|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lincoln High School in Tacoma, Wash., was built in 1913 and spent nearly a century morphing into a patchwork of outdated and confusing additions. A few years ago, the Tacoma School District picked Lincoln High School to be the first high school in the district to be part of its newly launched Small Learning Communities program, thus beginning a $74.2 million renovation of the 222,000-sf high school. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lincoln High School in Tacoma, Wash., was built in 1913 and spent nearly a century morphing into a patchwork of outdated and confusing additions. A few years ago, the Tacoma School District picked Lincoln High School, dubbed “Old Main,” to be the first high school in the district to be part of its newly launched Small Learning Communities program. The Building Team was given only 13 months to get the school ready to participate in the project. Community members, administrators, students, teachers, and parents worked with architects from the Seattle office of DLR Group to reconfigure the high school for new academy-based educational delivery methods. The architects led them through extensive scenario planning, overlaying each educational program component over the building plans.
The DLR plan divided the school into six zones (two zones in each wing, one on each floor) that would house six academies, each of which would function independently within the larger school building. Shared spaces were to include an auditorium, a cafeteria, a gymnasium, a library, and science labs. Funding for the $74.2 million renovation came from a bond issue and a grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. As work got under way in fall 2006, the existing 222,000-sf, L-shaped school received a number of structural upgrades and nips and tucks. To address seismic concerns, 13 shear walls (using double-sided plywood) were installed, running from grade all the way up to the attic floors. An existing 1980s addition was demolished; in its place arose a two-story structure that expands the school to 264,000 sf and houses the new library and science labs. The addition also acts as a buttress to the existing school structure, providing added seismic support. The school received all new plumbing and electrical systems, as well as new HVAC equipment that was installed in the attic. The Building Team specified aluminum equipment to diminish the weight load on the existing wood-frame structure. Insulation was beefed up to dampen equipment noise. Despite all that’s new with the school, much of its historic character remains intact. The Collegiate Gothic-style school’s original details were restored or replicated; some were relocated and reused in the addition to connect old and new. Also left intact were the school’s 75- to 80-year-old, three-by-seven-foot operable windows, some with original stained glass windows of Tacoma milk glass, so called because of its milky white color. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Project Summary Lincoln High School Tacoma, Wash. Building Team Submitting firm: DLR Group (architect, structural engineer) Owner: Tacoma School District Architectural consultant: TCF Architecture General contractor: Lease Crutcher Lewis Electrical engineer: Coffman Engineers Mechanical engineer: Hargis Engineers General Information Area: 264,000 sf Construction cost: $74.2 million Construction time: August 2006 to September 2007 |
Related Stories
| Jun 18, 2014
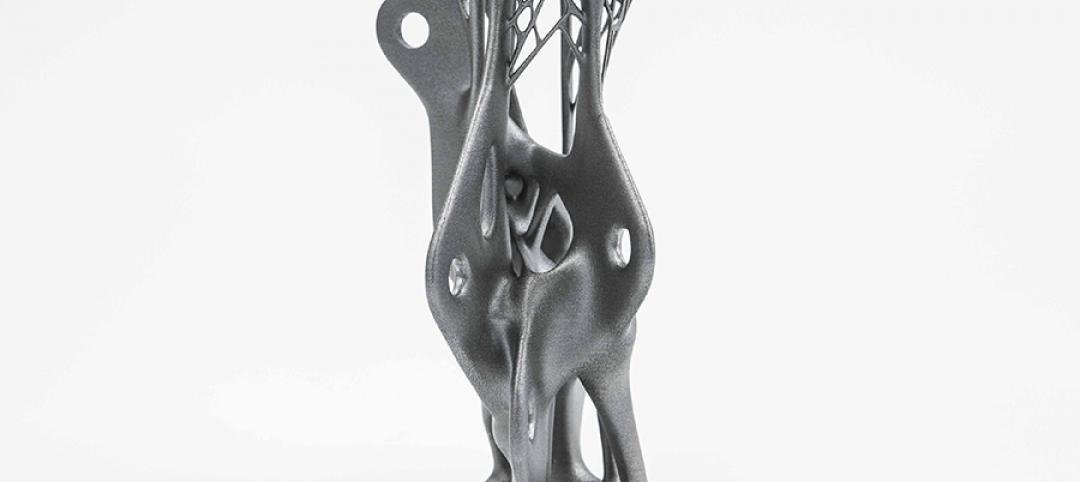
Arup uses 3D printing to fabricate one-of-a-kind structural steel components
The firm's research shows that 3D printing has the potential to reduce costs, cut waste, and slash the carbon footprint of the construction sector.
| Jun 12, 2014
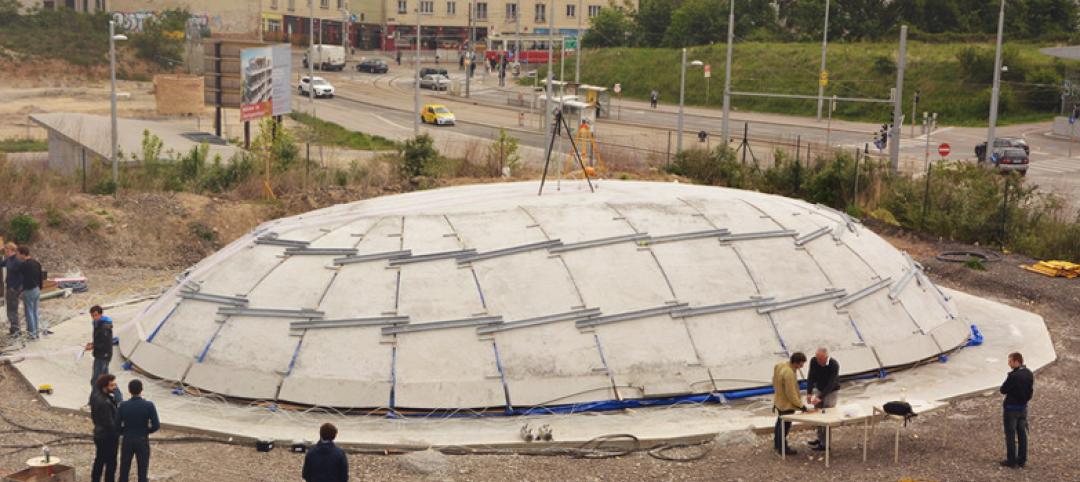
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 9, 2014
Green Building Initiative launches Green Globes for Sustainable Interiors program
The new program focuses exclusively on the sustainable design and construction of interior spaces in nonresidential buildings and can be pursued by both building owners and individual lessees of commercial spaces.
| May 29, 2014
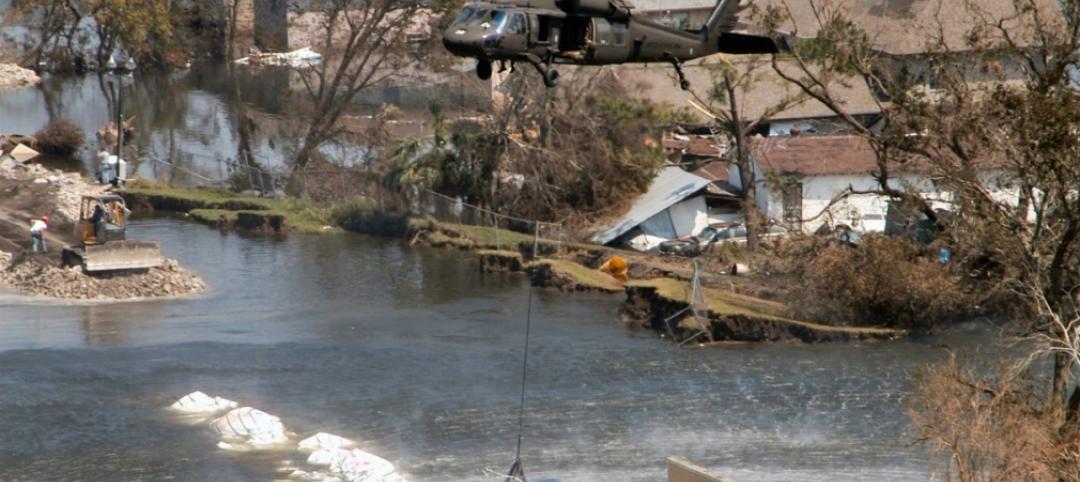
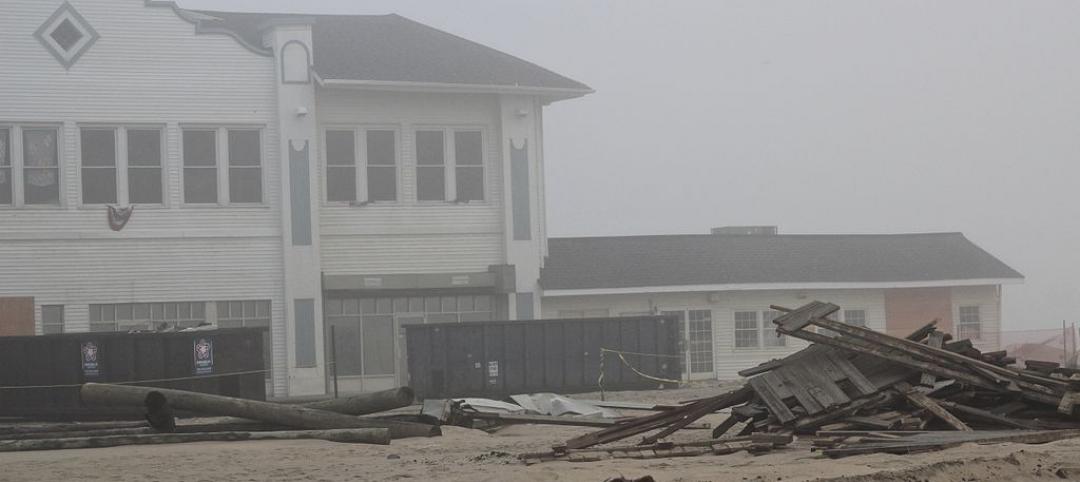
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 23, 2014
Top interior design trends: Gensler, HOK, FXFOWLE, Mancini Duffy weigh in
Tech-friendly furniture, “live walls,” sit-stand desks, and circadian lighting are among the emerging trends identified by leading interior designers.
| May 22, 2014
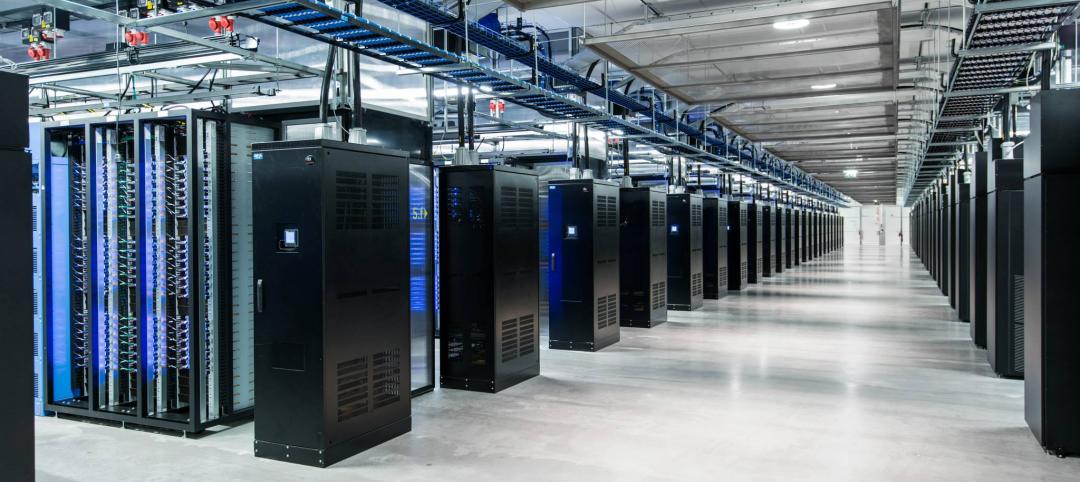
Big Data meets data centers – What the coming DCIM boom means to owners and Building Teams
The demand for sophisticated facility monitoring solutions has spurred a new market segment—data center infrastructure management (DCIM)—that is likely to impact the way data center projects are planned, designed, built, and operated.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 15, 2014
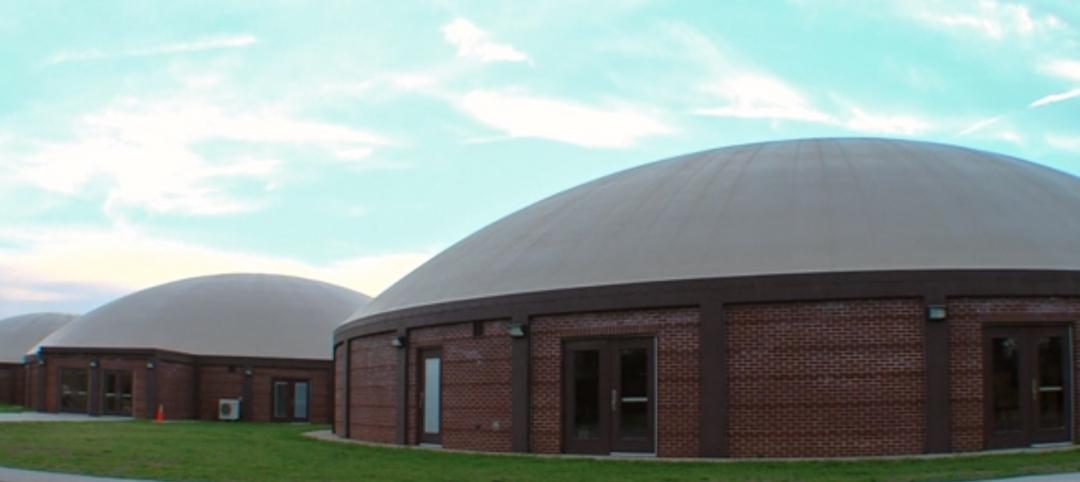
'Virtually indestructible': Utah architect applies thin-shell dome concept for safer schools
At $94 a square foot and "virtually indestructible," some school districts in Utah are opting to build concrete dome schools in lieu of traditional structures.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.