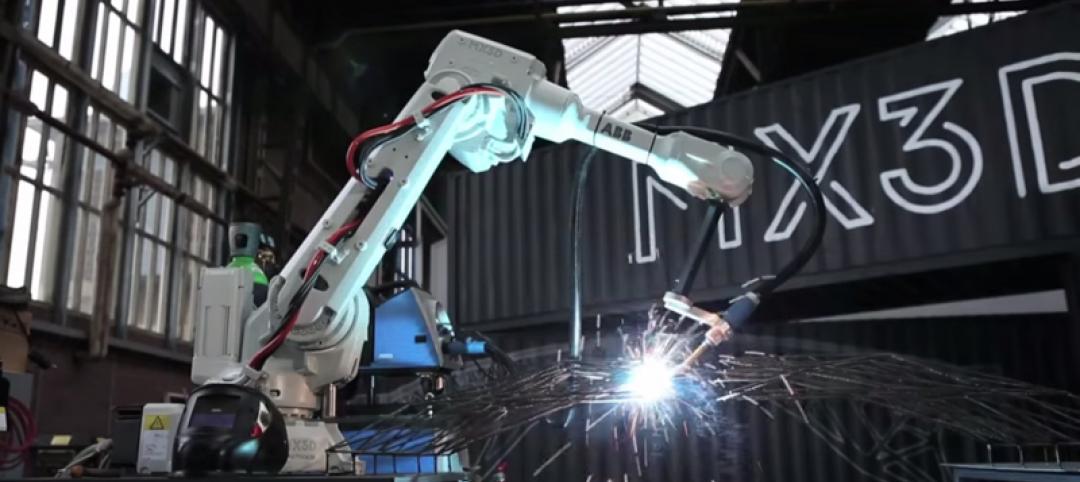
A steel bridge in Amsterdam will be 3D printed
To complete the bridge, multi-axis industrial robots will be fitted with 3D printing tools and controlled using custom software that enables the robots to print metals, plastics, and combinations of materials.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 21, 2015
11 tips for mastering 3D printing in the AEC world
Early adopters provide first-hand advice on the trials and tribulations of marrying 3D printing with the science of building technology.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 16, 2015
What’s next for 3D printing in design and construction?
The 3D printer industry keeps making strides in technology and affordability. Machines can now print with all sorts of powderized materials, from concrete to chocolate.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 15, 2015
Arup report predicts future of manufacturing
Human-robot collaboration, self-cleaning and self-healing materials, mass customization, and 3D printing will herald a new "golden age" of production.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 14, 2015
Deep data: How greater intelligence can lead to better buildings
The buzzword may be “Big Data,” but the reality is that Building Teams need to burrow deep into those huge datasets in the course of designing and building new facilities. Much of the information is free. You just need to dig for it.
Smart Buildings | Jun 11, 2015
Google launches company to improve city living
The search engine giant is yet again diversifying its products. Google has co-created a startup, called Sidewalk Labs, that will focus on “developing innovative technologies to improve cities.”
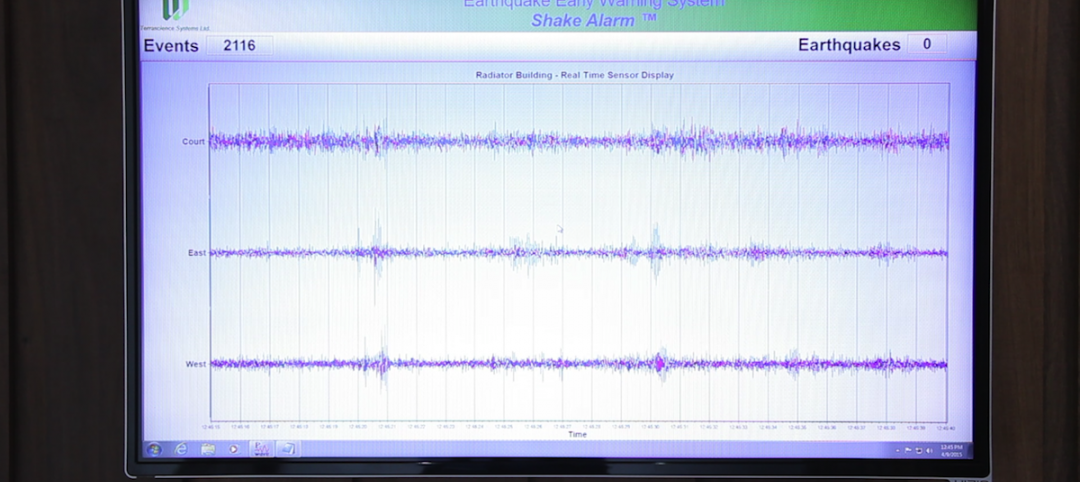
Seismic Design | Jun 9, 2015
First building-specific earthquake warning system installed in North Portland, Ore.
The ShakeAlarm system recognizes and quantifies the faster but lower-energy seismic P-wave, which is the precursor to the more damaging S-wave.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 8, 2015
Ready for takeoff: Drones await clearance for job site flights
The fog is finally lifting on who will be allowed to pilot unmanned aerial vehicles.